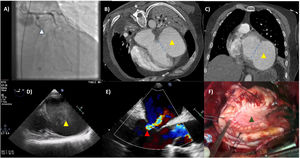
The importance of comprehensive imaging study by multiple techniques in the hyperacute clinical setting is highlighted. A paradigmatic example of massive cardiac pseudoaneurysm with mitral valve’s papillary muscle rupture due to myocardial infarction complicated with cardiogenic shock that required VA-ECMO support is shown. (A) White triangle identifies left circumflex occlusion on coronary angiography. (B) Yellow triangle (YT) identifies massive pseudoaneurysm on scanner with the anatomical neck in blue line. (C) YT identifies massive pseudoaneurysm on scanner’s orthogonal view. (D) Massive pseudoaneurysm (YT) on transesophageal echo (TE). (E) Red triangle identifies mitral regurgitation during in-surgery TE. (F) Green triangle identifies pericardia patch over the repaired tissue. Twelve hours after first symptom a successful surgical reparation with pericardial patch, mitral bioprosthesis implantation and venous bypass graft to the circumflex coronary artery was performed. To guarantee accurate emergent cardiovascular assistance, imaging, mechanical circulatory support options and neurological tests skills must be familiar to intensive care physicians.
FundingNone.
AuthorshipDr. CRG and Dr. RA prepared the original manuscript. Dr. AAL and Dr. TLS helped with imaging processing ant paper review. Dr. JTO and Dr. ODS actively reviewed and modified the original manuscript. Al authors are responsible for the contents of this manuscript.
Conflict of interestAuthors do not have any conflict of interest to disclose related to the matter discussed in this manuscript.