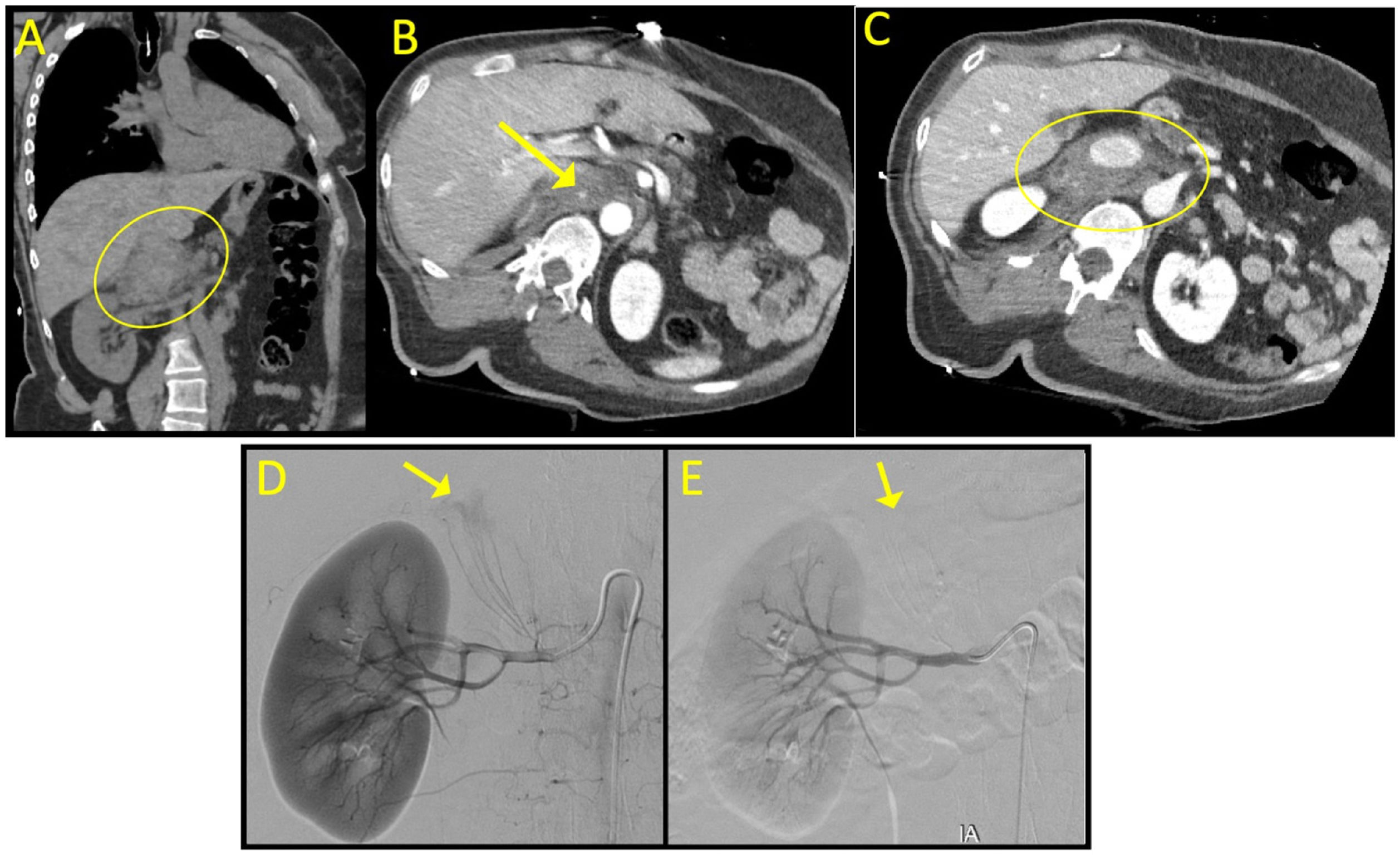
This is the case of a polytraumatized 57-year-old woman after falling from a seventh floor. When found the patient’s GCS was 13. A body CT scan reveals the presence of a SAH at the sulci of both temporal lobes, humerus proximal fracture, and multiple non-displaced rib fractures. Also, a localized hematoma of 7 cm in diameter is found in the right suprarenal region (Fig. 1A, yellow circle). Also, the CT scan reveals a thin fat plane of separation with the liver, diaphragmatic pillar, pancreas, and kidney. In the arterial phase active extravasation of contrast is seen (Fig. 1B, yellow arrow) consistent with an arterial hemorrhage. The preservation of a fat plane between the hematoma and the structures surrounding the suprarenal region (Fig. 1C, yellow circle) facilitated finding of the origin of bleeding. Previous knowledge through the CT scan of the probable vessel damaged shortens the necessary time to perform selective angiography and further embolization of the lesion (Fig. 1D, yellow arrow). The right suprarenal artery was embolized with Glubran® 2 + lipiodol (dilution 1:2), which confirmed its complete occlusion and the absence of bleeding in the final angiographic control (Fig. 1E, yellow arrow).
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más