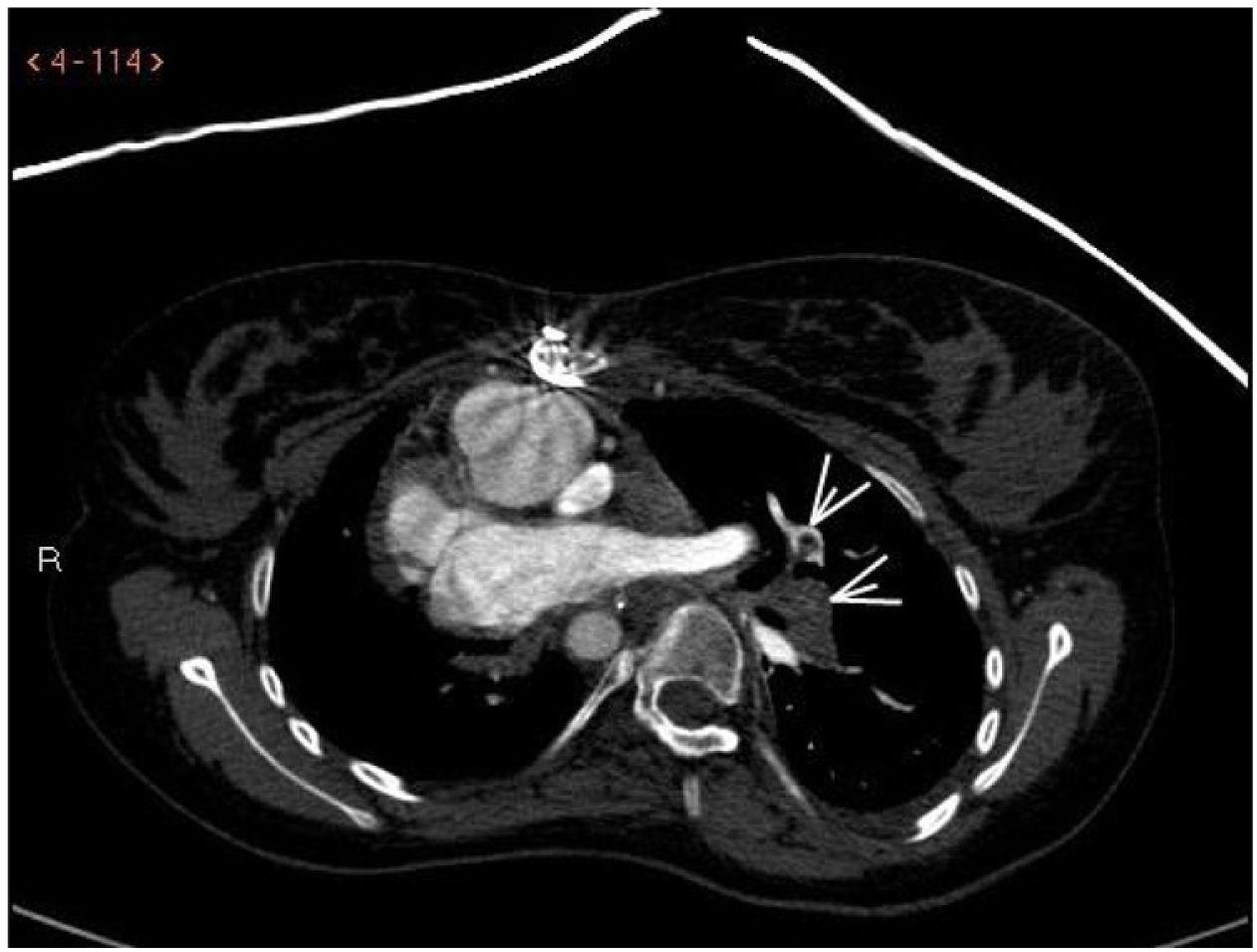
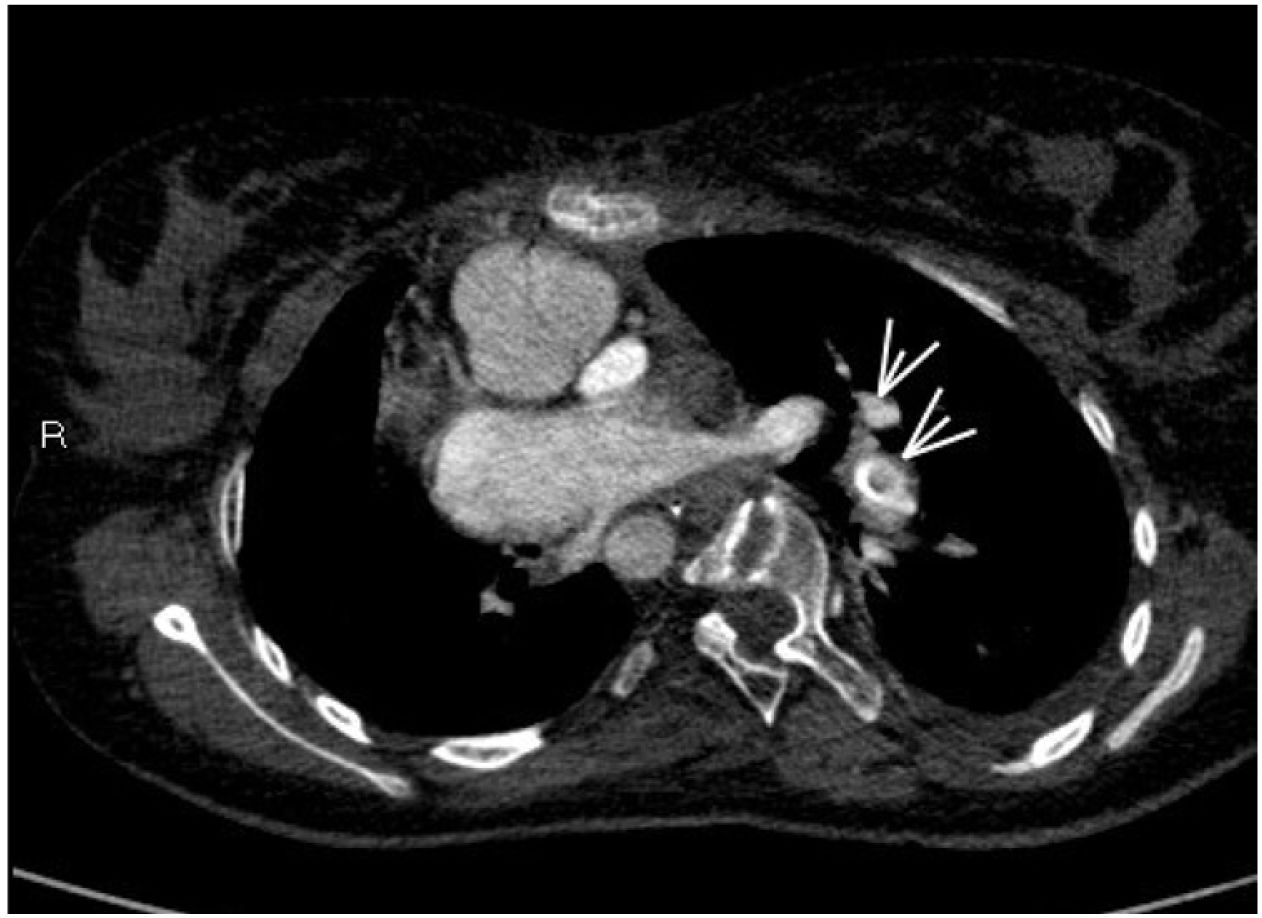
A 16-year-old female presented with a history of complex congenital heart disease requiring a right systemic-pulmonary fistula, with a bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis (Glenn procedure) at 6 years of age. She was admitted to the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit due to breathing difficulty and severe hypoxemia. With the suspicion of pulmonary thromboembolism, heparin sodium was started, and a new CT angiographic study was performed 24 hours later due to progressive clinical worsening. A thrombus was identified at the communication between the left superior vena cava and the left pulmonary artery, compatible with massive thromboembolism of the left lung (Fig. 1, see arrows). Treatment was started with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rTPA) in the form of an initial 30 mg bolus (0.5 mg/kg) followed by the perfusion of 0.04 mg/kg/h. After 36 hours, repeat control CT angiography evidenced important thrombus reduction with marked re-permeation (Fig. 2, see arrows).
FundingThe authors declare that no funding has been received for this study.