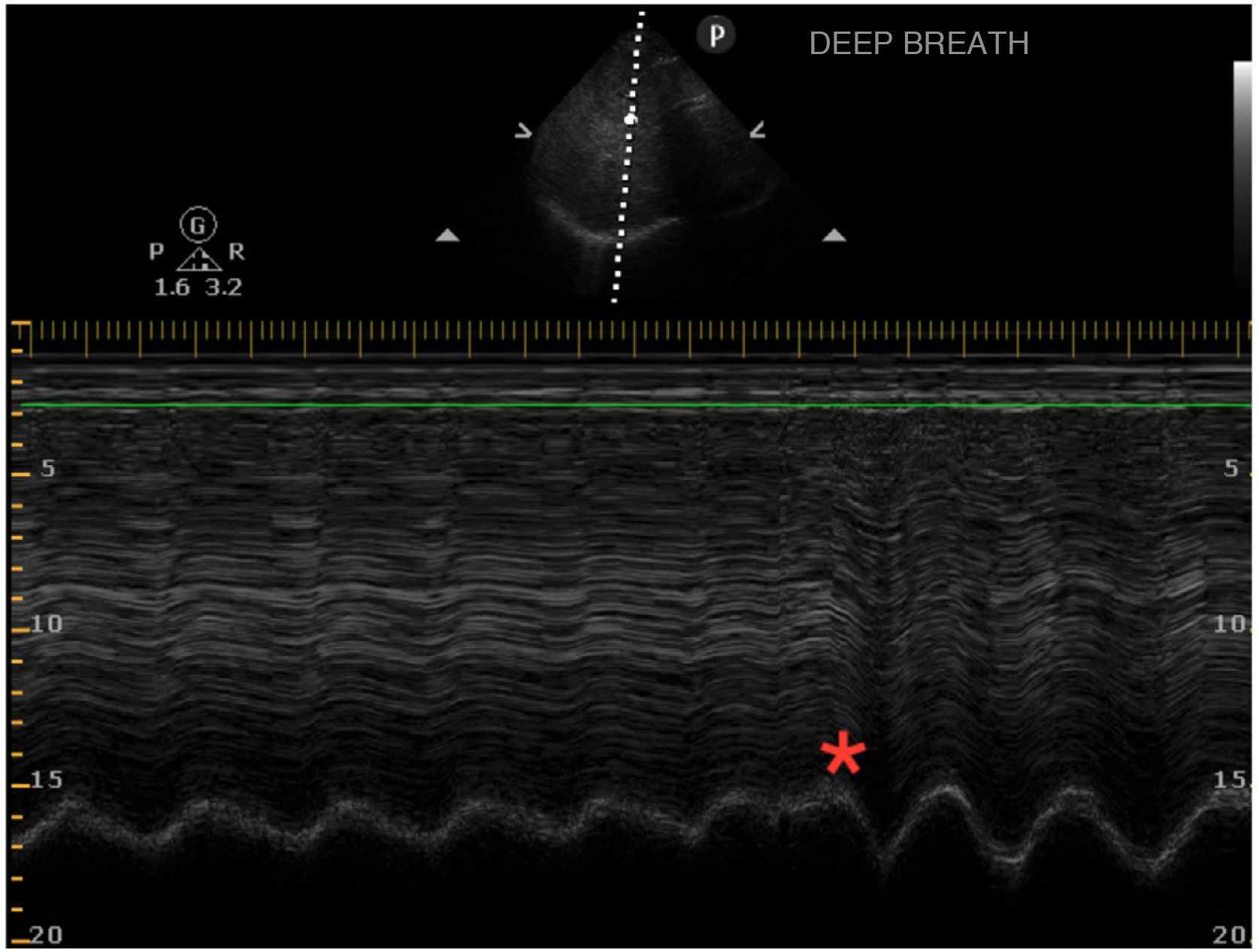
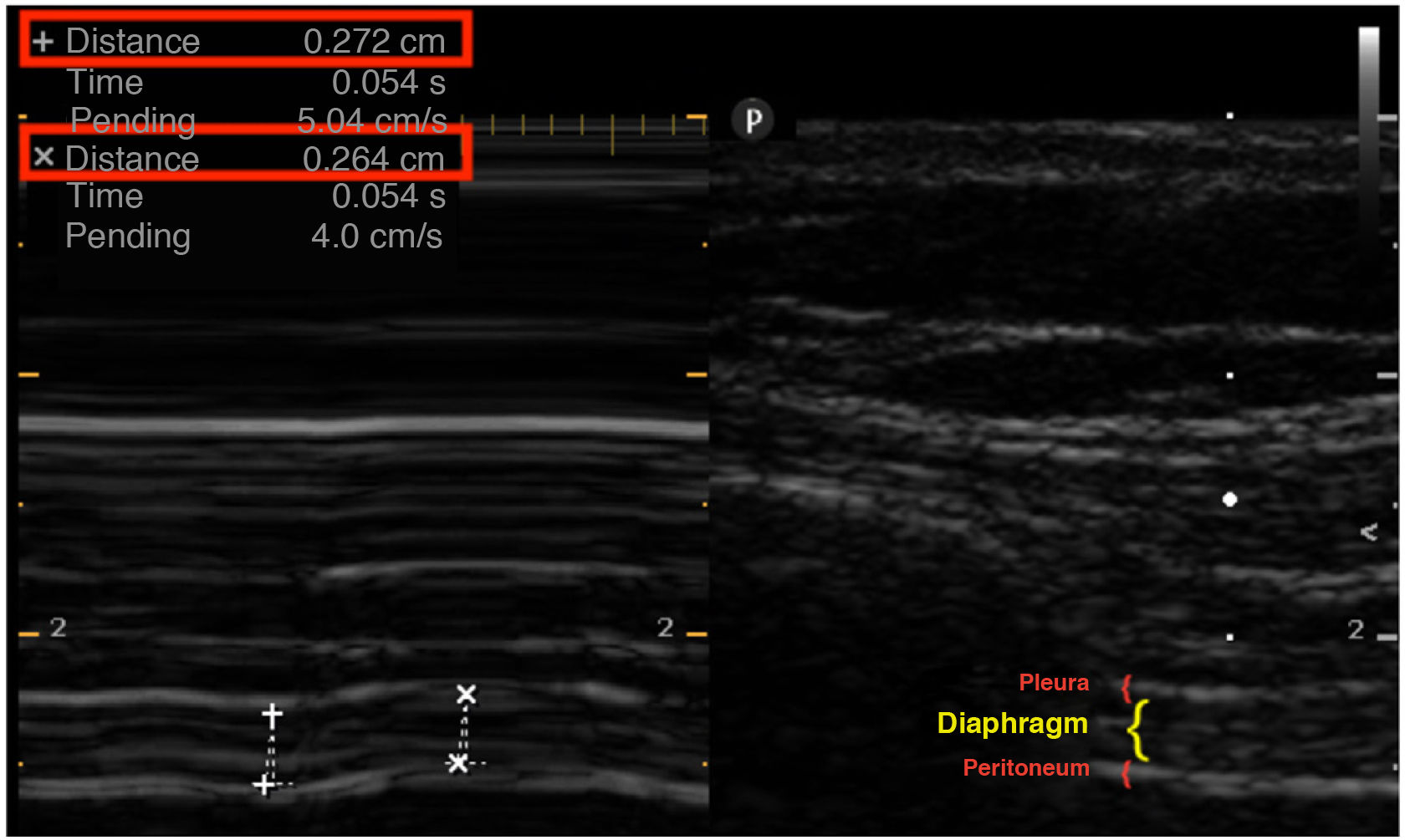
This is the case of a 66-year-old man admitted to the ICU due to COVID-19 after high-flow nasal oxygen failure at the conventional hospital ward setting. Non-invasive support (non-invasive ventilation) is initiated with the following parameters: BiPAP mode with IPAP of 12, EPAP of 9, and a FiO2 of 100% with a tidal volume of approximately 350−450 mL (6.25−8 mL/kg of ideal weight) with respiratory rate dropping from 30 to 23 breaths/min. The diaphragmatic ultrasound performed at admission reveals the presence of a regular diaphragmatic excursion of 2 cm. The patient is asked to take a deep breath (*). Inverted diaphragm motion occurs that triggers the use of accessory muscles. M mode is used. Diaphragmatic thickening of only 3% is reported. Nor the pressure or the volume change dramatically. Twenty-four hours later, failed later non-invasive ventilation is confirmed followed by the need for intubation. Figs. 1 and 2.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más