Hyponatremia constitutes the most common electrolyte abnormality found in patients with acquired brain injury,1,2 being present in up to 20% of patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) and 50% of patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).1
In most cases, the underlying cause of euvolemic hyponatremia in brain injured patients is the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).3 In this syndrome, an abnormal water/sodium handling is associated with an osmotic gradient that promotes the shift of water into brain cells, thereby worsening cerebral edema and resulting in deteriorating neurological condition with seizures, coma, increased intracranial pressure end eventually death.1,2,4 An appropriate correction of hyponatremia was associated with increased survival.5
In the recent years, tolvaptan, an orally active, selective, nonpeptide antagonist that blocks arginine vasopressin from binding to V2 receptors of the distal nephron inducing the excretion of electrolyte-free water (the so-called “aquaretic effect”) showed it effectiveness in the treatment of hyponatremia in randomized controlled trials,6 but its use in neurocritically ill patients remains limited.2 Concerns with the potential risk of overcorrection and secondary osmotic demyelinating syndrome (ODS) arose, although the incidence of overcorrection can be even higher when using the commonly accepted 3% hypertonic saline.7 When tolvaptan is used, initial doses of 7.5 or 15mg are recommended.8 Some authors recommend its use as a treatment of SIADH induced hyponatremia when first line therapies including fluid restriction have failed.9
In this report, we studied the effects of a single dose of tolvaptan in hyponatremic neurocritically ill patients.
The study was approved by our Hospital Research Committee. The need of informed consent was waived due to the descriptive and retrospective nature of the study.
All patients fulfilled the following definition of SIADH1:
Plasma sodium<135mEq/L
Plasma osmolality<280mOsm/kg of water
Urine osmolality>100mOsm/kg of water
Urine sodium>40mmol/L
Normal thyroid and adrenal function
Clinical euvolemia or hypervolemia
Absence of recent diuretics use
Overcorrection was defined when the Δ natremia was >8 mEq/L/24h.1
We retrospectively analyzed the effect on the sodium levels and fluid balance in the first 24h after tolvaptan was given. Quantitative data were reported as median (Interquartile Range (IQR) 25–75) and categorical data as number and percentage. Differences between natremia were compared using Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test and the association between 24h fluid balance and Δ natremia using linear regression. A value of p<0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS® 20 (IBM Corporation 2011).
Eight neurocritically ill patients admitted to our ICU fulfilled the above mentioned criteria of SIADH. During their ICU stay, all patients developed hyponatremia and were unsuccessfully treated with oral sodium chloride and 3% hypertonic saline. In such cases, an initial dose of 7.5mg tolvaptan was given in the morning shift (in one patient 15mg were administered). Of note, all patients increased their sodium levels and even in 3 patients (37.5%) no additional doses were deemed necessary. Only one patient (12.5%) presented overcorrection requiring treatment with intravenous dextrose and parenteral desmopressin. This patient received a 15mg initial dose and had risk factors for ODS such as advanced liver disease and alcoholism. No clinical features of ODS were observed in the follow up.
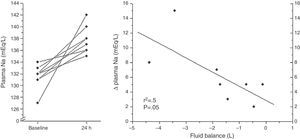
Baseline and clinical data in response to the administration of tolvaptan in the eight patients analyzed are shown (Table 1). A moderate association between Δ Natremia and 24h fluid balance was found (p=0.05) (Fig. 1).
Baseline and clinical data of the eight patients studied.
| Patient number | Diagnosis | Gender | Age (years) | Day | Natremia before tolvaptan | Natremia 24h after tolvaptan | Δ Natremia 24h | Natremia 48h after tolvaptan | 24h fluid balance (ml) | Follow up doses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ICH | Male | 45 | 15 | 132 | 135 | 3 | 135 | −1440 | Yes |
| 2* | ICH | Female | 55 | 11 | 127 | 142 | 15 | 139 | −3425 | No |
| 3 | TBI | Female | 45 | 12 | 131 | 138 | 7 | 137 | −1850 | Yes |
| 4 | SAH | Male | 48 | 21 | 132 | 137 | 5 | 136 | −122 | Yes |
| 5 | SAH | Female | 57 | 8 | 133 | 138 | 5 | 136 | −744 | Yes |
| 6 | Cerebral abcess | Male | 28 | 30 | 132 | 140 | 8 | 140 | −4372 | No |
| 7 | SAH | Male | 50 | 19 | 131 | 136 | 5 | 137 | −1726 | No |
| 8 | TBI | Male | 29 | 25 | 134 | 136 | 2 | 136 | −456 | Yes |
| Median (IQR) | 46 (33–54) | 17 (11–24) | 132 (131–133) | 138 (136–140) | 5 (4–8) | 136 (136–138) | −1600 (−3000 to −500) |
ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage; TBI: traumatic brain injury; SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Our results showed that a single 7.5mg dose of tolvaptan was effective and safe in the treatment of hyponatremia due to SIADH in neurocritically ill patients. Some issues must be taking into consideration when evaluating our results:
Tolvaptan resulted in an increase of sodium levels in all patients. The effect of a single dose of tolvaptan was enough to solve the hyponatremia in some cases, therefore minimizing the cost of the therapy. Follow up doses were used in 5 patients, when natremia decreased after the initial 48h. An initial increase lasting 48h has been previously described.2
Due to the etiology of severe injury, our patients had limited access to water. Unlimited access to water was deemed mandatory to avoid secondary hypovolemia.10 We believe that in the ICU setting and with close monitoring of fluid balance and sodium levels, such requirement should not be considered necessary.
Tolvaptan was safe at the 7.5mg dose in all cases. The only episode of overcorrection occurred with a 15mg dose in a patient with additional risk factors for overcorrection and ODS.11 Related factors include advanced liver disease, malnourishment, hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, etc.11 We would recommend using the 7.5mg dose for initiating tolvaptan in neurocritically ill patients. As stated, median Δ Natremia was 5 (4–8)mEq/24h in our sample. Moreover, we defined overcorrection as Δ natremia>8mEq/L/24h, but some authors would even accept Δ natremia 12mEq/L/24h safe in this setting.
The main limitation of this preliminary study is the retrospective and observational design. In addition, the limited number of patients generates weakness in the linear regression analysis due to extreme values and precludes more complex analysis.
In conclusion, in neurocritically ill patients, a low dose of 7.5mg of tolvaptan was effective and safe in the treatment of hyponatremia due to SIADH. Future studies will determine its exact role in the management of hyponatremia in the whole ICU population. A prospective comparison with 3% hypertonic saline is necessary.
Conflict of interestDr. Llompart-Pou declares having received honoraria from Otsuka for participating in a consensus document in the management of hyponatremia in critically ill patients.
Dr. Pérez-Bárcena, Novo and Raurich declare no financial disclosure.