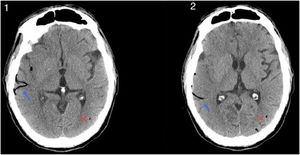
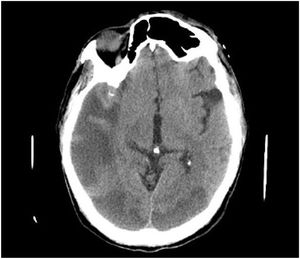
This is the case of a 47-yearl old man with a past medical history of native mitral aortic valve acute endocarditis who required valvular repair and supracoronary tube implantation. The patient is admitted to the ICU after a scheduled reintervention due to severe paravalvular leak followed by valvular replacement with mechanical prosthesis. Initially extubated and without neurologic focality. A few minutes after experiencing the early seizure the patient requires orotracheal intubation. The emergency cranial CT scan performed (Fig. 1) reveals the presence of air into the right middle cerebral artery territory, M2 (blue arrow [the color of the figure can only be seen on the electronic version]) and part of its cortical branches, as well as air bubbles into the left posterior cerebral artery (x) that consistent with gas embolism. The radiographic follow-up performed 48 h later (Fig. 2) reveals the presence of an extensive established right parietal-temporal-occipital and left occipital ischemic infarction with slight midline deviation.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más