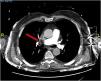
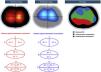
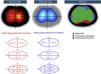
A 76-year-old man was admitted to the emergency department after suffering a syncope. Computed tomography revealed acute bilateral pulmonary embolism (PE), predominantly on the right side (Fig. 1). In the ICU, electrical impedance tomography (EIT) monitoring was started. A ventilation–perfusion (VQ) study revealed a perfusion defect in the right upper lung with preserved ventilation visible as a corresponding high VQ (blue colored) area in the VQ map and a ventilation deficit with preserved perfusion in the dorsal lung appearing as a low VQ (red colored) area (Fig. 2). After conventional clinical management including anticoagulation and PEEP optimization and clinical improvement, both hemodynamic parameters and a new VQ study revealed recovery of the perfusion defect and normalization of VQ matching in all lung regions (Fig. 3). This case illustrates the usefulness of EIT to detect and follow clinical management of severe PE.
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing processNo artificial intelligence was used in the preparation of the manuscript.
Fernando Suárez Sipmann is the president of the scientific committee of the Spanish Society of Intensive Care. He receives grants from Timpel Medical and Maquet.