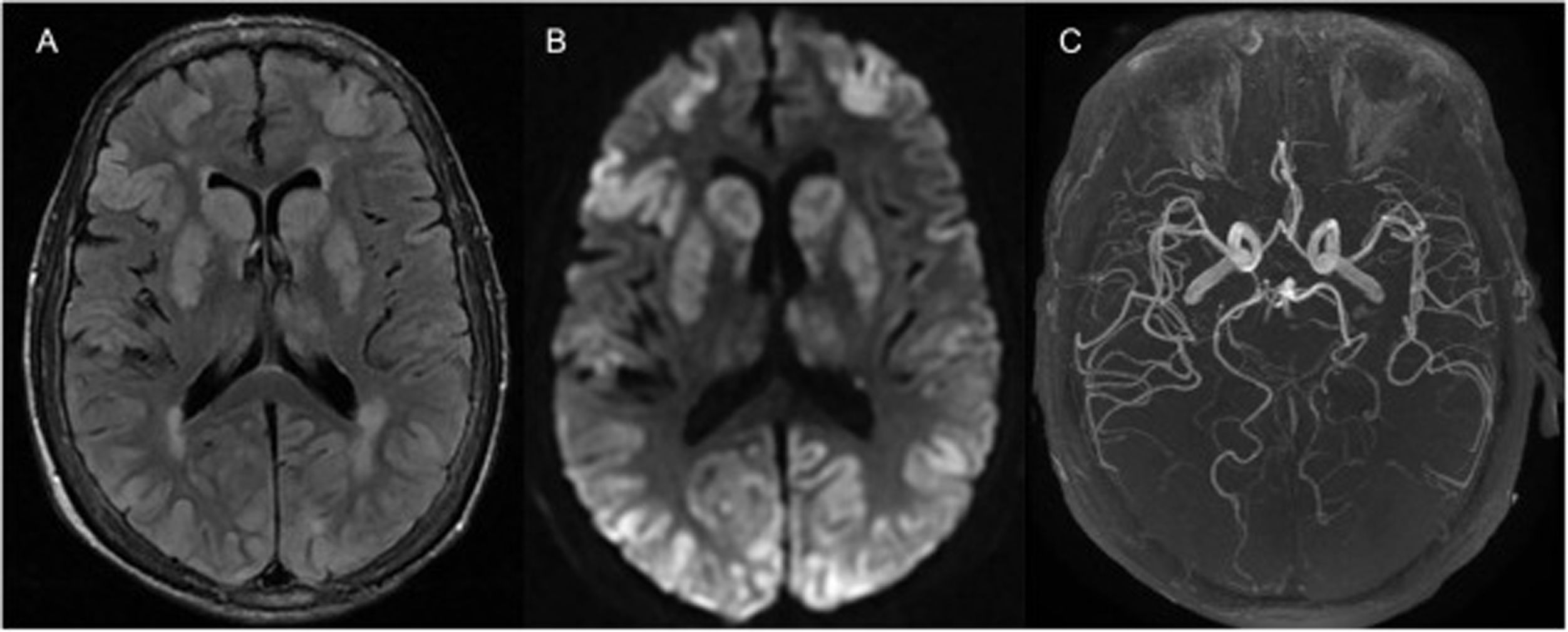
A 70-year-old woman with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and heart failure was transferred to our hospital after an episode of witnessed out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, for which she received 20min of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. At admission, she was comatose, requiring intubation. Neurological examination showed an absence of brainstem reflexes without any pharmacological influence. Twelve hours later, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain (Fig. 1) showed extensive bilateral, cortical–subcortical and basal ganglia hyperintensities on the fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence (A) with restricted diffusion (B) and normal arterial blood supply (C); findings consistent with hypoxic–ischemic brain injury (HIBI). The patient died 48h after admission. The current guidelines for HIBI suggest performing a brain MRI 2–5 days after the event, however recent data shows that the diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence on an MRI can predict neurological outcomes as early as 3h after this catastrophic event.
Consent statementWritten informed consent was obtained.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.