This study explored the association between body temperature and 28-day septic ICU hospital mortality.
DesignRetrospective cohort analysis.
Setting208 ICUs in the United States.
Patients or participantsSepsis patients from 2014–2015 eICU Collaborative Research Database.
InterventionsBinary logistic regression models, Generalized Additive Model (GAM), Two-Piece Binary Logistic Regression Model.
Main variables of interestBody temperature, 28-day inpatient mortality.
ResultsNonlinear relationship observed; hypothermia (≤36.67 ℃) associated with increased mortality (adjusted OR = 0.74, 95% CI: 0.70–0.80, p < 0.0001).
ConclusionsHypothermia in sepsis correlates with higher mortality; rewarming's potential benefit warrants further exploration.
Investigar la asociación entre la temperatura corporal y la mortalidad hospitalaria a los 28 días en pacientes sépticos en UCI.
DiseñoAnálisis de cohorte retrospectivo.
ÁmbitoUCI en los Estados Unidos.
Pacientes o participantesPacientes con sepsis de la base de datos de investigación colaborativa eICU de 2014-2015.
IntervencionesModelos de regresión logística binaria, Modelo Aditivo Generalizado (GAM), Modelo de Regresión Logística Binaria en Dos Partes.
Variables de interés principaleTemperatura corporal, mortalidad hospitalaria a los 28 días.
ResultadosSe observó una relación no lineal; la hipotermia (≤36.67℃) se asoció con mayor mortalidad (OR ajustada = 0.74, IC del 95% 0.70-0.80, p < 0.0001).
ConclusionesLa hipotermia en la sepsis se correlaciona con una mayor mortalidad; se justifica explorar más el posible beneficio del recalentamiento.
According to the latest definition of international consensus, sepsis is defined as a dysregulated host response to infection, leading to life-threatening organ dysfunction, thus constituting a significant global health challenge.1 Despite the incidence of sepsis morbidity and mortality has decreased in recent times, thanks to the adoption of guidelines and new technologies, data reveals that the number of sepsis patients in 2017 was approximately 48.9 million, with 11 million related deaths globally, accounting for 19.7% of all deaths.2 However, sepsis can be treated, and timely implementation of targeted, goal-oriented interventions can significantly improve the prognosis of patients with sepsis.3,4 Therefore, if critically ill patients can be identified in time, then they can be treated in a timely manner, which can prevent the progression of the disease and improve the prognosis, ultimately reducing the mortality rate of sepsis.
Many current clinical scoring systems that help diagnose or assess the progression of sepsis (e.g., APACHE IV, SAPS II, SIRS) include abnormalities in body temperature deviations from the normal range,4–6 and as a frequently measured vital sign in clinical work, body temperature is both a manifestation in the development of sepsis and has an impact on the progression and regression of the disease, There is reason for us to believe that body temperature plays an extremely important role in sepsis and maybe is a valuable tool for assessing the prognosis of septic patients.
Variability in body temperature, often falling below 36.0 ℃ or rising above 38.0 ℃, is a characteristic feature of sepsis patients and meets the criteria of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.1 The association between body temperature and sepsis prognosis has been extensively studied. Kushimoto et al. (2013) conducted a study on 624 patients with severe sepsis, wherein they grouped patients based on body temperature. They observed that hypothermia (body temperature ≤36.5 ℃) was linked to increased mortality and organ failure.7 Specifically, patients with body temperatures between 35.6–36.5 ℃ exhibited increased 28-day mortality (OR 2.032, P = 0.047), while patients with body temperatures ≤35.5 °C had the highest 28-day mortality (OR 3.096, P = 0.001). Increased body temperature, on the other hand, was not associated with increased disease severity or mortality risk. A meta-analysis in 2017 by Rumbuset al. pointed out fever in septic patients reduces mortality, while hypothermia increases mortality,8 however, most of the studies included in this literature were small and had high heterogeneity; a secondary analysis with public data in 2021 by Thomas-Rüddel et al. noted that fever and hypothermia are two distinct responses to sepsis in humans,9 whereas normothermia responses are rare; they divided the body temperature into small intervals and found that hypothermia was associated with higher mortality, however, this correlation was reduced after adjusting for other risk factors. At the same time, many studies on temperature management in patients with sepsis are underway in recent years, and current research suggests that febrile patients do not benefit from temperature control in the literature10–12; while rewarming of hypothermic patients is rarely carried out in clinical practice, and to date there are not enough clinical studies to demonstrate that hypothermic patients can benefit from active warming measures. In view of this, before conducting interventional treatment studies targeting body temperature in patients with sepsis, we need more detailed observational studies to understand the relationship between body temperature and prognosis.
Therefore, this study intends to conduct a multicenter cohort review of published data from 208 different ICU in the United States between 2014 and 2015 (from the Philips Healthcare eICU Database (eICU-CRD), to explore the association between body temperature and 28-day septic ICU hospital mortality, and to further look for body temperature thresholds that significantly increase the risk of sepsis death.
Materials and methodsData sourceOur study was conducted retrospectively through the eICU Collaborative Research Database (eICU-CRD),13 an online database that contains over 200,000 ICU admissions and is monitored by multiple centers throughout the continental United States. From 2014 to 2015, all data were recorded automatically and accessed electronically using the Philips Healthcare eICU software.13
The eICU-CRD has been utilized in prior observational research.14–16 We completed the Collaborative Institutional Training Initiative (CITI) program and obtained certification in compliance with the data usage agreement set by the PhysioNet Review Board. Access to the database aligns with the Safe Harbor provision of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Data access was granted based on completion of the CITI program, specifically ‘Data or Specimens Only Research’. Given the use of a publicly accessible database without patient involvement, we obtained certification from Privacert (Cambridge, MA) to ensure compliance with safe harbor standards regarding re-identification risk. As a result, the investigation did not require endorsement from the Institutional Review Board of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (record ID 47549485) or the acquisition of informed consent. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, adhering to all relevant rules and regulations.
Study populationThe subjects were all patients diagnosed with sepsis at the time of admission to ICU.
Sepsis was defined as suspected or confirmed infection, with a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score exceeding 2 points in the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) IV dataset.1,17 The eICU Collaborative Research Database contains ICD-9 codes that can be used to indicate infections.
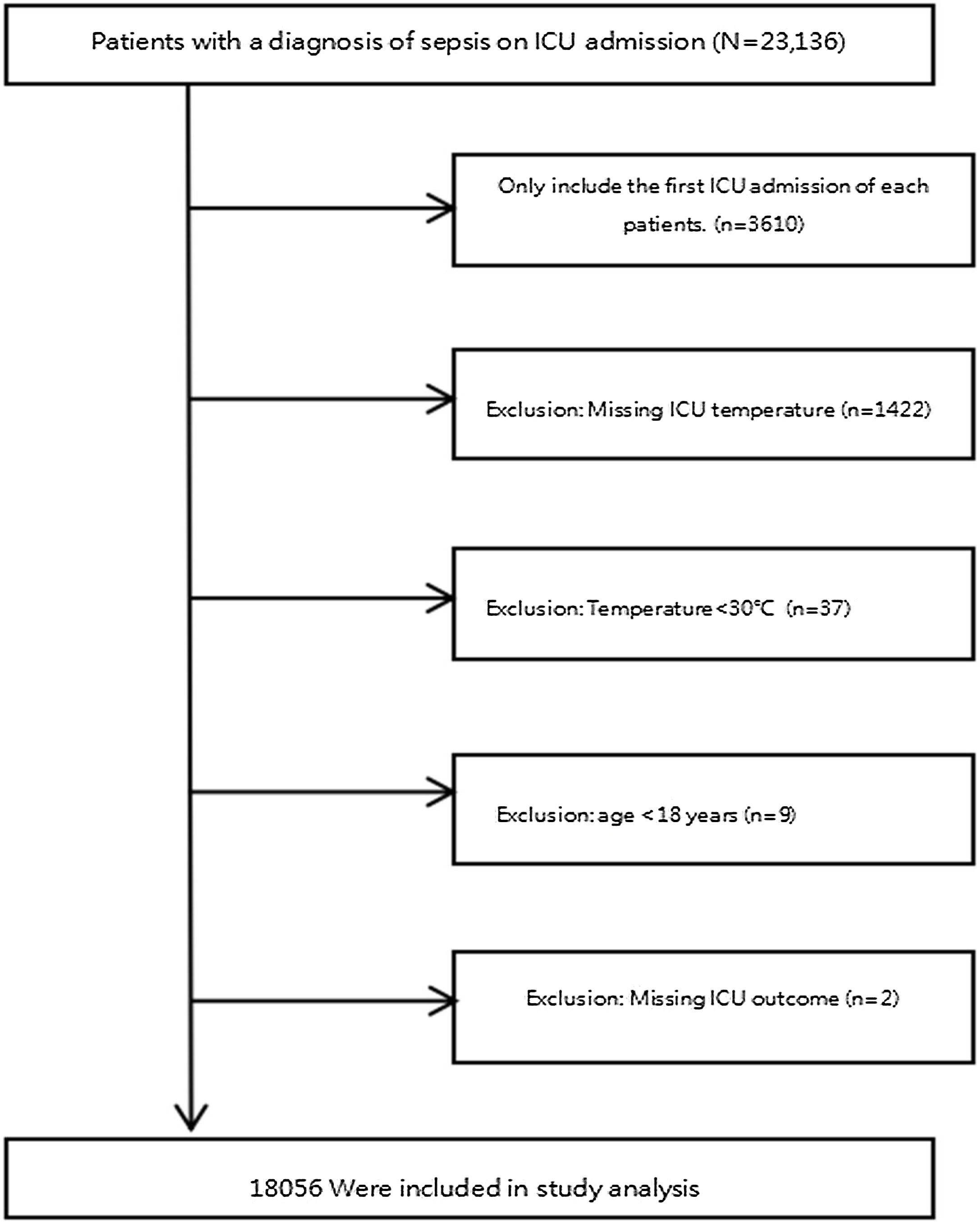
We applied the subsequent exclusion criteria: (1) Patients who were not admitted to the ICU for the first time; (2) missing temperature after ICU admission; (3) temperature < 30 °C; (4) age < 18 years old; (5) lacking of hospitalization outcome. Because it was a secondary analysis of the database, our study did not calculate the sample size. The study flowchart was presented in Fig. 1.
VariablesThe eICU database contains demographic information, physiological measurements from bedside monitors, diagnoses using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Edition, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes, severity of illness assessments, laboratory results, and treatment details.
Data was collected from the eICU-CRD for all participants within the first 24 hours after admission. Extracting baseline patient characteristics such as age, sex, race and weight from the patient table and the Apache Patient Result table; The physiological variables and treatment information of patients were obtained from Apache Aps Var table: Body temperature (°C), Respiratory Rate (RR), Heart Rate (HR), Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP), Mechanical ventilation use, Vasopressor use (1st 24 h) and Hemodialysis, laboratory indicators such as Initial lactate level, Creatinine, and White Blood Cells (WBC) were collected from the laboratory tables; Comorbidities including Metastatic cancer, Immunosuppression, Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), Arrhythmia, Congestive Heart Failure(CHF), Hepatic Failure, Diabetes, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease(COPD) were extracted from the APACHE IV score. In this study, the collected body temperature data represent the highest temperatures recorded within the first 24 hours after patients were admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), primarily obtained through oral and rectal thermometry. Additionally, we identified diagnostic codes for sepsis from the diagnostic form, measuring disease severity by SOFA score, APACHEIV score and Acute Physiology score III. To address potential bias stemming from missing covariates in the modeling process, this study adopts multiple imputation techniques for managing absent data. This strategy aims to enhance the precision of statistical analysis on the intended sample.18,19
OutcomesThe study investigated all-cause mortality occurring within 28 days following admission to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU).
Statistical analysisWe used means ± standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile ranges (IQR) to represent continuous variables, while categorical data were presented using counts and percentages. To analyze differences among body temperature tertiles, we utilized one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for continuous variables and chi-squared tests for categorical variables (Table 1). Furthermore, unadjusted correlations between baseline metrics and 28-day mortality were also compared (Table 2).
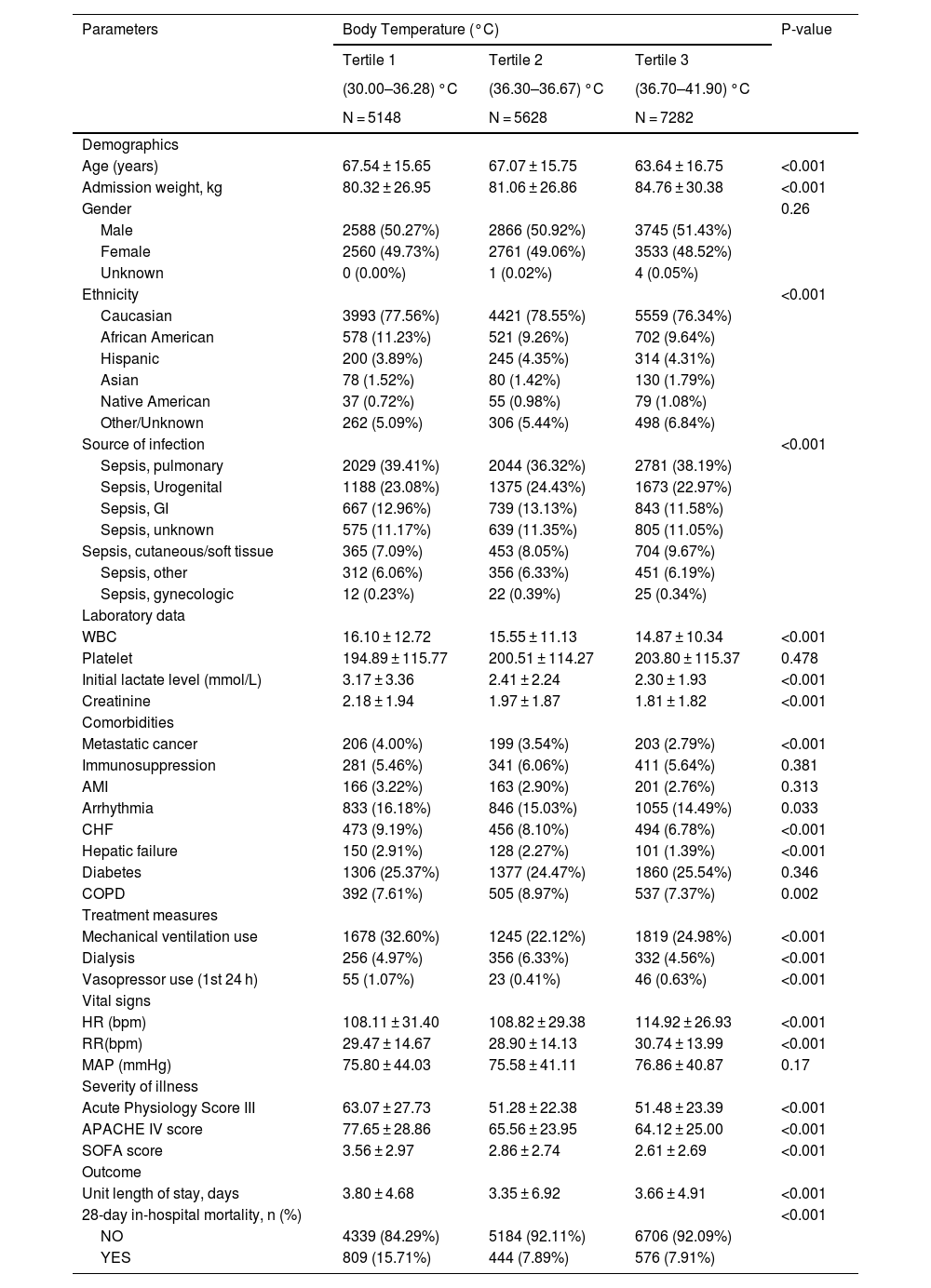
Baseline characteristics and 28-day mortality according to the tertiles of body temperature (n = 18056).
| Parameters | Body Temperature (°C) | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tertile 1 | Tertile 2 | Tertile 3 | ||
| (30.00–36.28) °C | (36.30–36.67) °C | (36.70–41.90) °C | ||
| N = 5148 | N = 5628 | N = 7282 | ||
| Demographics | ||||
| Age (years) | 67.54 ± 15.65 | 67.07 ± 15.75 | 63.64 ± 16.75 | <0.001 |
| Admission weight, kg | 80.32 ± 26.95 | 81.06 ± 26.86 | 84.76 ± 30.38 | <0.001 |
| Gender | 0.26 | |||
| Male | 2588 (50.27%) | 2866 (50.92%) | 3745 (51.43%) | |
| Female | 2560 (49.73%) | 2761 (49.06%) | 3533 (48.52%) | |
| Unknown | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (0.02%) | 4 (0.05%) | |
| Ethnicity | <0.001 | |||
| Caucasian | 3993 (77.56%) | 4421 (78.55%) | 5559 (76.34%) | |
| African American | 578 (11.23%) | 521 (9.26%) | 702 (9.64%) | |
| Hispanic | 200 (3.89%) | 245 (4.35%) | 314 (4.31%) | |
| Asian | 78 (1.52%) | 80 (1.42%) | 130 (1.79%) | |
| Native American | 37 (0.72%) | 55 (0.98%) | 79 (1.08%) | |
| Other/Unknown | 262 (5.09%) | 306 (5.44%) | 498 (6.84%) | |
| Source of infection | <0.001 | |||
| Sepsis, pulmonary | 2029 (39.41%) | 2044 (36.32%) | 2781 (38.19%) | |
| Sepsis, Urogenital | 1188 (23.08%) | 1375 (24.43%) | 1673 (22.97%) | |
| Sepsis, GI | 667 (12.96%) | 739 (13.13%) | 843 (11.58%) | |
| Sepsis, unknown | 575 (11.17%) | 639 (11.35%) | 805 (11.05%) | |
| Sepsis, cutaneous/soft tissue | 365 (7.09%) | 453 (8.05%) | 704 (9.67%) | |
| Sepsis, other | 312 (6.06%) | 356 (6.33%) | 451 (6.19%) | |
| Sepsis, gynecologic | 12 (0.23%) | 22 (0.39%) | 25 (0.34%) | |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| WBC | 16.10 ± 12.72 | 15.55 ± 11.13 | 14.87 ± 10.34 | <0.001 |
| Platelet | 194.89 ± 115.77 | 200.51 ± 114.27 | 203.80 ± 115.37 | 0.478 |
| Initial lactate level (mmol/L) | 3.17 ± 3.36 | 2.41 ± 2.24 | 2.30 ± 1.93 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine | 2.18 ± 1.94 | 1.97 ± 1.87 | 1.81 ± 1.82 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Metastatic cancer | 206 (4.00%) | 199 (3.54%) | 203 (2.79%) | <0.001 |
| Immunosuppression | 281 (5.46%) | 341 (6.06%) | 411 (5.64%) | 0.381 |
| AMI | 166 (3.22%) | 163 (2.90%) | 201 (2.76%) | 0.313 |
| Arrhythmia | 833 (16.18%) | 846 (15.03%) | 1055 (14.49%) | 0.033 |
| CHF | 473 (9.19%) | 456 (8.10%) | 494 (6.78%) | <0.001 |
| Hepatic failure | 150 (2.91%) | 128 (2.27%) | 101 (1.39%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 1306 (25.37%) | 1377 (24.47%) | 1860 (25.54%) | 0.346 |
| COPD | 392 (7.61%) | 505 (8.97%) | 537 (7.37%) | 0.002 |
| Treatment measures | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation use | 1678 (32.60%) | 1245 (22.12%) | 1819 (24.98%) | <0.001 |
| Dialysis | 256 (4.97%) | 356 (6.33%) | 332 (4.56%) | <0.001 |
| Vasopressor use (1st 24 h) | 55 (1.07%) | 23 (0.41%) | 46 (0.63%) | <0.001 |
| Vital signs | ||||
| HR (bpm) | 108.11 ± 31.40 | 108.82 ± 29.38 | 114.92 ± 26.93 | <0.001 |
| RR(bpm) | 29.47 ± 14.67 | 28.90 ± 14.13 | 30.74 ± 13.99 | <0.001 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 75.80 ± 44.03 | 75.58 ± 41.11 | 76.86 ± 40.87 | 0.17 |
| Severity of illness | ||||
| Acute Physiology Score III | 63.07 ± 27.73 | 51.28 ± 22.38 | 51.48 ± 23.39 | <0.001 |
| APACHE IV score | 77.65 ± 28.86 | 65.56 ± 23.95 | 64.12 ± 25.00 | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 3.56 ± 2.97 | 2.86 ± 2.74 | 2.61 ± 2.69 | <0.001 |
| Outcome | ||||
| Unit length of stay, days | 3.80 ± 4.68 | 3.35 ± 6.92 | 3.66 ± 4.91 | <0.001 |
| 28-day in-hospital mortality, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| NO | 4339 (84.29%) | 5184 (92.11%) | 6706 (92.09%) | |
| YES | 809 (15.71%) | 444 (7.89%) | 576 (7.91%) | |
Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, median (interquartile range), or percentage. Among the 18056 patients, the number of participants with missing data of admission weight 374 (2.07%), Ethnicity 3254 (18.02%), WBC 2185 (12.10%), creatinine 45 (0.25%), Initial lactate level (mmol/L) 6815 (37.74%), Respiratory rate (bpm) 53 (0.29%), Heart rate (bpm) 16 (0.09%), MAP (mmHg) 40 (0.22%), SOFA 532 (2.95%), APACHE IV score 2041 (11.30%), Acute Physiology Score III 2041 (11.30%).
OR: Odds ratios; CI: Confidence; Ref: Reference; SD: Standard deviation; n: number; WBC: White blood cell; MAP: Mean arterial pressure; AMI: Acute myocardial infarction; CHF: Congestive heart failure; COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; MAP: Mean arterial pressure; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
The unadjusted association between baseline variables and 28-day mortality (n = 18056).
| Variable | Statistics | OR 95%CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Admission weight, kg | 82.39 ± 28.42 | 1.00 (0.99, 1.00) | <0.0001 |
| WBC | 15.24 ± 11.32 | 1.02 (1.02, 1.02) | <0.0001 |
| Initial lactate level (mmol/L) | 2.39 ± 2.53 | 1.33 (1.31, 1.35) | <0.0001 |
| Creatinine | 1.95 ± 1.87 | 1.14 (1.11, 1.16) | <0.0001 |
| Temperature (°C) | 36.60 ± 1.11 | 0.75 (0.71, 0.78) | <0.0001 |
| HR (bpm) | 111.06 ± 29.20 | 1.01 (1.01, 1.01) | <0.0001 |
| RR (bpm) | 29.79 ± 14.25 | 1.02 (1.02, 1.03) | <0.0001 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 76.18 ± 41.88 | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | <0.0001 |
| Age (years) | |||
| <=65 | 8165 (45.22%) | Ref | |
| >65, <=80 | 6097 (33.77%) | 1.42 (1.27, 1.59) | <0.0001 |
| >80 | 3794 (21.01%) | 1.62 (1.43, 1.84) | <0.0001 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 9197 (50.94%) | Ref | |
| Female | 8854 (49.04%) | 0.99 (0.90, 1.09) | 0.7996 |
| Unknown | 5 (0.03%) | 0.00 (0.00, inf.) | 0.9430 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Caucasian | 13971 (77.38%) | Ref | |
| African American | 1801 (9.97%) | 0.99 (0.84, 1.16) | 0.8654 |
| Hispanic | 759 (4.20%) | 0.90 (0.70, 1.15) | 0.3956 |
| Asian | 288 (1.60%) | 0.88 (0.58, 1.32) | 0.5225 |
| Native American | 171 (0.95%) | 0.91 (0.54, 1.53) | 0.7239 |
| Other/Unknown | 1066 (5.90%) | 1.04 (0.85, 1.27) | 0.7328 |
| Source of infection | |||
| Sepsis, pulmonary | 6854 (37.96%) | Ref | |
| Sepsis, Urogenital | 4234 (23.45%) | 0.48 (0.41, 0.55) | <0.0001 |
| Sepsis, GI | 2249 (12.46%) | 1.19 (1.03, 1.37) | 0.0153 |
| Sepsis, unknown | 2019 (11.18%) | 0.95 (0.81, 1.11) | 0.5303 |
| Sepsis, cutaneous/soft tissue | 1522 (8.43%) | 0.53 (0.42, 0.65) | <0.0001 |
| Sepsis, other | 1119 (6.20%) | 0.91 (0.74, 1.11) | 0.3389 |
| Sepsis, gynecologic | 59 (0.33%) | 0.69 (0.28, 1.73) | 0.4322 |
| Metastatic cancer | |||
| NO | 17448 (96.63%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 608 (3.37%) | 1.72 (1.38, 2.15) | <0.0001 |
| Immunosuppression | |||
| NO | 17023 (94.28%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 1033 (5.72%) | 1.13 (0.93, 1.38) | 0.2230 |
| AMI | |||
| NO | 17526 (97.06%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 530 (2.94%) | 1.41 (1.10, 1.82) | 0.0075 |
| Arrhythmia | |||
| NO | 15322 (84.86%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 2734 (15.14%) | 1.57 (1.39, 1.77) | <0.0001 |
| CHF | |||
| NO | 16633 (92.12%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 1423 (7.88%) | 1.32 (1.12, 1.55) | 0.0010 |
| Hepatic failure | |||
| NO | 17677 (97.90%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 379 (2.10%) | 2.64 (2.07, 3.38) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes | |||
| NO | 13513 (74.84%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 4543 (25.16%) | 0.68 (0.60, 0.77) | <0.0001 |
| COPD | |||
| NO | 16622 (92.06%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 1434 (7.94%) | 0.88 (0.73, 1.06) | 0.1684 |
| Mechanical ventilation use | |||
| NO | 13314 (73.74%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 4742 (26.26%) | 3.11 (2.81, 3.43) | <0.0001 |
| Dialysis | |||
| NO | 17112 (94.77%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 944 (5.23%) | 1.22 (1.00, 1.50) | 0.0530 |
| Vasopressor use (1st 24 h) | |||
| NO | 17931 (99.31%) | Ref | |
| Yes | 125 (0.69%) | 2.84 (1.88, 4.29) | <0.0001 |
| SOFA categorical | |||
| <=2 | 9061 (50.18%) | Ref | |
| >2, <=4 | 4469 (24.75%) | 2.32 (2.02, 2.66) | <0.0001 |
| >4, <=15 | 4507 (24.96%) | 5.28 (4.68, 5.96) | <0.0001 |
| >15 | 19 (0.11%) | 22.52 (9.10, 55.72) | <0.0001 |
| Acute Physiology Score III categorical | |||
| <=48 | 8228 (45.57%) | Ref | |
| >48, <=68 | 5423 (30.03%) | 2.69 (2.31, 3.14) | <0.0001 |
| >68 | 4405 (24.40%) | 9.31 (8.11, 10.69) | <0.0001 |
| APACHE IV score categorical | |||
| <=60 | 7558 (41.86%) | Ref | |
| >60, <=80 | 5423 (30.03%) | 2.93 (2.48, 3.47) | <0.0001 |
| >80 | 5075 (28.11%) | 10.64 (9.14, 12.37) | <0.0001 |
Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, or percentage. OR: Odds ratios, CI: Confidence, Ref Reference; SD: Standard deviation; n number; WBC: White blood cell; MAP: Mean arterial pressure, AMI: Acute myocardial infarction; CHF: Chronic heart failure; COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; MAP: Mean arterial pressure; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
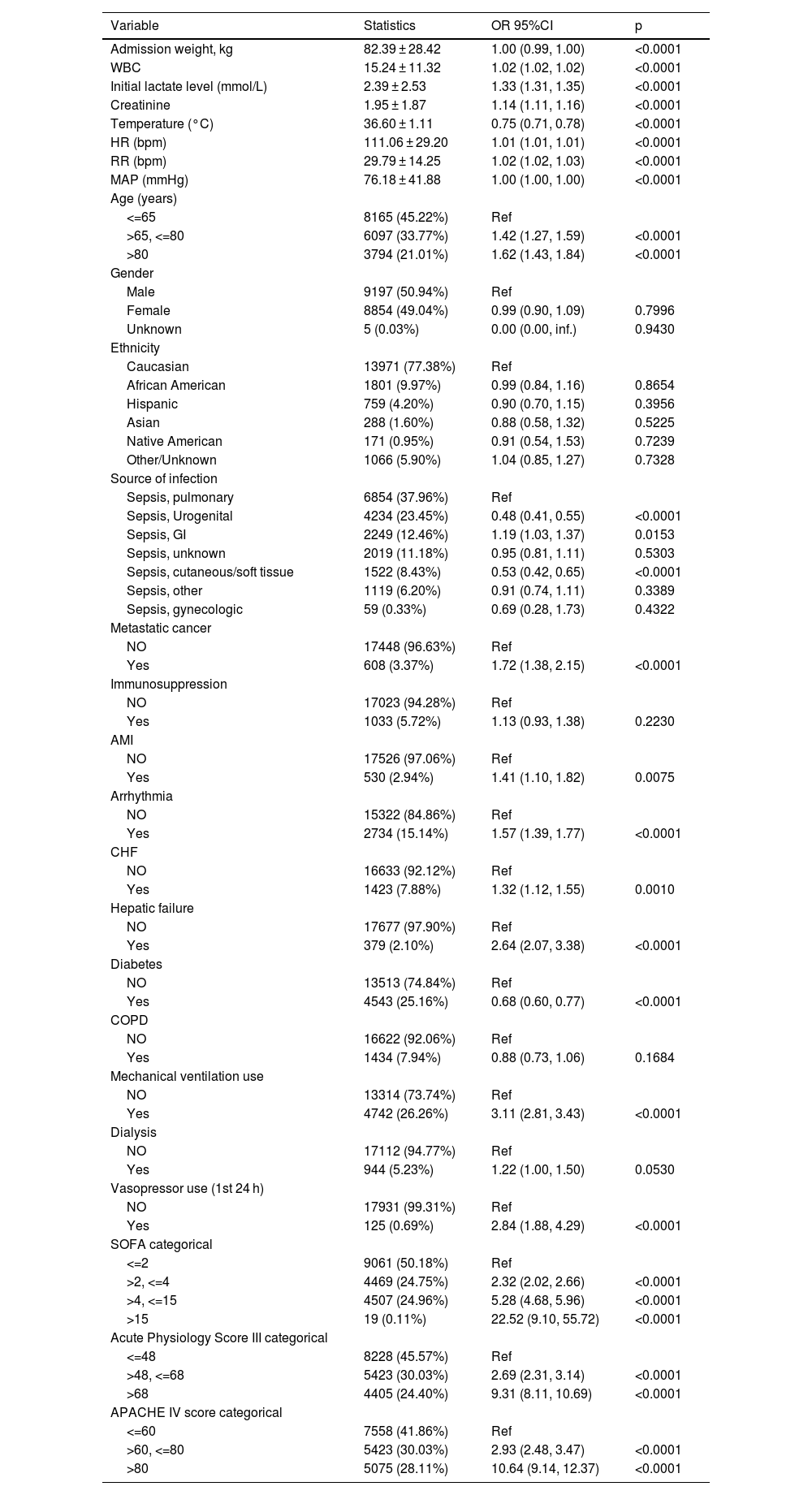
Univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses were performed, and three models were constructed to evaluate the association between body temperature and 28-day mortality: model 1 did not consider any covariates, model 2 adjusted for sociodemographic data, and model 3 included the covariates from model 2 as well as other confounding factors (as shown in Table 3). The adjustment of other covariates was guided by clinical expertise, literature findings, and the outcomes of univariate analysis (detailed in Table 2): Source of infection, WBC, creatinine, Initial lactate level, Respiratory Rate (bpm), Heart Rate (bpm), MAP (mmHg), SOFA score, Mechanical ventilation use, Dialysis, Vasopressor use (1st 24 h), Metastatic cancer, Arrhythmia, CHF, Hepatic failure, COPD.
Relationship between body temperature and 28-day mortality in different models (n = 18056).
| Exposure | Crude model | Model I | Model II | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | P | OR (95% CI) | P | OR (95% CI) | P | |
| T1(36.30–36.67) °C N = 5628 | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| T2(30.00–36.28) °CN = 5148 | 2.18 (1.93, 2.47) | <0.0001 | 2.17 (1.92, 2.46) | <0.0001 | 1.57 (1.37, 1.80) | <0.0001 |
| T3(36.70–41.90) °C N = 7282 | 1.00 (0.88, 1.14) | 0.9591 | 1.06 (0.93, 1.21) | 0.3716 | 1.07 (0.93, 1.23) | 0.3464 |
Crude mode1: we did not adjust other covariates.
Model I: we adjusted Age; Admission weight; Ethnicity.
Model II: we adjusted Age; Admission weight; Ethnicity; WBC; Creatinine; Initial lactate level; Respiratory rate; Heart rate; MAP; SOFA; Mechanical ventilation use; Dialysis; Vasopressor use (1st 24 h); Metastatic cancer; Arrhythmia; CHF; Hepatic failure; COPD; Source of infection.
T1: Temperature (°C) 36.30–36.67; T2: Temperature (°C) 30.00–36.28; T3: Temperature (°C) 36.70–41.90; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence; Ref: Reference.
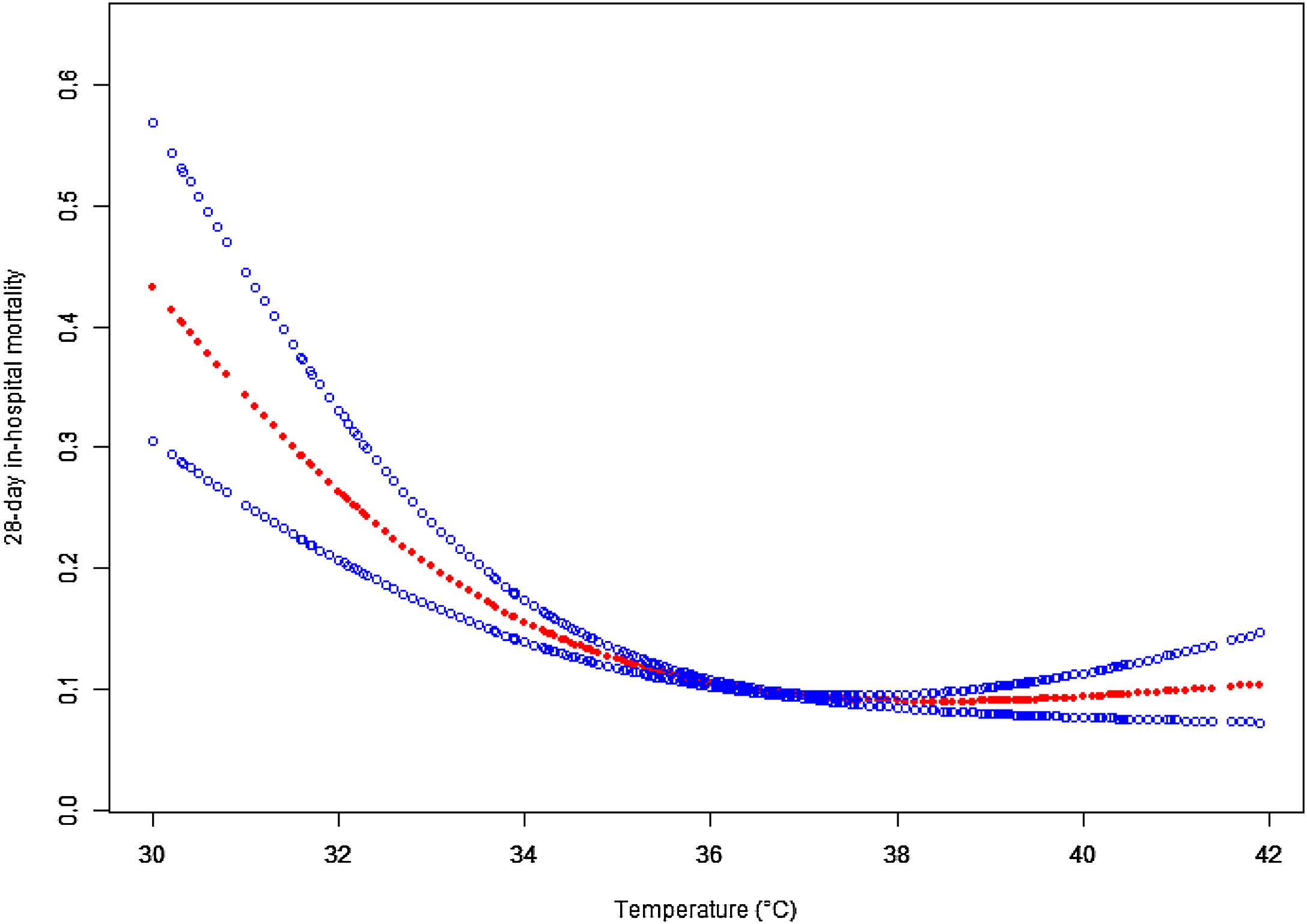
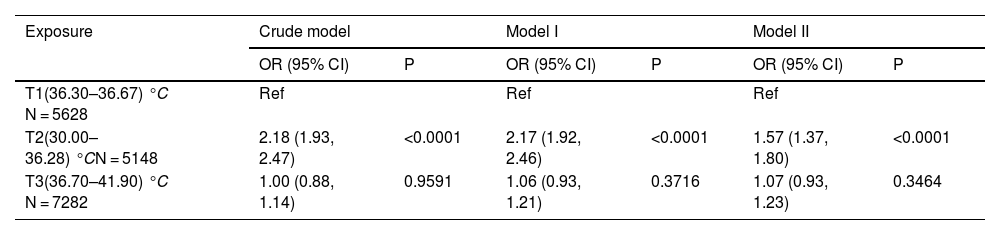
Given that logistic regression is unable to account for nonlinear relationships, we employed a penalized spline method for smooth curve fitting to account for the possibility of a nonlinear association between body temperature and 28-day mortality, as shown in Fig. 2. In cases where nonlinearity was identified, we used a recursive algorithm to estimate the inflection point, followed by a bootstrapping algorithm to determine the range of the inflection point and calculate its confidence interval (CI). Subsequently, we developed a two-phase linear regression model on either side of the inflection point.20,21 We determined the best-fit model (linear regression model vs. two-phase linear regression model) based on the p-values obtained from the log likelihood ratio test (Table 4). We employed this approach to account for the possibility of a nonlinear association between body temperature and 28-day mortality.
Associations between body temperature and 28-day mortality in all patients with sepsis. A threshold, nonlinear association between the body temperature and 28-day mortality was found in a generalized additive model (GAM). Solid rad line represents the smooth curve fit between variables. Blue bands represent the 95% of confidence interval from the fit. Adjusted for Admission weight; Ethnicity; WBC; Creatinine; Initial lactate level; Respiratory rate; Heart rate; MAP; SOFA; Mechanical ventilation use; Dialysis; Vasopressor use (1st 24 h); Metastatic cancer; Arrhythmia; CHF; Hepatic failure; COPD; Source of infection.
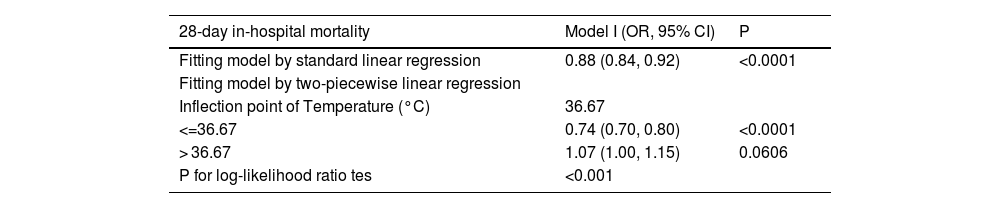
The result of two-piecewise linear regression model.
| 28-day in-hospital mortality | Model I (OR, 95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|
| Fitting model by standard linear regression | 0.88 (0.84, 0.92) | <0.0001 |
| Fitting model by two-piecewise linear regression | ||
| Inflection point of Temperature (°C) | 36.67 | |
| <=36.67 | 0.74 (0.70, 0.80) | <0.0001 |
| > 36.67 | 1.07 (1.00, 1.15) | 0.0606 |
| P for log-likelihood ratio tes | <0.001 |
We adjusted Age; Admission weight; Ethnicity; WBC; Creatinine; Initial lactate level; Respiratory rate; Heart rate; MAP; SOFA; Mechanical ventilation use; Dialysis; Vasopressor use (1st 24 h); Metastatic cancer; Arrhythmia; CHF; Hepatic failure; COPD; Source of infection. OR: Odds ratios; CI: Confidence; Ref: Reference.
In our study, the number of participants with missing data of Admission weight, Ethnicity, WBC, Creatinine, Initial lactate level (mmol/L), Respiratory rate (bpm), Heart rate (bpm), MAP (mmHg), SOFA, APACHE IV score, Acute Physiology Score III was 374(2.07%), 3254(18.02%), 2185(12.10%), 45(0.25%), 6815(37.74%), 53(0.29%, 16(0.09%), 40(0.22%), 532(2.95%), 2041(11.30%) respectively. To prevent a decrease in statistical test power and bias resulting from the direct exclusion of missing values, we employed multiple imputation using chained equations (MICE) based on SAS to estimate the missing data. The imputed data were then analyzed,18,19 and the interpolated data had little effect on the outcome. The analyses were performed with the statistical software packages R (http://www.R-project.org, The R Foundation) and Empower Stats (http://www.empowerstats.com, X&Y Solutions, Inc, Boston, MA). P values less than 0.05 (two-sided) were considered statistically significant.
ResultsBaseline characteristicsAnalyzed in this study were data from 18,056 patients, with an average age of 65.82 ± 16.23 years, and nearly half of them (50.94%) were male. Table 1 illustrates a comparison of various aspects among patients in different body temperature tertiles, including demographics, vital signs, laboratory test results, site of infection, treatment details, and severity of illness. The table indicates that compared to the highest temperature group, the hypothermia group had older and lighter patients upon admission, elevated levels of creatinine and lactate, higher SOFA scores, APACHE IV scores, acute physiology scores, and longer ICU stays. Notably, the hypothermia group exhibited the highest mortality rate among the three groups, reaching 15.71%.
Table 2 displays the results of the univariate logistic regression modelsThe results of the univariate logistic regression analysis presented in Table 2 indicate several key associations between baseline variables and 28-day mortality among the 18,056 sepsis patients. Significant positive correlations were observed with initial lactate level, creatinine, heart rate, respiratory rate, advanced age (>65 years), SOFA score, APS III score, and APACHE IV score (all p < 0.0001). Notably, metastatic cancer, acute myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, chronic heart failure, hepatic failure, mechanical ventilation use, and vasopressor use within the first 24 hours were also associated with increased mortality risk. Conversely, body temperature and diabetes were negatively associated with 28-day mortality (p < 0.0001). No significant associations were found with gender, ethnicity, immunosuppression, COPD, or dialysis.
The findings of the multivariate analyses employing the binary logistic regression model are presented belowWe utilized the binary logistic regression model to construct three models for the purpose of examining the potential association between body temperature and the 28-day mortality rate of sepsis patients, the effect sizes and 95% CIs are listed in Table 3. In Model 1, an unadjusted model, hypothermia (T2: 30.00–36.28 °C) was significantly associated with an increased risk of 28-day mortality (OR = 2.18, 95% CI: 1.93–2.47, p < 0.0001), indicating that hypothermia is positively associated with mortality. After adjusting for socio-demographic variables (age, weight, ethnicity) in Model 2, the results remained consistent, with hypothermia showing a positive association with 28-day mortality (OR = 2.17, 95% CI: 1.92–2.46, p < 0.0001). In the fully-adjusted model (Model 3), which accounted for additional covariates listed in Table 2, hypothermia continued to be positively associated with 28-day mortality (OR = 1.57, 95% CI: 1.37–1.80, p < 0.0001). Conversely, the hyperthermia group (T3: 36.70–41.90 °C) did not show a statistically significant association with 28-day in-hospital mortality across any of the models, including the fully-adjusted Model 3 (OR = 1.07, 95% CI: 0.93–1.23, p = 0.3464).
A nonlinear association was observed between body temperature and 28-day mortalityA nonlinear dose-response relationship between body temperature and 28-day ICU in-hospital mortality was observed using a generalized summation model and curve fitting (Fig. 3). The inflection point for body temperature was determined to be 36.67 °C using a recursive algorithm. To account for this nonlinear relationship, a two-piecewise binary logistic regression model was developed on either side of the inflection point. The model was compared to a standard linear regression model, and the p-value of the log-likelihood ratio test indicated a significantly better fit for the two-piecewise model (p < 0.0001; Table 4). As shown in Table 4, when body temperature was ≤36.67 °C, each 1 °C decrease in body temperature was associated with a significant increase in 28-day in-hospital mortality (OR = 0.74, 95% CI: 0.70–0.80, p < 0.0001), indicating that lower body temperatures are linked to higher mortality risk. In contrast, for patients with body temperature >36.67 °C, there was no statistically significant association between temperature and mortality (OR = 1.07, 95% CI: 1.00–1.15, p = 0.0606), suggesting that hyperthermia might not have a substantial impact on 28-day in-hospital mortality among sepsis patients.
DiscussionIn this retrospective cohort study, we utilized the eICU-CRD database, encompassing 208 distinct ICUs across the United States during 2014–2015, to investigate the relationship between body temperature and 28-day in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis.
The findings showed hypothermia as an independent risk factor for sepsis prognosis and we further explored the hypothermia threshold of 36.67 ℃. To our knowledge, such a clear hypothermia threshold has not been elaborated in previous literature.
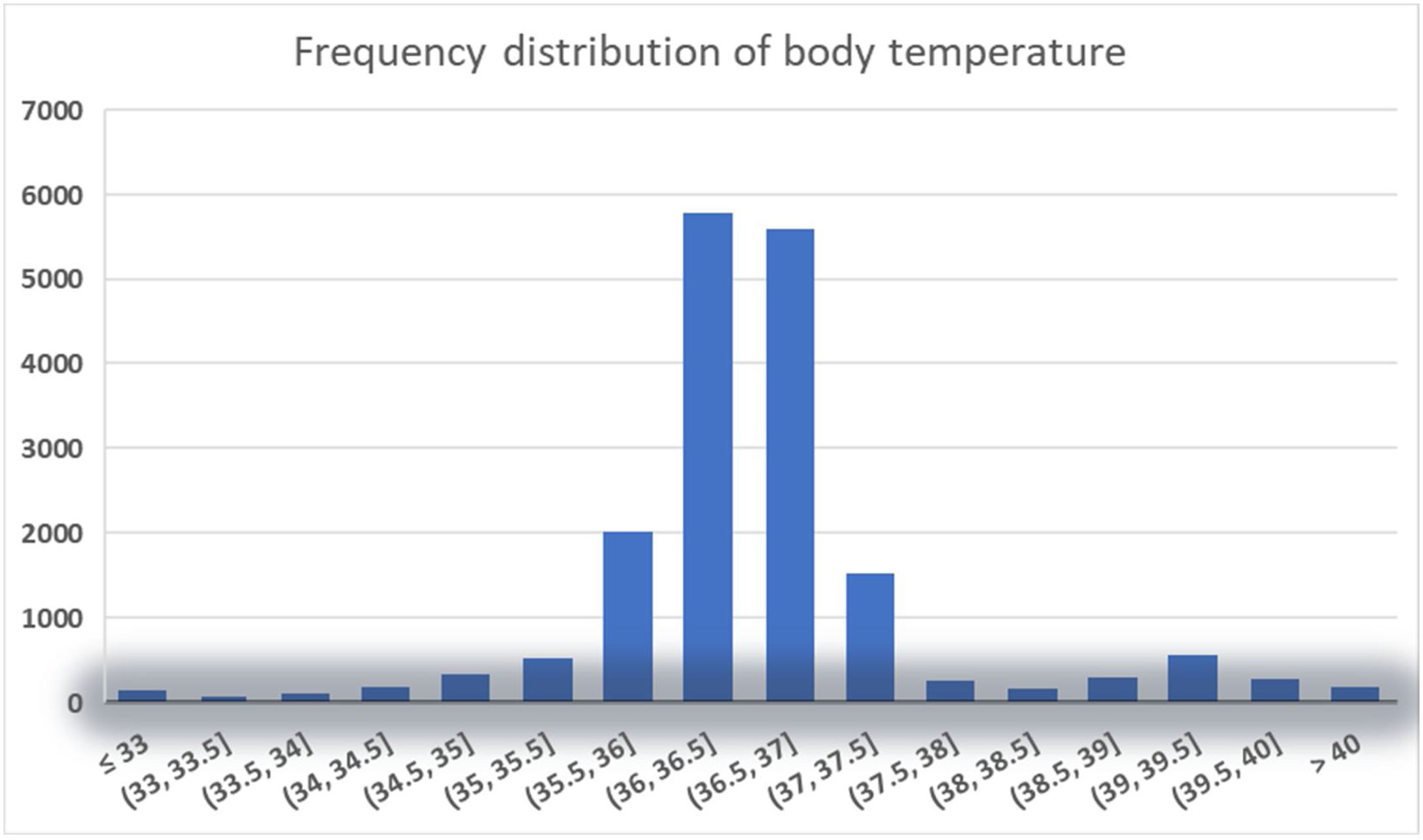
The management of body temperature in sepsis is a gap in the guidelines and has no concrete and feasible basis in clinical practice1,22; while in actual clinical practice, physicians and nurses are more concerned about febrile patients and act more quickly on them23,24; and In our current study, normothermic patients accounted for a large proportion (see Fig. 2), which is inconsistent with the article in 2021 Thomas-Rüddel et al. stating that normothermic responses are rare in patients with sepsis9; Our study also revealed similar findings to the 2013 Kushimoto et al. study, which investigated the relationship between body temperature and mortality in patients with severe sepsis,7 Specifically, our results demonstrated that hyperthermia did not exhibit a significant link with 28-day in-hospital mortality among sepsis patients, while hypothermia was identified as an independent risk factor for 28-day in-hospital mortality. In the Kushimoto et al. study, grouping body temperature, they also found that hypothermia (≤36.5 ℃) was associated with a significantly higher risk of mortality, whereas elevated temperature was not associated with an increased disease severity or risk of mortality.7 We adjusted for more and more comprehensive confounders in our study, probed in a larger population, and came to the similar conclusion: hypothermia is associated with increased mortality in sepsis, In addition, our study revealed a significant inverse relationship between body temperature and 28-day mortality in sepsis patients with a body temperature below the hypothermia threshold of 36.67 ℃, with mortality decreasing by 26% for every 1 ℃ increase in body temperature. This further supports the important role of body temperature in the prognosis of sepsis patients.
However, to our knowledge, most of the existing studies on temperature management in sepsis still focus on cooling therapy,23 but the benefit of temperature control in febrile patients are not clear,25–28 and some studies have even been forced to interrupt treatment because of invalidity,29 Based on our study results, we did not find a significant association between hyperthermia and 28-day in-hospital mortality in sepsis patients. Therefore, it can be inferred that elevated body temperature might not invariably have an adverse effect on the prognosis of sepsis patients. Additionally, cooling therapy may not necessarily improve the prognosis in these patients. In contrast, very few studies on rewarming have been conducted, probably because clinical staffs are not sufficiently aware of the dangers of hypothermia. Therefore, we believe that awareness of the dangers of hypothermia among health care professionals needs to be enhanced, because that hypothermia was found to be an independent risk factor for 28-day in-hospital mortality in sepsis patients, while hyperthermia was not significantly associated with mortality Our study suggests that the weight of hypothermia in the prognostic assessment of sepsis should be given greater consideration than that of fever. In particular, the weight of hypothermia should not be underestimated, as it predicts a more severe stage of sepsis and is associated with worse clinical outcomes. Current scoring systems, such as SIRS, APACHE IV, and PIRO, may not adequately account for the prognostic value of hypothermia, and future modifications may be necessary to more accurately assess the severity of sepsis. So, clinicians should pay closer attention to the presence of hypothermia in sepsis patients and consider it a potential warning sign of poor prognosis. At the same time, we could encourage the development of more RCT studies on rewarming, which, if proven effective, it could lead to a new breakthrough in the treatment of sepsis. Additionally, guidelines for temperature management could be developed based on the results of such studies, which may further improve clinical outcomes in sepsis patients.
Our study has several limitations, including unmeasured confounders such as health insurance status and pre-admission cooling therapy, which may have influenced mortality risk. This limitation is inherent to observational studies, and we were unable to estimate the extent to which these unmeasured confounders may have impacted our calculated odds ratios. Although we adjusted for various factors including age, sex, weight, and clinical parameters, we did not include APACHE IV or acute physiological scores due to the inclusion of body temperature as a parameter. Additionally, body temperatures below 30 °C were excluded from the analysis, which may have led to an underestimation of the association between hypothermia and mortality. The EICU database does not specify the method of body temperature measurement, which could influence the accuracy of our findings. Furthermore, our study relied on ICD-9 codes for diagnosis and lacked detailed cause-of-death information, potentially limiting our understanding of the mechanisms linking temperature with mortality. Although multiple imputation techniques were used to handle missing data, this approach does not completely eliminate the potential for bias. Future research should address these limitations to provide more robust results.
ConclusionThis study provides evidence of a nonlinear relationship and threshold effect between body temperature and 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis. Notably, we found that hypothermia was significantly and negatively associated with septic death when body temperature was below 36.5 ℃, and that mortality increased significantly with a decrease of 1 ℃ in body temperature.
CRediT authorship contribution statementAll Authors contributed to the study concept, design, and acquisition data.
Dan Zhou and Hui Peng contributed in the data compilation and analysis, contributed in interpretation of data as well as drafting and critical revision of manuscript.
Weifeng Chen and Huilin Jiang designed the study and revised the manuscript.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for publicationNot applicable.
FundingShenzhen Second People's Hospital Clinical Research Fund of Guangdong Province High-level Hospital Construction Projects (NO. 2023yjlcyj010).