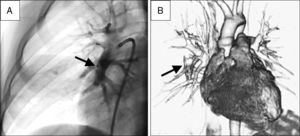
A 12 year-old patient with non-suffocating hemoptysis, with a history of acute lymphoblastic leukemia receiving chemotheraphy and pneumonia a month earlier. Pulmonary CT showed a pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm (PAP) (Fig. 1A). By femoral venous approach, we performed several angiographic projections (Fig. 1B) and implanted in the neck of the PAP an occluder device of ductus arteriosus, Amplatzer Duct Occluder⢢ (St. Jude Medical) 10í8, leaving initial minimal residual flow (Fig. 2A). At the sixth month the CT scan showed total occlusion of the PAP and permeability of the compromised pulmonary vessel (Fig. 2B). Hospital discharge: 48h. Follow-up: 18 months. The percutaneous treatment of PAP is safe and effective, and may prevent surgery that may require lobectomy.
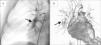
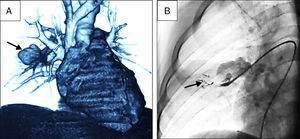
(A) Initial CT scan. 3D reconstruction showing the pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm (arrow) in the right interlobar artery of 25í22mm with short neck and ostium of 7.8mm in diameter. (B) Initial Angiography. Extravasation of contrast of the eroded pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm to pulmonary parenchyma (arrow).
None.
Conflict of interestsNone.