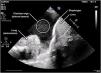
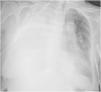
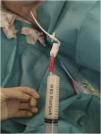
A 77-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital for bowel obstruction. A central line was placed in the right subclavian vein to initiate parenteral nutrition in the setting of a non-operative management strategy. On admission day 4, the patient developed acute respiratory failure, requiring ICU admission. Point-of-care pleural ultrasound revealed a complex, non-septated massive right pleural effusion with swirling, punctiform internal echoes (plankton sign) (Fig. 1, Video 1). A chest X-ray prior to drainage insertion confirmed the massive effusion (Fig. 2) and revealed displacement of the tip of the central line, compared to the immediate control after its insertion. A thoracostomy catheter was placed, demonstrating a milky-white output from the pleural space (Fig. 3), with high triglyceride (2503 mg/dL), low cholesterol (<20 mg/dL), and high glucose (682 mg/dL) levels, consistent with nutrithorax. Although uncommon, vascular trauma or direct leakage may cause nutrithorax that may be identified with ultrasound.
Statements and declarationsThese images have not been previously published.
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approvalInformed consent was waived according to local regulations.
Financial supportNone.