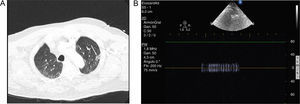
Central bronchial reflex is a sign of pulmonary infarction explored by pulmonary ultrasound. This finding appears in late pulmonary infarction as an expression of bronchial constriction and compression due to surrounding edema and pulmonary bleeding.
We present a case of massive pulmonary embolism with pulmonary infarction. The patient was on mechanical ventilation due to right heart failure and severe hypoxemia. Pulmonary CT showed in the lung parenchyma an area of triangular morphology in peripheral location with increased density and frosted glass appearance compatible with pulmonary infarction on the left upper lobe (Fig. 1, Panel A, arrow). Over the same location, central bronchial reflex is seen as an hyperechoic structure surrounded by hypoechoic tissue on ultrasound exam. Bronchus can be identified by pulsed-Doppler, showing the flow of gas insufflated by ventilator (Fig. 1, Panel B).
FundingThis work has been done without any funding.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.