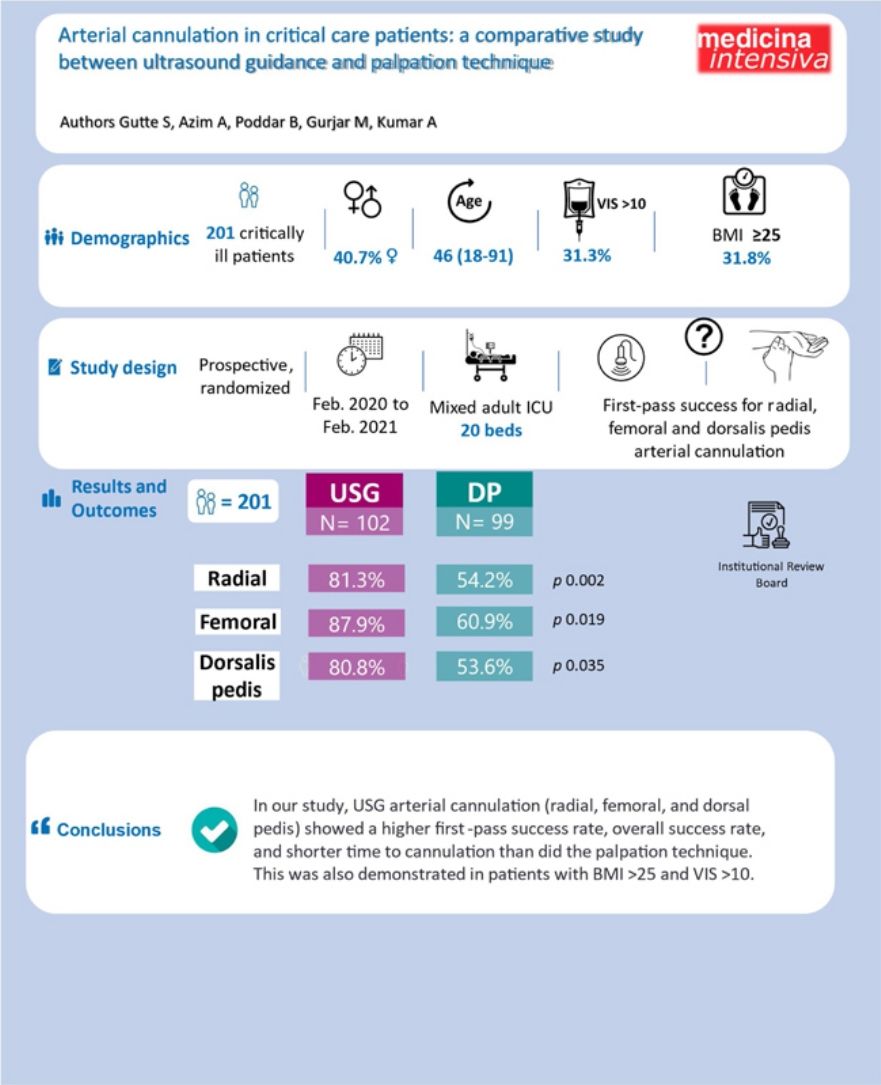
To compare first attempt success rate for ultrasound-guided (USG) versus direct palpation (DP) for radial, femoral, and dorsalis pedis artery cannulations in adult intensive care unit (ICU) patients.
DesignProspective randomized clinical trial.
SettingMixed adult ICU of a University Hospital.
ParticipantsAdult patients (≥18 years) admitted to the ICU requiring invasive arterial pressure monitoring were included. Exclusion criteria were patients with a pre-existing arterial line and cannulated with other than a 20-gauge cannula for radial and dorsalis pedis artery.
InterventionComparison of arterial cannulation by USG versus palpation technique in radial, femoral and dorsalis pedis arteries.
Main variables of interestPrimary outcome was first attempt success rate, secondary outcomes were assessing time for cannulations, number of attempts, overall success rate, complications, and comparison of two techniques on patients requiring vasopressor.
Results201 patients were enrolled in study, with 99 randomized to DP group and 102 to USG group. Arteries (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral) cannulated in both groups were comparable (P = .193). Arterial line was placed on first attempt in 85 (83.3%) in USG group versus 55 (55.6%) in DP group (P = .02). Cannulation time in USG group was significantly shorter compared to DP group.
ConclusionsIn our study, USG arterial cannulation, compared to palpatory technique, had a higher success rate at first attempt and a shorter cannulation time.
Clinical Trial Registry of India numberCTRI/2020/01/022989.
Comparar la tasa de éxito al primer intento de la técnica eco-dirigida (USG) versus la técnica palpatoria para la canulación de la arteria radial, femoral y dorsal del pie en pacientes adultos de la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI).
DiseñoEnsayo clínico aleatorizado prospectivo.
ÁmbitoUCI mixta de adultos de un Hospital Universitario.
ParticipantesSe incluyeron pacientes adultos (≥18 años) ingresados en la UCI que requirieron monitorización invasiva de la presión arterial. Los criterios de exclusión fueron la presencia de un catéter arterial preexistente y canulados con una cánula distinta del calibre 20 para la arteria radial y dorsal del pie.
IntervenciónComparación de la canulación arterial por USG versus la técnica palpatoria en la arteria radial, femoral y pedia.
Principales variables de interésEl resultado primario fue la tasa de éxito al primer intento; los resultados secundarios fueron evaluar el tiempo requerido para lograr una canulación exitosa, el número de intentos, la tasa de éxito general, las complicaciones y la comparación de dos técnicas en pacientes que requirieron vasopresores.
Resultados201 pacientes fueron reclutados en el estudio, con 99 aleatorizados al grupo DP y 102 al grupo USG. El número de canulaciones en las tres arterias fue similar entre ambos grupos (P = ,193). La línea arterial se colocó en el primer intento en 85 (83,3%) en el grupo USG versus 55 (55,6%) en el grupo DP (P = ,02). El tiempo de canulación en el grupo USG fue significativamente menor en comparación con el grupo de DP.
ConclusionesEn nuestro trabajo, la canulación arterial ecodirigida, en comparación con la técnica palpatoria, tuvo una mayor tasa de éxito al primer intento y un menor tiempo de canulación.
Número del Registro de EnsayosClínicos de la IndiaCTRI/2020/01/022989.
Blood pressure monitoring is crucial in managing hemodynamically unstable patients in the adult intensive care unit (ICU). Invasive measurement from an arterial line is considered the gold standard when compared to non-invasive blood pressure measurement,1,2 despite the recognition that errors could also be introduced by erroneous transducer systems.1,3,4
Under normal physiological conditions, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) measurement in peripheral arteries is similar in the aorta (central artery).4 However, recent literature showed that, in critically ill patients with shock the MAP measured in more distal arteries may underestimate the MAP in central arteries. This may lead to using inappropriate high doses of vasopressors when measuring the MAP in distal arteries.5–7 This difference in MAP gradient may be due to the differential peripheral vasoconstriction or decrease in arterial elastance in the peripheral artery compared to the central artery.6 The dorsalis pedis artery maximizes the distortion effect, where the systolic blood pressure (SBP) is 10−20 mmHg higher, and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is 10−20 mmHg lesser than the central aorta.8,9
Arterial line placement is a routine procedure in ICU patients as it leads to early recognition of changes in blood pressure, adjustment of vasoactive drugs, and frequent arterial blood gas sampling. The catheter is usually inserted using the palpation (DP) technique, although ultrasound-guided (USG) is being increasingly used according with current guidelines and recommendations.10–12 However, inserting the arterial catheter can sometimes be difficult, requires multiple attempts requires and can cause patient discomfort and complications.13
Nowadays, intensivists are familiar with USG central venous catheter (CVC) access, and arterial catheters cannulation. The standard approach of arterial cannulation is by traditional DP puncture of the artery by locating its pulse by palpation, followed by inserting an 18 or 20 Gauge (20 G) catheter depending on vessel diameter for peripheral arteries and 16 G for femoral artery. Alternatively, ultrasound can locate the vessel and guide needle insertion. The radial artery is the most common artery used for arterial cannulation because of its anatomic accessibility, dual arterial supply, and low rate of complications.14 In hypotensive patients, DP arterial cannulation can fail. Repeat attempts can lead to arterial spasms which may lead to a failed cannulation.
Recent studies have shown the usefulness of ultrasound for arterial cannulation. USG radial artery catheterization was associated with increased first-attempt success, less time consumption, and fewer complications compared to the traditional DP technique. In most studies, radial artery cannulation has been compared in a DP versus USG cannulation.15–18 A recent meta-analysis showed that the use of real-time two-dimensional ultrasound guidance for femoral artery catheterization decreases life-threatening vascular complications and improves first-pass success rate.20,21
The potential complications of the procedure are primarily minor and comprise hematoma formation, local infection, or bleeding from the puncture site. Major complications include pseudoaneurysm and occlusion which may be limb-threatening.
Literature on cannulation of USG vs. DP arterial cannulation of dorsalis pedis artery is scarce.22 To the best of the literature search by authors, none of the studies yet have compared the success rate, number of attempts, complications, and time consumption for cannulation of other peripheral arteries except radial and femoral artery in traditional DP palpation method vs. USG technique.
The present study was done to determine the effectiveness of US-guided arterial cannulation compared to the traditional DP insertion in the adult ICU.
ObjectivesThe primary objective of this study was to compare the first attempt success rate for DP versus USG for radial, femoral, and dorsalis pedis artery cannulations in adult ICU patients. Secondary outcomes include time to achieving cannulation, number of attempts, complications (such as hematoma), and comparison of both techniques on patients requiring vasopressors.
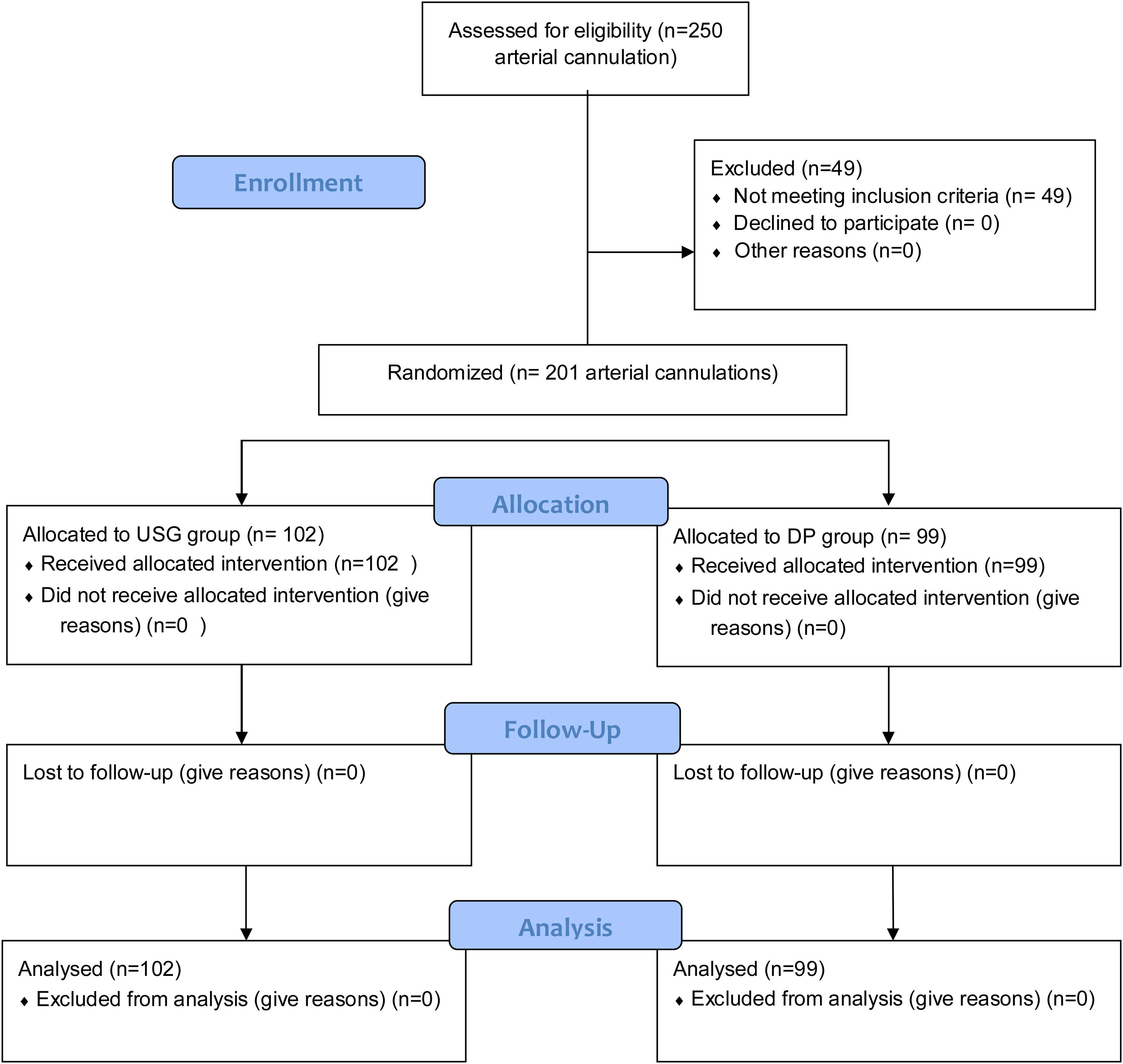
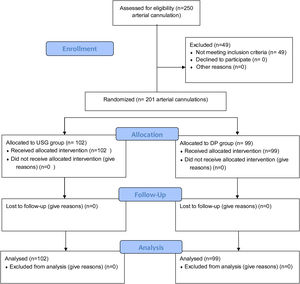
Materials and methodsDesignIt is a prospective study conducted in a 20-bedded mixed ICU of a tertiary care center. As arterial line placement is universal in the ICU for hemodynamically unstable patients, a waiver of consent was applied and approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB). After the Clinical trial registry of India (CTRI) registration, patients were randomized to either DP or USG groups by a computer-generated random number from February 2020 to February 2021. Inclusion criteria were adult patients (age ≥ 18 years) admitted to the ICU requiring invasive arterial pressure monitoring. Exclusion criteria include patients admitted with a pre-existing arterial catheter and cannulated with other than a 20-gauge (G) cannula for radial and dorsalis pedis artery [Fig. 1]. Trainee intensivists who had at least 20 successfully USG arterial cannulations performed the procedures. The trainee intensivist selected the site for cannulation upon their discretion.
Cannulation techniquesDP method: For radial and dorsalis pedis arterial cannulations, the artery was palpated and punctured at the site of maximal pulsation. Then a 20 G BD Venflon™ Pro IV Cannula (32 mm in length) was advanced over the needle until a flash of blood was seen in the hub of the cannula. For femoral artery cannulation, the artery was palpated and punctured at the site of maximal pulsation, and a 16 G (5 French) ARROW® REF CV-50016 cannula (20 cm in length) was placed by Seldinger technique.
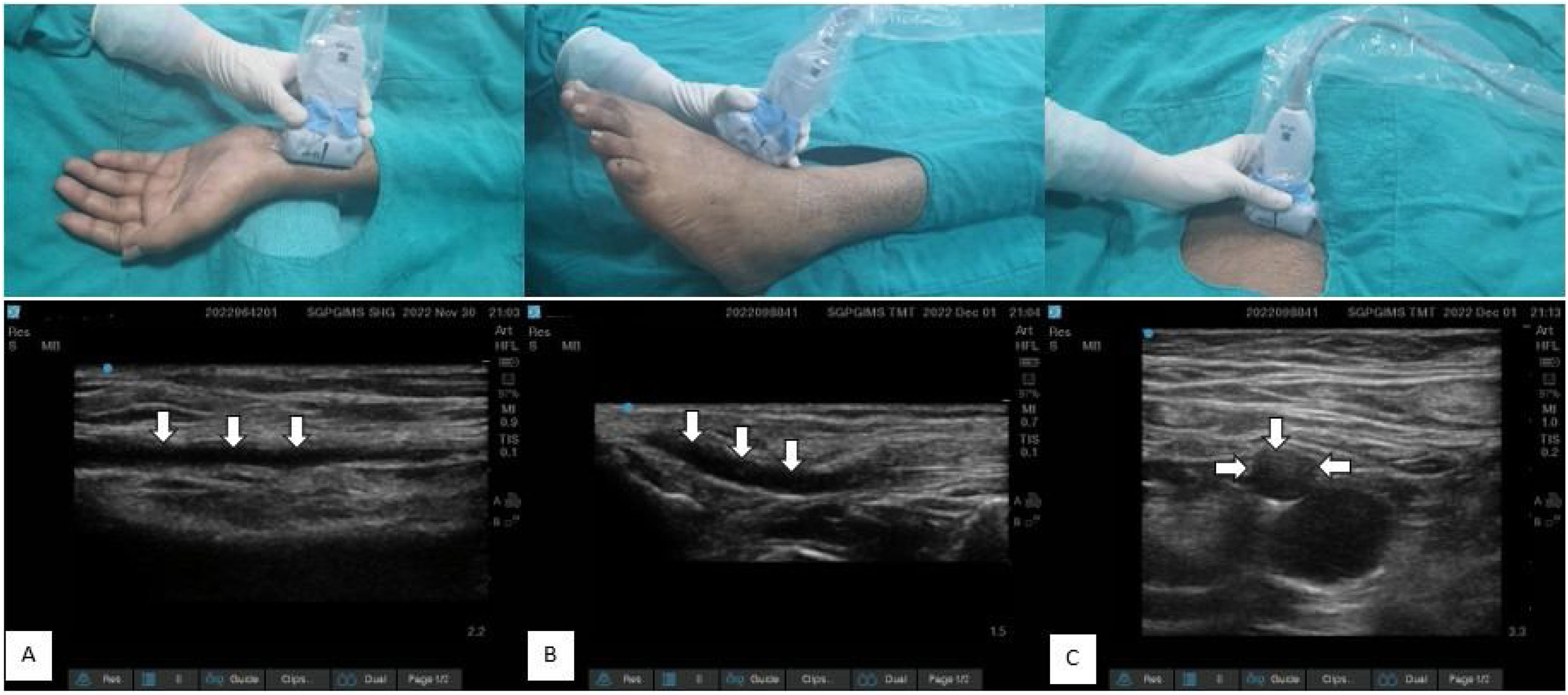
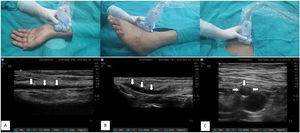
USG techniquePre-procedure scan- For all procedures, the artery was assessed by scanning through the transverse and longitudinal axis. Vessel size, distance to the skin, and vessel course were taken into consideration for the selection of the artery [Fig. 2].
Ultrasound and clinical images with linear transducer (13-6 MHz) position corresponds to each other in upper and lower panel. White arrow showing vessel course and location of artery. A) Radial artery in in-plane view, B) dorsalis pedis artery in in-plane view, C) femoral artery in out-of-plane view.
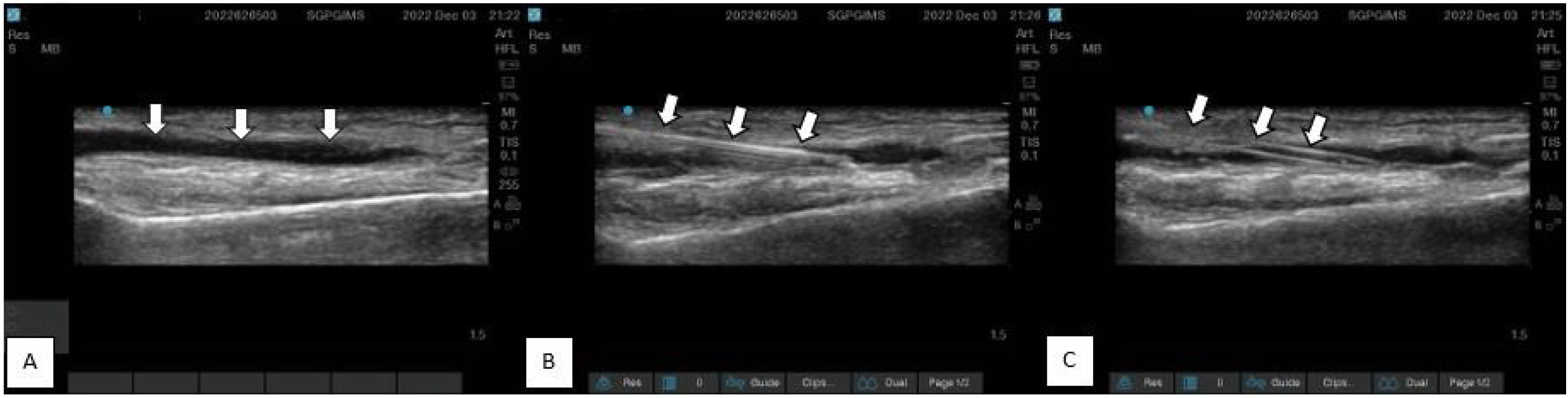
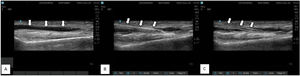
Procedure scan- For radial and dorsalis pedis artery, the artery was identified using USG with a linear transducer in longitudinal axis view after preparing the transducer with a sterile cover. Approximately 0.5 cm distal to the probe, a 20 G BD Venflon™ Pro IV Cannula was introduced in-plane and advanced at 15−30° to the skin until the tip of the needle was in contact with the anterior wall of the artery. The needle was advanced until blood appeared as a flash in the hub. Then the catheter was advanced over the needle. For femoral artery cannulations, the artery was assessed using a linear transducer in transverse plane. Then, the out-of-plane technique was used for catheter insertion. A 16 G ARROW® REF CV-50016 cannula was inserted using the Seldinger technique. (USG machine - Sonosite Edge II, Bothell, WA, Linear probe [13-6 MHz]) [Fig. 3].
Ultrasound image with linear probe (13-6 MHz) showing radial artery cannulation procedure. A) Pre-procedural Scan- White arrow showing radial artery course B) Procedural Scan- White arrow showing radial artery cannulation with 20 G cannula with needle in situ. C) Post-procedural scan- White arrow showing catheter position after removal of needle.
Post-procedure scan- It was performed in all patients to confirm catheter position, distal flow, thrombosis, and hematoma formation.
Time for cannulationFor the traditional DP palpation technique, time is taken from palpation of a patient's artery to arterial line placement, i.e., when the catheter was successfully placed into the vessel was noted. In the ultrasound group, the linear probe was prepared with a sterile probe cover and gel. Time was calculated from pre-procedural scan until the catheter was successfully placed into the vessel. The total time taken for insertion was calculated in seconds. Cannulation attempts were defined as the number of needle tips completely withdrawn from the skin. If there was a failure to cannulate on a third attempt, the cannulation site was changed.
Additional data collection included demographic profile, attempts for a successful cannulation, complications (hematoma, thrombosis, infection, and vasospasm), number of cannulae used, vitals before and after cannulations, and vasoactive inotropic score (VIS) for patients in septic shock21 [Table1].
Demographics, Comparison of baseline characteristics in Ultrasound and direct palpation group (n = 201).
| Demographical parameter | USG (n = 102) | DP (n = 99) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 46 ± 17.68 | 46.0 ± 17.93 | .890 |
| Female (n %) | 36 (35.3%) | 46 (46.5%) | .107 |
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 24 ± 2.76 | 23.6 ± 2.66 | .634 |
| Primary diagnosis (n %) | |||
| Neurology | 15 (14.7%) | 16 (16.2%) | .769 |
| Cardiology | 11 (10.8%) | 2 (2%) | .011 |
| Respiratory | 12 (11.8%) | 16 (16.2%) | .369 |
| Gastroenterology | 11 (10.8%) | 12 (12.1%) | .773 |
| Nephrology | 3 (2.9%) | 6 (6.1%) | .273 |
| Hematology | 0 (0%) | 1 (1%) | – |
| Immunology | 7 (6.9%) | 2 (2%) | .094 |
| Tropical fever | 9 (8.8%) | 6 (6.1%) | .468 |
| Obstetric | 3 (2.9%) | 6 (6.1%) | .274 |
| Trauma | 8 (7.8%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| Poisoning | 2 (2%) | 3 (3%) | .650 |
| Endocrinology | 15 (14.7%) | 22 (22.2%) | .171 |
| Hepatology | 5 (4.9%) | 7 (7.1%) | .512 |
| Gynecology | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| Co-morbidities (n %) | |||
| None | 72 (70.6%) | 66 (66.7%) | .552 |
| Stroke | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | 1.00 |
| HTN/CAD/CHF | 15 (14.7%) | 5 (5.1%) | .023 |
| COPD | 2 (2%) | 4 (4%) | .406 |
| CKD | 1 (1%) | 6 (6.1%) | .050 |
| DM | 4 (3.9%) | 6 (6.1%) | .474 |
| Malignancy | 1 (1%) | 3 (3%) | .311 |
| Chronic liver disease | 1 (1%) | 3 (3%) | .311 |
| Immunosuppressed | 5 (4.9%) | 5 (5.1%) | .948 |
| Vitals before cannulation [median (IQR)] | |||
| Heart Rate | 96 (84.5,121.5) | 100 (86,120) | .965 |
| SBP | 110 (100–130) | 110 (100–130) | .558 |
| DBP | 70 (60–80) | 62 (59–80) | .615 |
| Sp02 | 99 (99,99) | 99 (99,99) | 1.00 |
| No. of patients on vasopressors (n %) | 69 (67.6%) | 61 (61.6%) | >.05 |
| Dose of Injection Noradrenaline | 0.10 (0.05–0.20) | 0.10 (0.057–0.30) | .033 |
| Patients with VIS > 10 (n %) | 34 (33.33%) | 28 (28.28%) | >.05 |
| Patients with BMI ≥ 25 (n %) | 32 (31.37%) | 32 (32.32%) | >.05 |
| Complication (Hematoma N/Y) | 100/2 | 98/1 | 1.00 |
| Number of cannulae used | 121 | 136 | .019 |
BMI: Body mass index, CAD: Coronary artery disease, CHF: Congestive heart failure, DBP: Diastolic blood pressure in mm of Hg, DP Group: direct palpation group, Dose of injection noradrenaline presented in microgram/kg/minute, Hematoma N/Y: Hematoma No/Yes, HTN: Hypertension, SBP: Systolic blood pressure in mm of Hg, USG Group: ultrasound-guided group, VIS: Vasoactive inotropic score. VIS was calculated as a weighted sum of all administered inotropes and vasoconstrictors, reflecting pharmacological support for the cardiovascular system. A score of more than 10 represents sicker patients. It was calculated as, VIS = dopamine dose [μg kg−1 min−1] + dobutamine [μg kg−1 min−1] + 100 × epinephrine dose [μg kg−1 min−1] + 50 × levosimendan dose [μg kg−1 min−1] + 10 × milrinone dose [μg kg−1 min−1] + 10 000 × vasopressin [units kg−1 min−1] + 100 × norepinephrine dose [μg kg−1 min−1].13P-value <.05 is considered significant.
The sample size was estimated using G-Power software®. Under the following assumptions: P1 (first attempt success rate with USG technique) = 0.50, P2 (first attempt success rate with DP technique) = 0.30, α (level of significance) = 0.05, 1-β (power of the study) = 0.80, and one-sided independent test for proportion, the sample size is 74 in each group (USG group and direct palpation group). Appropriate statistical measures and tests are used for analysis. A P-value <.05 was considered statistically significant. A statistical package for social science version 23 (SPSS-23 IBM, USA®) was used.
ResultsAmong 250 arterial cannulations performed during the study period, 49 patients were excluded (10 pediatric arterial cannulations, 10 failure/crossover, and 29 arterial cannulations done with other than 20 G cannula) [Fig. 1]. Two hundred and one patients were enrolled in the study, with 99 randomized to the DP group and 102 to the USG group. There were no differences between demographics and vitals before cannulation between the groups (P > .05) [Table 1]. Table 1 also shows primary organ system involvement and comorbidities. Patients in both groups (USG and DP) were similar (P > .05) in terms of demographics and vitals at the individual arterial site [Table 2].
Comparison of baseline characteristics at the individual arterial sites (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral) after initial randomization to USG and DP groups.
| Artery Cannulated | Radial artery (n = 91) | P-value | Dorsalis pedis artery (n = 54) | P-value | Femoral artery (n = 56) | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique of cannulation | USG | DP | USG | DP | USG | DP | |||
| Arteries cannulated (n%) | 43 (47.25%) | 48 (52.7%) | .441 | 26 (48.14%) | 28 (51.85%) | .599 | 33 (58.92%) | 23 (41%) | .011 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 47.2 ± 14.72 | 49.3 ± 18.17 | .544 | 44.8 ± 22.7 | 41.5 ± 17.8 | .548 | 45.9 ± 17.1 | 43.7 ± 15.4 | .630 |
| Female (n %) | 10 (23.25%) | 24 (48%) | .08 | 10 (38.46%) | 10 (35.71%) | .838 | 16 (48.48%) | 12 (52.17%) | .790 |
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 23.7 ± 2.6 | 23.8 ± 2.6 | .834 | 23.0 ± 3.0 | 23.0 ± 4.5 | .969 | 23.6 ± 2.6 | 23.9 ± 2.9 | .983 |
| Heart Rate (mean ± SD) | 103 ± 22.0 | 106.7 ± 19.1 | .459 | 111.7 ± 21.0 | 107.3 ± 12.9 | .361 | 129 ± 15.3 | 125.5 ± 10.4 | .352 |
| SBP (mean ± SD) | 127.0 ± 23.7 | 121.0 ± 23.6 | .233 | 115 ± 24.0 | 114.1 ± 28.2 | .909 | 102.1 ± 13.8 | 100.3 ± 15.2 | .647 |
| DBP (mean ± SD) | 70.0 ± 13.6 | 70.6 ± 15.2 | .840 | 69.5 ± 16.7 | 70.5 ± 13.2 | .802 | 62.7 ± 11.5 | 58.6 ± 9.8 | .172 |
| Sp02 (mean ± SD) | 98.9 ± 0.15 | 98.7 ± 0.89 | .076 | 98.8 ± 0.63 | 98.2 ± 1.4 | .056 | 98.7 ± 1.0 | 98.2 ± 1.5 | .182 |
BMI: Body mass index, DBP: Diastolic blood pressure in mm of Hg, DP Group: direct palpation group, SBP: Systolic blood pressure in mm of Hg, USG Group: ultrasound-guided group. P-value <.05 is considered significant.
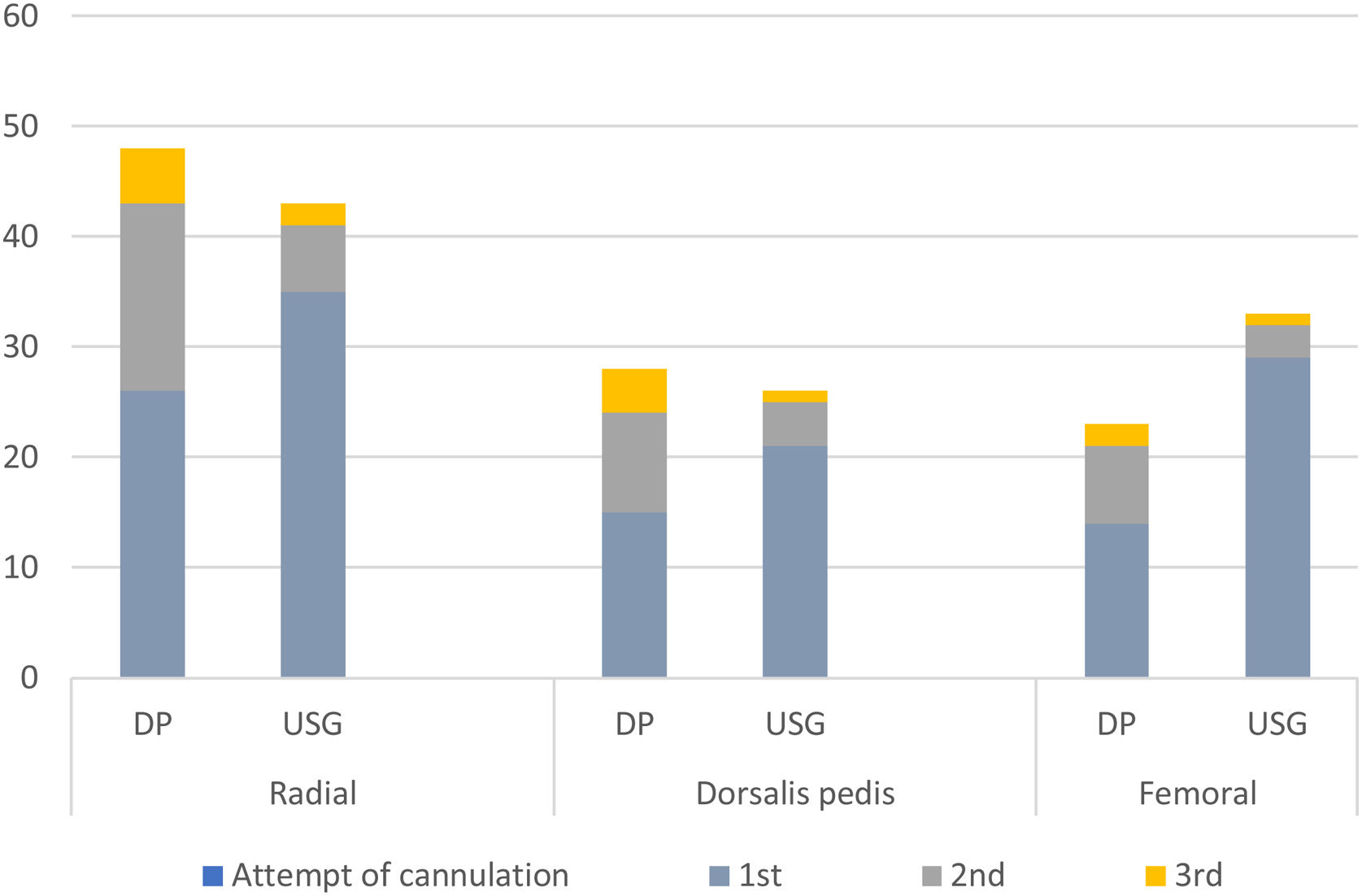
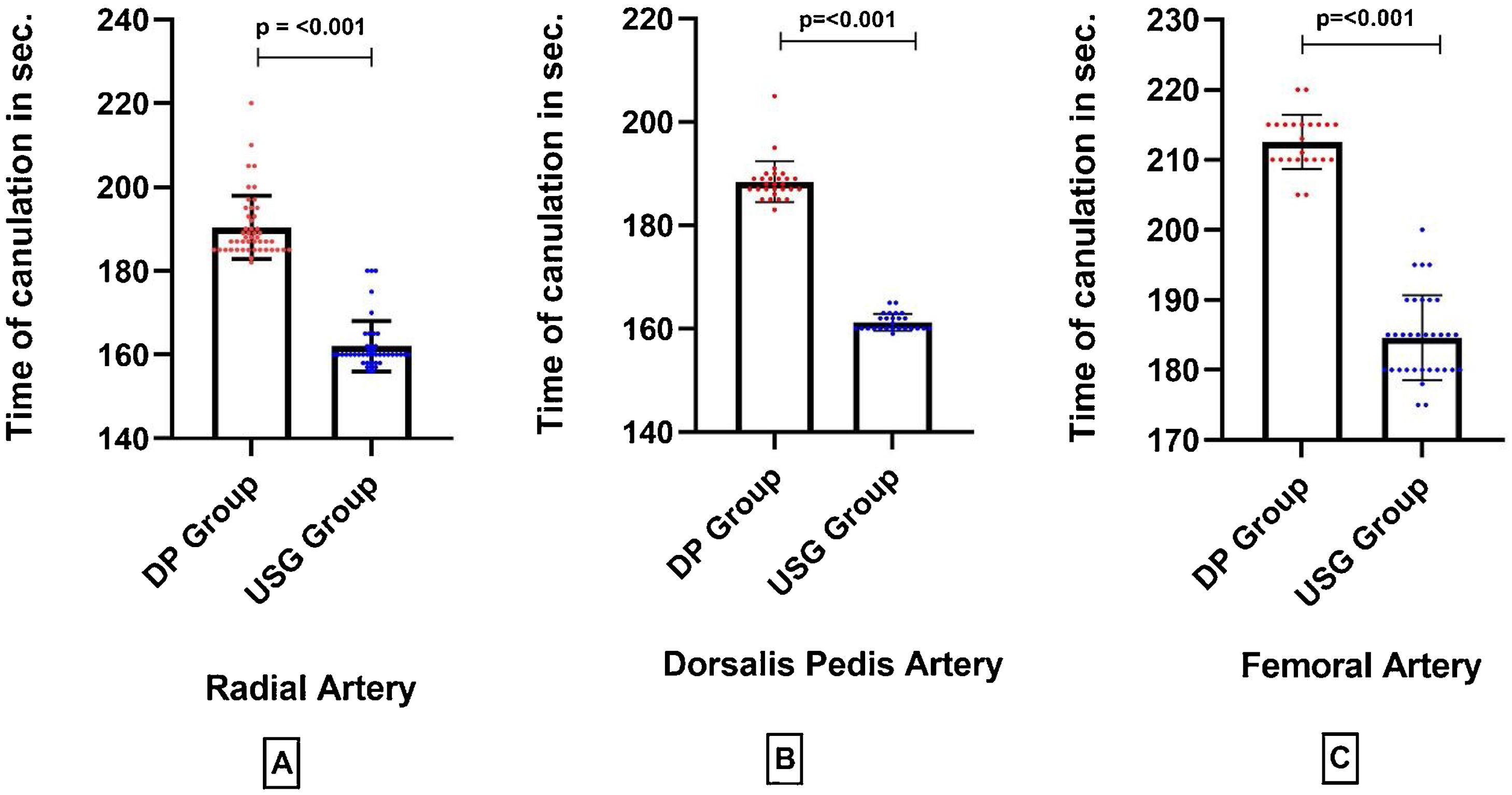
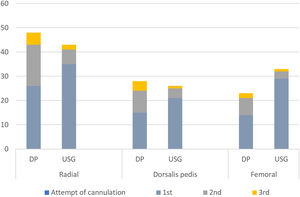
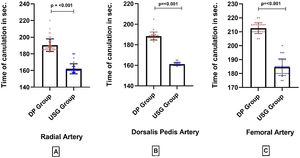
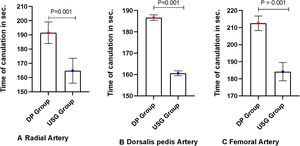
Arteries (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral) cannulated in both groups were also similar (P = .193) [Table 2]. An arterial line was placed on the first attempt in 85 (83.3%) patients in the USG group versus 55 (55.6%) in the DP group (P = .02) [Fig. 4]. First pass success rate in all arterial sites was significantly higher in the USG group [radial artery: USG 35 (81.3%) vs DP 26(54.2%), P = .002; femoral artery: USG 29(87.9%) vs DP 14(60.9%), P = .019; dorsalis pedis artery: USG 21(80.8%) vs DP 15(53.6%), P = .035] [Fig. 4]. Time for cannulation (seconds, mean ± SD) in USG group was significantly shorter compared to DP group for radial, femoral and dorsalis pedis artery [radial artery: USG 162 ± 6.0, DP 190.3 ± 7.5, P < .001; femoral artery: USG 184 ± 6.0, DP 212 ± 3.8, P < .001; dorsalis pedis artery: USG 161.2 ± 1.65, DP 188.4 ± 3.9, P < .001] [Fig. 5]. Complications (subcutaneous hematoma) in both groups were similar [USG 2 (1.9%) vs. DP 1 (1.01%), P = >.05]. The number of cannulae used was significantly reduced in the USG group (P = .019) [Table 1].
Bar diagram showing attempt of cannulation in the Ultrasound guided (USG) group versus in the Direct palpation (DP) group. In USG group first attempt success rate was significantly higher compared to DP group in radial, femoral and Dorsalis pedis artery (Radial artery: USG (81.4%) vs. DP (54.2%), P = .002; Dorsalis pedis artery: USG (80.8%) vs. DP (53.6%), P = .035; Femoral artery: USG (87.9%) vs. DP (60.9%), P = .019).
A Box plot diagram showing a comparison of Time of cannulation in ultrasound versus DP in (seconds, mean ± SD). In USG group time of cannulation was significantly reduced compared to DP group in radial, femoral and Dorsalis pedis artery (Radial artery: USG vs. DP, P < .001; Femoral artery: USG vs. DP, P < .001; Dorsalis pedis artery: USG vs. DP, P < .001).
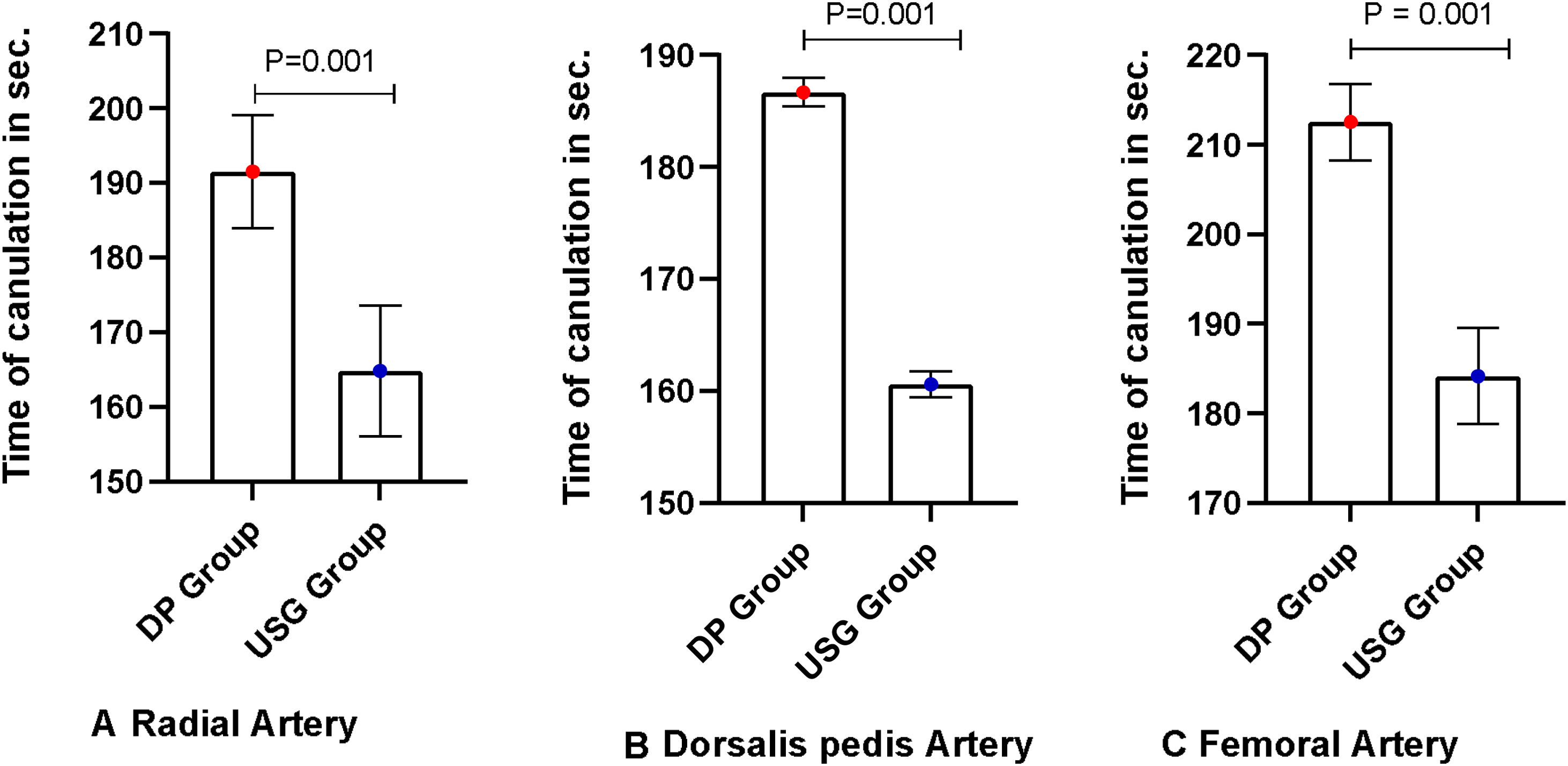
Number of patients who were on vasopressor support in both groups were similar [USG 69 (67.6%) vs. DP: 61 (61.6%), P > .05]. First pass success rate in patients with vasopressors was also significantly higher in USG group [USG 56 (81.2%) vs DP 35 (57.4%), P = .003]. Number of patients with VIS > 10 (n = 63) in both groups were similar [USG 34 (33.33%) vs DP 28 (28.28%), P-value >.05]. First pass success rate was significantly higher in USG group [USG 28 (82.4%) vs DP 15 (53.6%), P-value = .01]. Time for cannulation (seconds, mean ± SD) was significantly shorter in the USG group compared to DP group for the three cannulating arteries in patients with VIS > 10 [radial artery: USG 164.8 ± 8.8, DP 191.5 ± 7.3, P < .001; femoral artery: USG 184.2 ± 5.38, DP 212.56 ± 4.26, P < .001; dorsalis pedis artery: USG 160.6 ± 1.2, DP 186.75 ± 1.26, P < .001] [Fig. 6].
A Box plot diagram showing a comparison of Time of cannulation in ultrasound versus DP in (seconds, mean ± SD) in patients with VIS SCORE > 10 (n = 63). Time for cannulation in USG group was significantly reduced compared to DP group in radial, femoral and dorsalis pedis artery in patients with VIS > 10 (Radial artery: USG vs. DP, P < .001; Femoral artery: USG vs. DP, P < .001; Dorsalis pedis artery: USG vs. DP, P < .001). VIS: Vasoactive inotrope score. USG Group: ultrasound-guided group, DP Group: direct palpation group.
Patients who have a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 (n = 64), were similar in both groups [USG 32 (50%) vs DP 32 (50%), P-value >.05]. The arteries (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral) cannulated in both groups with BMI ≥ 25 were similar. In patients with BMI ≥ 25, first-pass success rate in the USG group was significantly higher than DP group [USG 28 (87.5%) vs DP 16 (50%), P-value <.001]. In patients with BMI ≥ 25, time for cannulation (seconds, mean ± SD) in the USG group was significantly shorter compared to DP group for radial, femoral and dorsalis pedis artery [radial artery: USG 160 ± 2.5, DP 189 ± 6.2, P < .001; femoral artery: USG 184 ± 6.4, DP 214 ± 3.4, P < .001; dorsalis pedis artery: USG 161 ± 1.5, DP 188.4 ± 3.6, P < .002] [Additional material Fig. 1A].
DiscussionAgency for Health Care Policy and Research and Agency for Health Care Research and Quality (AHCPR/AHRQ guidelines) reported that placing a vascular catheter with the help of ultrasound guidance was one of the most underused procedures and that its incorporation into medical practice would improve the safety of patients.14 There is a positive trend toward using the USG cannulation technique in critically-ill patients.15,16 Studies for USG arterial cannulations are mostly from per operative and emergency department (ED) settings.8,17,18,23
Attempt of cannulationIn our study, USG arterial cannulations showed a high first-pass success rate in all three arterial cannulation sites (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral).
Radial arteryIn a meta-analysis by Bhattacharjee S et al., USG radial artery cannulation is associated with a higher first-attempt success rate of cannulation in comparison to digital palpation [OR (95% CI) 2.76 (186, 4.10); P < .001].18,19 Similarly, a meta-analysis by Wan-Jie Gu et al. published in 2016 including 546 patients showed a first pass success rate of 48.5% vs 30.3% for USG and DP group, respectively.24 Levin et al. reported that ultrasound guidance improved the first-pass success rate (USG, 62% vs. DP, 34%) and decreased the number of attempts.25 Our study results resembles the findings of the aforementioned studies.
Dorsalis pedis arteryIn an earlier study in operation theatre settings in neurosurgical patients by Anand et al., ultrasound guidance showed a trend towards an improved first-attempt success rate over the direct palpation technique (76.7% vs. 60%, P-value .267), though this was not statistically significant.22 In contrast, our study showed that the first pass success rate was significantly higher with USG compared with DP.
Femoral arteryOne recent randomized controlled trial reported that ultrasound guidance increased the procedural success rate when compared with the landmark technique for femoral artery cannulation (USG 96% vs landmark technique 78%, P-value .004).26 In our study, USG femoral artery cannulation showed a higher first-pass success rate compared with the DP technique.
Time taken for cannulationA systematic review by Flumignan et al. reported that real-time B-mode ultrasound guidance might improve the time needed for a successful procedure for radial artery catheterization compared to palpation.27 A study comparing ultrasound guidance vs. palpation method for dorsalis pedis artery cannulation showed a statistically similar total procedure time (sum of both assessment and cannulation time, P = .8882).22 In our study, USG arterial cannulation also reduced the time significantly to cannulate in all three arterial cannulation sites (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral) when compared to the DP palpation technique.
VIS > 10In our study, out of 201 patients, 130 patients were on vasopressor support (69 in the ultrasound group and 61 in the DP group). A VIS higher than 10 represents a predictor of poor outcome, prolonged ICU stay, and an increased number of days on mechanical ventilation.28,29 In our study, out of 130 patients on vasopressor support, 63 patients (USG group = 34 vs. DP group = 28) had VIS more than 10. Invasive BP measurement in this group of critically ill patients may aid in the best titrating vasopressor dose. First-attempt success rate and time for cannulation at all arterial cannulation sites (radial, dorsalis pedis, femoral) were significantly higher in the USG group when compared to the DP group in patients with VIS of more than 10 (Fig. 6). This is an important new finding of our study.
BMI ≥ 25USG arterial cannulation is particularly helpful in patients who are obese.30 In our study, 64 patients had BMI ≥ 25. In our study, the first-attempt success rate was significantly higher in the ultrasound group when compared to the DP group. In addition, time for cannulation at all three sites (radial, dorsalis, femoral) were significantly reduced in the ultrasound group. This is an important new finding of our study.
Compared to the palpation technique that uses anatomical landmarks, USG arterial cannulation reduces the number of attempts resulting in a lower complication rate.31,32 Hematoma formation was an uncommon complication in our study, without clinical relevance. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first study in ICU settings to compare all arterial site cannulation.
Limitations of the studyThis was a single-center study with small sample size. A large sample size would have allowed researchers to determine the average values of data better and avoid errors from testing a small number of possible atypical samples. The study population was randomized at technique allocation only but not at individual arterial sites. This study looked only for immediate complications and not for long-term complications. Operator expertise should also be taken under consideration, given that the results may not be replicated in less experienced hands.
Strengths of the studyBy virtue of inclusion criteria operator experience, trainee intensivists who had cannulated at least 20 arterial lines under ultrasound guidance reduced bias. Data generation at 3 different arterial sites was not done previously in any studies. Comparison of both techniques in VIS > 10 and BMI ≥ 25 subsets of the population was a unique part of our study.
ConclusionIn our study, US-guided arterial cannulation (radial, femoral, and dorsalis pedis arteries) had a higher first-pass success rate, overall success rate, and lower cannulation time compared with the palpation technique. This was also demonstrated in patients with septic shock and those with a BMI > 25. Studies in larger populations are needed to confirm our findings.
Authors contributionConception and design of the study- AA, Acquisition of data- SG, Analysis, and interpretation of data- AK, SG, Drafting the article- AA, SG, MG, Revising it critically for important intellectual content- AA, BP, MG, Final approval of the version- AA, BP, MG, AK, SG.
FundingThis is a non-funded study.
Conflict of interestAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the submitted work.