The relationship between different power equations and the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate various power equations: total mechanical power, total elastic power (comprising elastic static and elastic dynamic power), and resistive power, in a cohort of mechanically ventilated patients with and without ARDS. Bayesian analysis was employed to refine estimates and quantify uncertainty by incorporating a priori distributions.
DesignA Bayesian post-hoc analysis was conducted on data from the Mechanical Power Day study.
Setting113 intensive care units across 15 countries and 4 continents.
PatientsAdults who received invasive mechanical ventilation in volume-controlled mode, with (mild and moderate/severe ARDS) and without ARDS.
InterventionsNone.
Main variables of interestARDS, Elastic static power.
ResultsElastic static power was 5.8 J/min (BF: 0.3) in patients with mild ARDS and 7.4 J/min (BF: 0.9) in moderate/severe ARDS patients. Bayesian regression and modeling analysis revealed that elastic static power was independently correlated with mild (a posteriori Mean: 1.3; 95% Credible Interval [Cred. Interval]: 0.2–2.2) and moderate/severe ARDS (a posteriori Mean: 2.8; 95% Cred. Interval: 1.7–3.8) more strongly than other power equations.
ConclusionsElastic static power was found to have the strongest correlation with ARDS severity among the power equations studied. Prospective studies are needed to further validate these findings.
La relación entre diferentes ecuaciones de poder mecánico y la gravedad del síndrome de distrés respiratorio agudo (SDRA) no ha sido aclarada. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar distintas ecuaciones de poder: el poder mecánico total, el poder elástico total (que incluye: poder elástico estático y poder elástico dinámico) y el poder resistivo, en una cohorte de pacientes en ventilación mecánica, con y sin SDRA. Utilizamos análisis Bayesianos para refinar las estimaciones y cuantificar la incertidumbre mediante la incorporación de distribuciones a priori.
DiseñoAnálisis Bayesiano post hoc de los datos del estudio Mechanical Power Day.
Ámbito113 unidades de cuidados intensivos de 15 países y 4 continentes.
PacientesAdultos en ventilación mecánica invasiva en modo de volumen controlado, con (leve y moderado/severo) y sin SDRA.
IntervencionesNinguna.
Variables de interés principalesSDRA, Poder elástico estático.
ResultadosEl poder elástico estático fue de 5,8 J/min (BF: 0,3) en pacientes con SDRA leve y de 7,4 J/min (BF: 0,9) en pacientes con SDRA moderado/grave. El análisis de regresión y modelización Bayesiana reveló que el poder elástico estático se correlacionó con el SDRA leve (media a posteriori: 1,3; intervalo de credibilidad [Int de Cred] del 95%: 0,2 a 2,2) y con el moderado/severo (media a posteriori: 2,8; Int de Cred del 95%: 1,7 a 3,8) con más fuerza que otras ecuaciones de poder analizadas.
ConclusionesEl poder elástico estático tenía la correlación más fuerte con la gravedad del SDRA entre las distintas ecuaciones de poder analizadas. Se necesitan estudios prospectivos para validar estos resultados.
Total elastic power has been associated with an increased risk of developing ventilator-associated lung injury (VALI), as demonstrated by both experimental1,2 and clinical studies.3 The total elastic power is composed of several components: (a) elastic power,1 which includes positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) representing static strain, (b) driving power, encompassing driving pressure as a surrogate for strain in volume-controlled ventilation, and (c) minute ventilation (V′E), which includes tidal volume (VT) and respiratory rate (RR), representing dynamic strain. Together, these components reflect the dynamic loop that may explain the potential injury associated with the elastic energy transmitted by the ventilator to the lungs.4,5
Experimental studies suggest that the cyclic speed of energy delivery, a dynamic component, is a key factor in ergotrauma mechanisms. However, the capacity of lung tissue to absorb this energy and the time allowed for assimilation also play critical roles.6 Any alteration in these mechanisms of energy absorption may increase the risk of VALI.5
In experimental models of ARDS, elastic power has been identified as a crucial component of energy transfer implicated in the development of VALI.1,7 However, at present, no clinical study has evaluated the association between various power equations and the severity of ARDS.
We therefore conducted a secondary analysis of data from the Mechanical Power Day (MPD) international multicenter analytical cross-sectional study.8 This study aimed to evaluate various power equations: total mechanical power, total elastic power (comprising elastic static and elastic dynamic power), and resistive power, in a cohort of mechanically ventilated patients with and without ARDS.
Patients and methodsThis study is a post-hoc analysis of data from the Mechanical Power Day (MPD)8 study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03936231). The MPD study involved 113 intensive care units (ICUs) across 15 countries and 4 continents. The original study received approval from the Clinical Research Ethics Committee (CEIC) of the leading center, with subsequent approvals obtained from the CEICs of each participating center, ensuring compliance with ethical standards across all sites. Additionally, the study was approved by the Scientific Committee of the Spanish Society of Intensive Care Medicine and Coronary Units (SEMICYUC), the Spanish Society of Anesthesiology and Resuscitation (SEDAR), the Spanish Society of Pediatric Intensive Care (SECIP), and the Spanish Society of Neonatology (SENeo).
The MPD study aimed to analyze the prevalence of ARDS in the different ICUs using a cross-sectional design. Variables were collected from patients on invasive mechanical ventilation, both with and without ARDS. The specific timing of data collection during hospitalization was not specified in the study design.
Data collection occurred in two phases in 2019: the first phase in November for patient selection and the second phase in December for follow-up. Inclusion criteria for this analysis were adults ≥18 years old, admitted to the ICU, with or without ARDS (non-ARDS), and receiving invasive volume-controlled mechanical ventilation. Patients receiving mechanical ventilation with modes other than volume-assisted-controlled ventilation were excluded. The original MPD study aimed to determine the value of mechanical power used in daily clinical practice using formulas from the literature on controlled mechanical ventilation patients.
The following formulas used for the analysis were:
where VT is tidal volume (liters), RR is respiratory rate (breaths per minute), Pplat is plateau pressure (cmH2O), PEEP is positive end-expiratory pressure (cmH2O), Ppeak is peak pressure (cmH2O), and DP is the driving pressure (cmH2O). Power is expressed in J/min.Initially, ARDS severity was classified using the Berlin definition.11,12 Due to the low number of severe cases, ARDS was subsequently classified into two groups: mild ARDS (PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300 mmHg) and moderate/severe ARDS (PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 200 mmHg), to ensure sample homogeneity.13
Statistical analysisIn Bayesian statistics, the a priori choice of variables is crucial, as it integrates prior knowledge or assumptions about the parameters before data analysis. Bayesian methods rely on an a priori probability distribution, informed by previous data or expert knowledge. This prior information is then combined with the observed data to update our beliefs and calculate the posterior probability distribution.
For the primary aim, a Bayesian descriptive statistical analysis was performed to evaluate different arterial blood gases (ABG), ventilatory variables, and power equations in patients without ARDS and those with varying severities of ARDS (mild, moderate/severe). Results are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). To compare variables across different ARDS severities and the non-ARDS group (used as the comparator), Bayesian T-contrast for independent samples was employed.
Comparisons were made using contingency tables derived from Bayesian ordinal logistic regression, implemented with the Metropolis-Hastings (MH) adaptive algorithm. A priori informative distributions were used to calculate the covariance of a multivariate normal distribution, applying the Laplace-Metropolis approximation. Results were expressed through Bayes Factors (BF) and were obtained by comparing the non-ARDS model with the mild ARDS and moderate/severe ARDS models. For all models, we considered an acceptance rate of over 20% for the convergence of Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) iterations and an efficiency of over 10% for the MH algorithm as satisfactory.
For the power equations, the selection of predictor variables for final model components was based on the computation of a posteriori inclusion probability (PIP). This was performed using Beta-binomial a priori non-informative Bayesian regressions (Bayesian Model Averaging), with a sampling correlation of 0.99. Post-estimation (random seed: 50, simulations: 10,000) was conducted to calculate a posteriori probabilities for each power equation model concerning ARDS severity.
Multiple Bayesian linear regression models were used to determine correlations between ARDS severity (mild and moderate/severe) and power equations (total mechanical power, total elastic power, elastic static power, elastic dynamic power, and resistive power), with the no-ARDS group as the comparator. This analysis employed an informative a priori Beta-binomial model and Random-walk Metropolis-Hastings sampling. Comparative testing was conducted by confirming the parsimonious convergence of models to their respective a posteriori distributions. Results are presented as means with 95% credible intervals (Cred. Interval).
Finally, to analyze the components of elastic static power and identify the most relevant component within the power equation, we used multiple Bayesian a priori informative linear regressions with Random-walk Metropolis-Hastings sampling. All statistical analyses and figures were performed using Stata v.18 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
ResultsThe original MPD study included 372 patients, with respiratory failure being the primary cause of tracheal intubation (33%; 95% CI, 12–63), followed by neurological impairment (31%; 95% CI, 11–60). Among these, 181 patients (68.4% female) who were receiving volume-controlled ventilation were analyzed. The mean age of these patients was 58.2 years (SD, 17.5 years), with a mean height of 167.5 cm (SD, 9.1 cm), a mean weight of 76.8 kg (SD, 16.7 kg), and a mean predicted body weight of 60.7 kg (SD, 7.3 kg). Of the patients analyzed, 68% met the criteria for ARDS, including 33.2% with mild ARDS and 33.9% with moderate/severe ARDS. Among these patients, 85.7% were receiving continuous sedation infusion, while 14.4% were on continuous neuromuscular blockade.
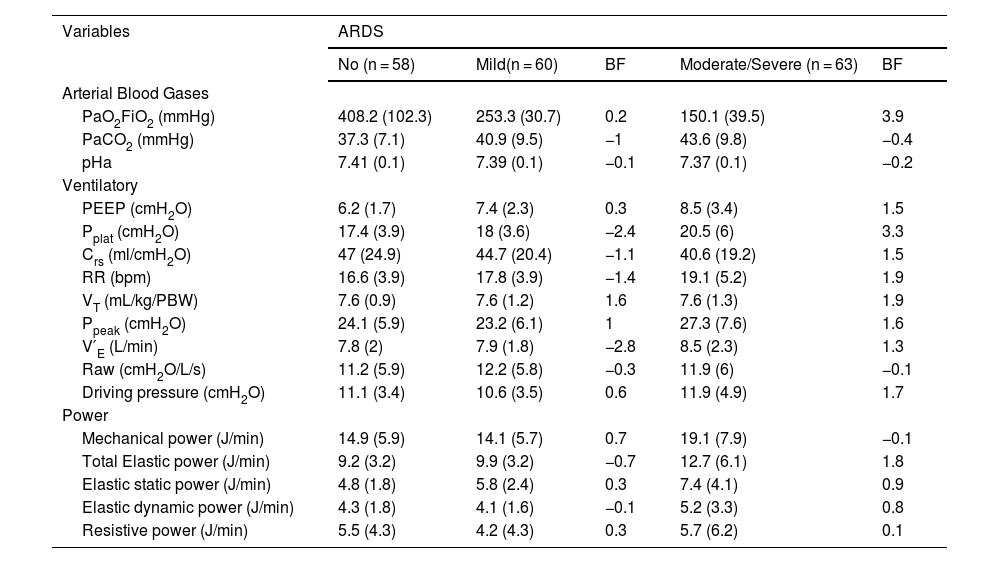
Arterial blood gas (ABG), ventilatory, and power equations are summarized in Table 1.
Description of different respiratory variables according to ARDS severity.
| Variables | ARDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 58) | Mild(n = 60) | BF | Moderate/Severe (n = 63) | BF | |
| Arterial Blood Gases | |||||
| PaO2FiO2 (mmHg) | 408.2 (102.3) | 253.3 (30.7) | 0.2 | 150.1 (39.5) | 3.9 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 37.3 (7.1) | 40.9 (9.5) | −1 | 43.6 (9.8) | −0.4 |
| pHa | 7.41 (0.1) | 7.39 (0.1) | −0.1 | 7.37 (0.1) | −0.2 |
| Ventilatory | |||||
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 6.2 (1.7) | 7.4 (2.3) | 0.3 | 8.5 (3.4) | 1.5 |
| Pplat (cmH2O) | 17.4 (3.9) | 18 (3.6) | −2.4 | 20.5 (6) | 3.3 |
| Crs (ml/cmH2O) | 47 (24.9) | 44.7 (20.4) | −1.1 | 40.6 (19.2) | 1.5 |
| RR (bpm) | 16.6 (3.9) | 17.8 (3.9) | −1.4 | 19.1 (5.2) | 1.9 |
| VT (mL/kg/PBW) | 7.6 (0.9) | 7.6 (1.2) | 1.6 | 7.6 (1.3) | 1.9 |
| Ppeak (cmH2O) | 24.1 (5.9) | 23.2 (6.1) | 1 | 27.3 (7.6) | 1.6 |
| V′E (L/min) | 7.8 (2) | 7.9 (1.8) | −2.8 | 8.5 (2.3) | 1.3 |
| Raw (cmH2O/L/s) | 11.2 (5.9) | 12.2 (5.8) | −0.3 | 11.9 (6) | −0.1 |
| Driving pressure (cmH2O) | 11.1 (3.4) | 10.6 (3.5) | 0.6 | 11.9 (4.9) | 1.7 |
| Power | |||||
| Mechanical power (J/min) | 14.9 (5.9) | 14.1 (5.7) | 0.7 | 19.1 (7.9) | −0.1 |
| Total Elastic power (J/min) | 9.2 (3.2) | 9.9 (3.2) | −0.7 | 12.7 (6.1) | 1.8 |
| Elastic static power (J/min) | 4.8 (1.8) | 5.8 (2.4) | 0.3 | 7.4 (4.1) | 0.9 |
| Elastic dynamic power (J/min) | 4.3 (1.8) | 4.1 (1.6) | −0.1 | 5.2 (3.3) | 0.8 |
| Resistive power (J/min) | 5.5 (4.3) | 4.2 (4.3) | 0.3 | 5.7 (6.2) | 0.1 |
Data are presented as means and standard deviation (parenthesis). Mild ARDS is defined as a PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300 mmHg and moderate/severe as PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 200 mmHg. Each variable is analyzed as an individual model with respect to the same dependent variable (ARDS severity), and adjust by weight.
The non-ARDS variable is the common comparator for each model corresponding to the different severity of ARDS.
BF: Bayes factor; ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome; Ratio of arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2), PaCO2: arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide; pHa: arterial pH; PEEP: positive end-expiratory pressure; Pplat: plateau pressure; Crs: compliance of respiratory system; RR: respiratory rate; VT: tidal volume; Ppeak: peak pressure; V′E: minute ventilation; Raw: airway resistance.
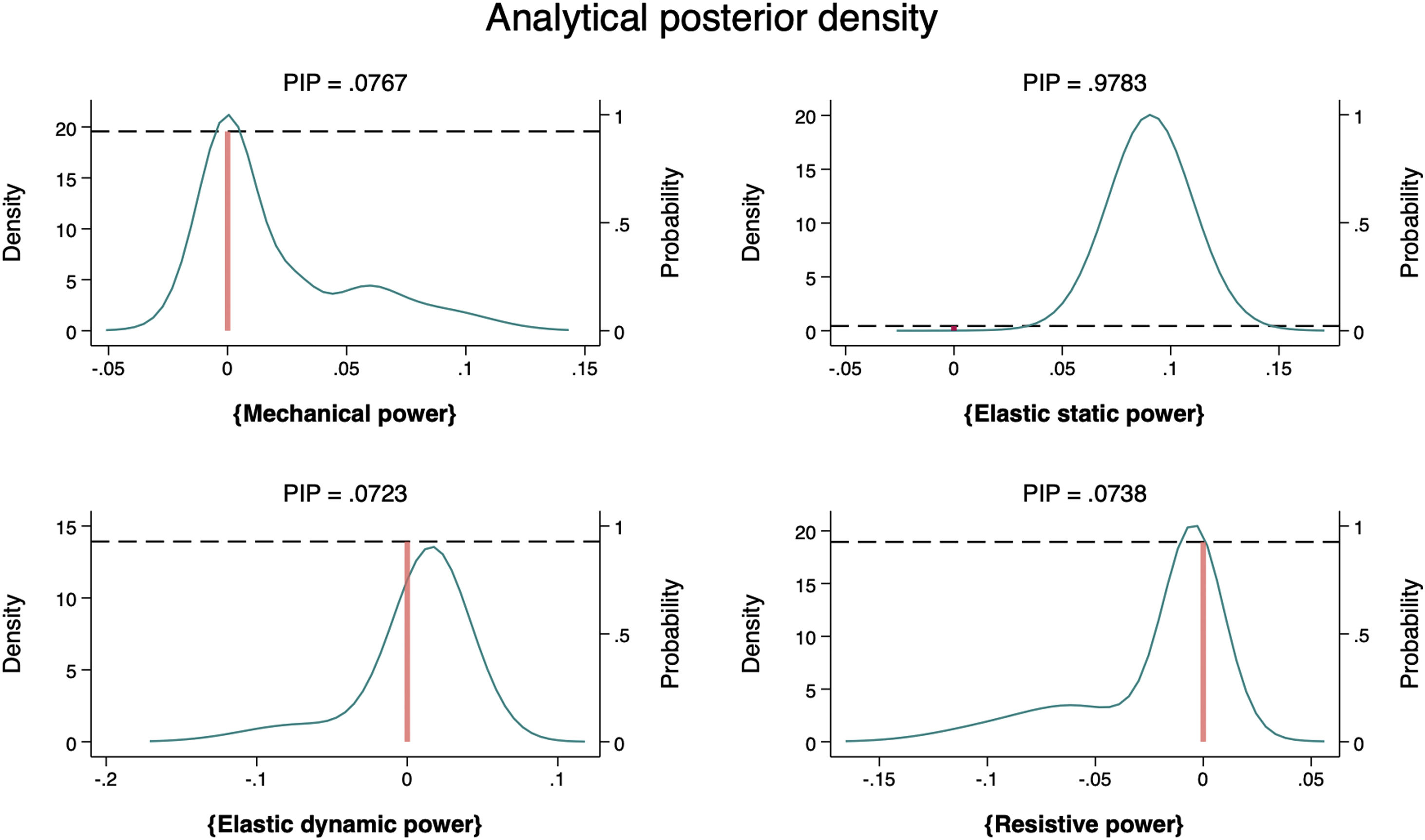
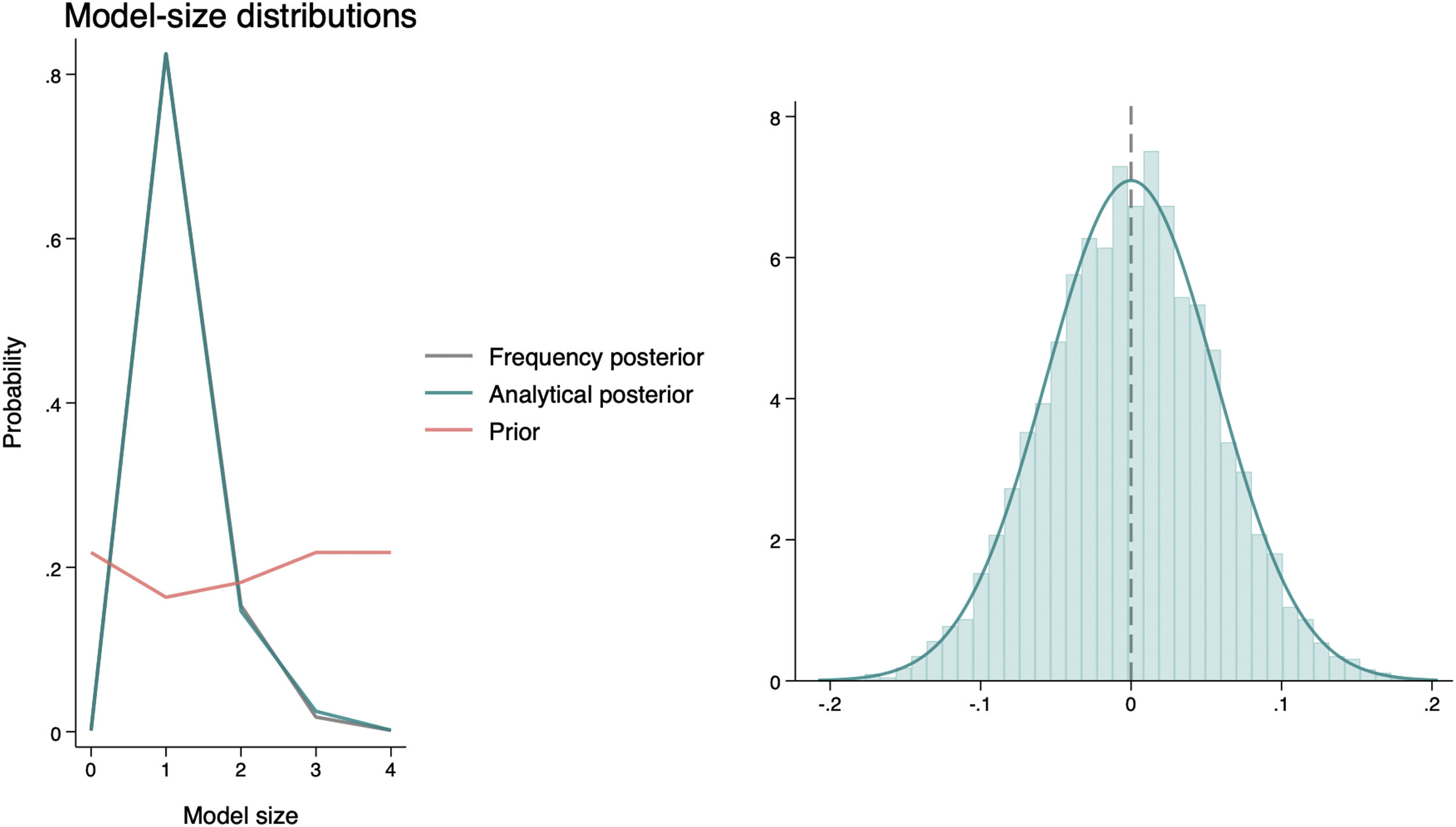
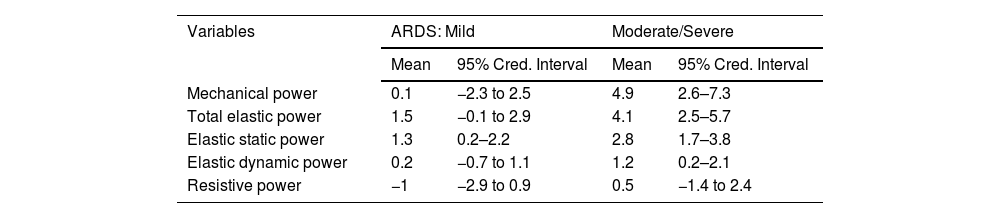
Bayesian regression analysis identified the best models associated with ARDS severity. Elastic static power demonstrated the highest a posteriori inclusion probability (PIP) of 0.978 (Mean, 0.09; SD, 0.02), followed by total mechanical power with a PIP of 0.08 (Mean, 0.001; SD, 0.01), resistive power with a PIP of 0.07 (Mean, -0.001; SD, 0.01), and elastic dynamic power with a PIP of 0.07 (Mean, 0.0005; SD, 0.01) [Fig. 1]. Post-estimation analysis confirmed that elastic static power had the highest probability of a posteriori correlation with ARDS severity (Mean, 0.09; 95% Cred. Interval, 0.02–0.13). The model with a posteriori probability inclusion, as determined by post-estimation, showed an analytical mean probability of 1.2 and followed a normal distribution. The final model, along with the results of this post-estimation probability analysis, is depicted in Fig. 2.
Bayesian analytical posterior density: a posteriori inclusion probability (PIP) of power equations according to ARDS severity. On the abscissa axis are represented the a posteriori means. On the ordinate axis, on the left is represented the density, and on the right the a posteriori inclusion probability.
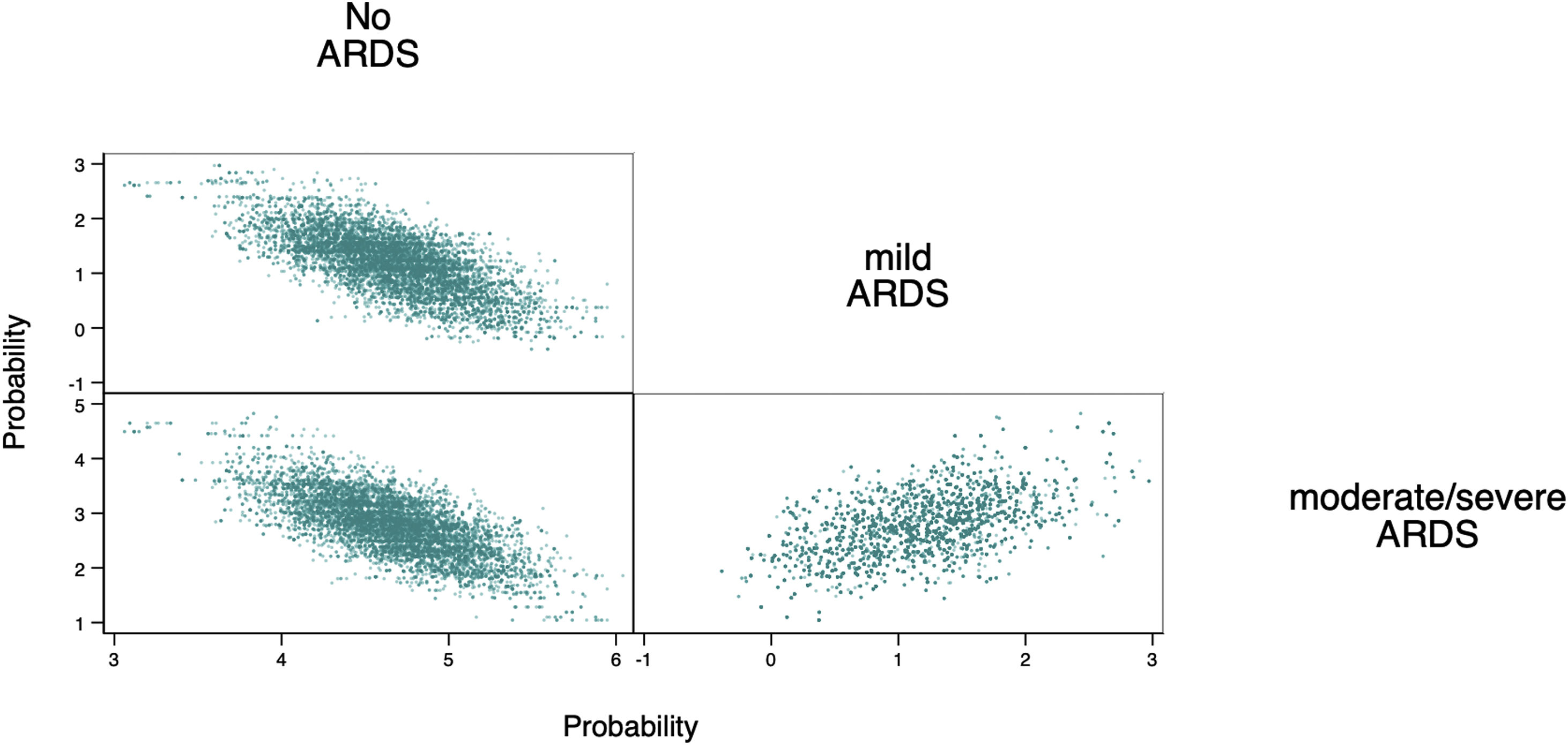
Further analysis of the Bayesian a posteriori probabilities of the relationship between different severities of ARDS and the respiratory power variables revealed that elastic static power was the only power equation consistently correlated with both mild (Mean, 1.3; 95% Cred. Interval, 0.2–2.2) and moderate/severe ARDS (Mean, 2.8; 95% Cred. Interval, 1.7–3.8). Fig. 3 shows the Bayesian matrix plot representing the a posteriori probability distribution of the correlation between elastic static power and ARDS severity, in comparison with non-ARDS. Additional results are presented in Table 2.
Bayesian regression analysis of different respiratory power equations according to ARDS severity.
| Variables | ARDS: Mild | Moderate/Severe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95% Cred. Interval | Mean | 95% Cred. Interval | |
| Mechanical power | 0.1 | −2.3 to 2.5 | 4.9 | 2.6–7.3 |
| Total elastic power | 1.5 | −0.1 to 2.9 | 4.1 | 2.5–5.7 |
| Elastic static power | 1.3 | 0.2–2.2 | 2.8 | 1.7–3.8 |
| Elastic dynamic power | 0.2 | −0.7 to 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.2–2.1 |
| Resistive power | −1 | −2.9 to 0.9 | 0.5 | −1.4 to 2.4 |
Power equations are expressed as a posteriori means and their respective 95% credible intervals (Cred. Interval), adjusted for patient weight.
The non-ARDS variable is the common comparator for each model corresponding to the different severity of ARDS.
Each power equation is analyzed as an individual model with respect to the same dependent variable (ARDS severity).
ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome.
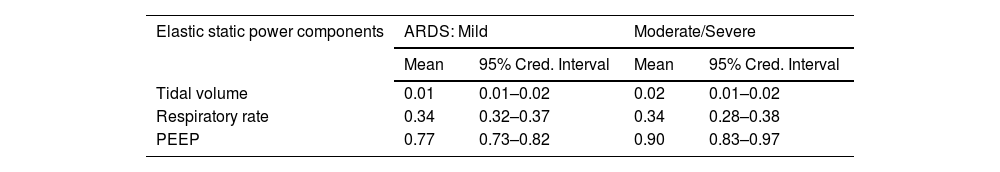
Finally, analysis of the components of elastic static power showed that PEEP was the most relevant variable in this power equation. It was significantly correlated with higher a posteriori probability of both mild (Mean, 0.77; 95% Cred. Interval, 0.73–0.82) and moderate/severe ARDS (Mean, 0.90; 95% Cred. Interval, 0.83–0.97) [Table 3].
Bayesian regression analysis of elastic static power components according to ARDS severity.
| Elastic static power components | ARDS: Mild | Moderate/Severe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95% Cred. Interval | Mean | 95% Cred. Interval | |
| Tidal volume | 0.01 | 0.01–0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01–0.02 |
| Respiratory rate | 0.34 | 0.32–0.37 | 0.34 | 0.28–0.38 |
| PEEP | 0.77 | 0.73–0.82 | 0.90 | 0.83–0.97 |
Elastic static power components are expressed as a posteriori means and their respective 95% credible intervals (Cred. Interval), adjusted for patient weight.
The non-ARDS variable is the common comparator for each model corresponding to the different severity of ARDS.
Each component is analyzed as an individual model with respect to the same dependent variable (ARDS severity).
ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome.
In this post-hoc analysis of a large international cross-sectional study, we found that values of elastic static power higher than 4.8 J/min were indicative of a higher energy load related to ARDS (Table 1). Among the various power equations, elastic static power showed the highest a posteriori inclusion probability in the Bayesian model, making it the most accurate predictor of ARDS severity. Although both mechanical power and total elastic power showed correlation with moderate/severe ARDS, neither of these power equations showed correlation with mild ARDS. In summary, elastic static power was the power equation mostly strongly associated with both the presence and severity of ARDS.
Our study has several strengths. First, we analyzed data from a large sample of mechanically ventilated patients collected through a multicenter, international observational study, enhancing the applicability of our results across different clinical settings. To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine the correlation between various power equations and ARDS severity (mild, moderate/severe). The advanced Bayesian analyses employed in our study provide a compelling hypothesis regarding the clinical utility of elastic static power as a metric that could enhance the understanding of energy transfer in mechanical ventilation. By utilizing real data known a priori for model calculations and a posteriori probabilities, our study robustly supports the relevance of elastic static power in ARDS severity. Bayesian statistics offer several advantages over traditional frequentist methods, making it a powerful tool for data analysis and interpretation in our study.14
Another finding is that PEEP was an important component of elastic static power in both ARDS (<8 cmH2O) and non-ARDS (<6 cmH2O) groups, according to Bayesian statistical analysis. It appears that the primary characteristics of power transmission are not solely related to lung status but rather to the interaction between lung condition and ventilatory strategy. Thus, commonly accepted notions such as “higher power equals more lung damage” and “lower power equals more lung protection” warrant careful re-evaluation.
Static variables (plateau and driving pressures) are relevant for energy generation, but dynamic variables (such as respiratory rate) are also part of the power equation.15 While these components contribute to energy transfer, they do not fully explain it. The cyclic variability of lung volume (strain and strain rate) plays a role in injury from energy inputs16 (stress and stress raisers).17 As demonstrated by Syed et al.,9 PEEP is crucial for providing a baseline strain, which adds to the global strain depending on the lung's elastic properties. PEEP likely establishes a critical baseline in the total elastic configuration of the lung, influencing the total inflation energy.18
The interaction of these power forms may better characterize the energy transfer within the mechanical ventilator-lung complex. Additionally, energy accumulated at the end of each ventilatory cycle19 and subsequent alterations in lung microarchitecture may contribute to ventilator-associated lung injury (VALI).20 PEEP may also lead to heterogeneous effects across different degrees of ARDS (BF,0.3 for mild and BF,1.5 for moderate/severe ARDS) compared with no-ARDS.
Dianti et al.21 conducted a meta-regression analysis of clinical trials involving 4731 patients with ARDS to identify an association between mechanical power and mortality. They found moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 55.8%) and concluded a weak association between elastic power and mortality. Their finding that increased elastic power was proportional to higher PEEP levels (difference 5; 95% CI, 3.5–6.6) aligns with our Bayesian analysis results.
Syed et al.,9 explored the impact of elastic power in a study with 213 patients, comparing those with and without severe hypoxemia. They found that for non-obese patients without severe hypoxemia, the mean elastic power was 9.8 J/min (range, 8.4–11.3 J/min), while for those with severe hypoxemia, it was 16.4 J/min (range, 14.8–17.8 J/min), with a statistically significant difference (P < .01). These findings are consistent with our study, where non-obese patients without hypoxemia had a mean elastic power of 4.5 J/min (range, 3.9–5.1 J/min) and those with severe hypoxemia had a mean of 6.5 J/min (range, 5.9–7.1 J/min), similar to our analysis values (≥7.6 J/min).
Similarly, Gonzalez-Castro et al.22 performed a retrospective longitudinal analysis of 253 patients to evaluate the energy burden associated with mechanical ventilation in obese patients with severe hypoxemia secondary to SARS-CoV-2. They found a mean dynamic power value of 14.6 J/min, which differs from the results of our analysis (mean 5.2 J/min). This discrepancy is mainly due to the difference in conceptualization of the power equations, as there is currently no consensus on this matter. Nevertheless, we used the data available from the work of González-Castro et al. to calculate the elastic static power, finding a mean of 9.7 J/min in obese patients with severe hypoxemia. These values are similar to those found in our study (mean 7.4 J/min) for patients with severe hypoxemia.
Finally, resistive energy was not prominently featured in our analysis, likely because the resistance, both in patients with and without ARDS, was within safe or normal ranges. Given that average respiratory rates in our dataset were around 20 breaths per minute, the energy required to overcome such resistance was minimal.18
LimitationsDespite being multicentre and international, and employing sophisticated Bayesian analysis, our study has limitations inherent to its cross-sectional design. We used physiologic variables measured at a single time point, necessitating validation of our hypotheses through future randomized clinical trials. Additionally, the lack of standardization regarding the timing of variable collection poses another limitation. Nevertheless, our focus on ARDS severity, which can vary significantly over time, highlights the importance of identifying critical moments in the clinical progression of ARDS.
ConclusionsIn the current post-hoc analysis of the Mechanical Power Day study, elastic static power correlated with a higher risk for the development and severity of ARDS. Further clinical trials are required on different degrees of ARDS severity incorporating power variables as instruments for bedside measurement of the transferred energy load.
CRediT authorship contribution statementAF-C, AG-C, VMA, MI-E, CC-M, AM, PEA designed the study; AF-C take full responsibility for the accuracy of the data presented and analyzed in this article and performed the statistical analysis; AF-C, DB, PRMR, CR, PP wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors have approved the submitted version of the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for any part of the work.
FundingThis work has not received any funding. P.R.M.R. was supported by the Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development (408124/2021-0) and the Rio de Janeiro State Research Foundation (E-26/010.001488/2019).
Data availabilityThe datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.