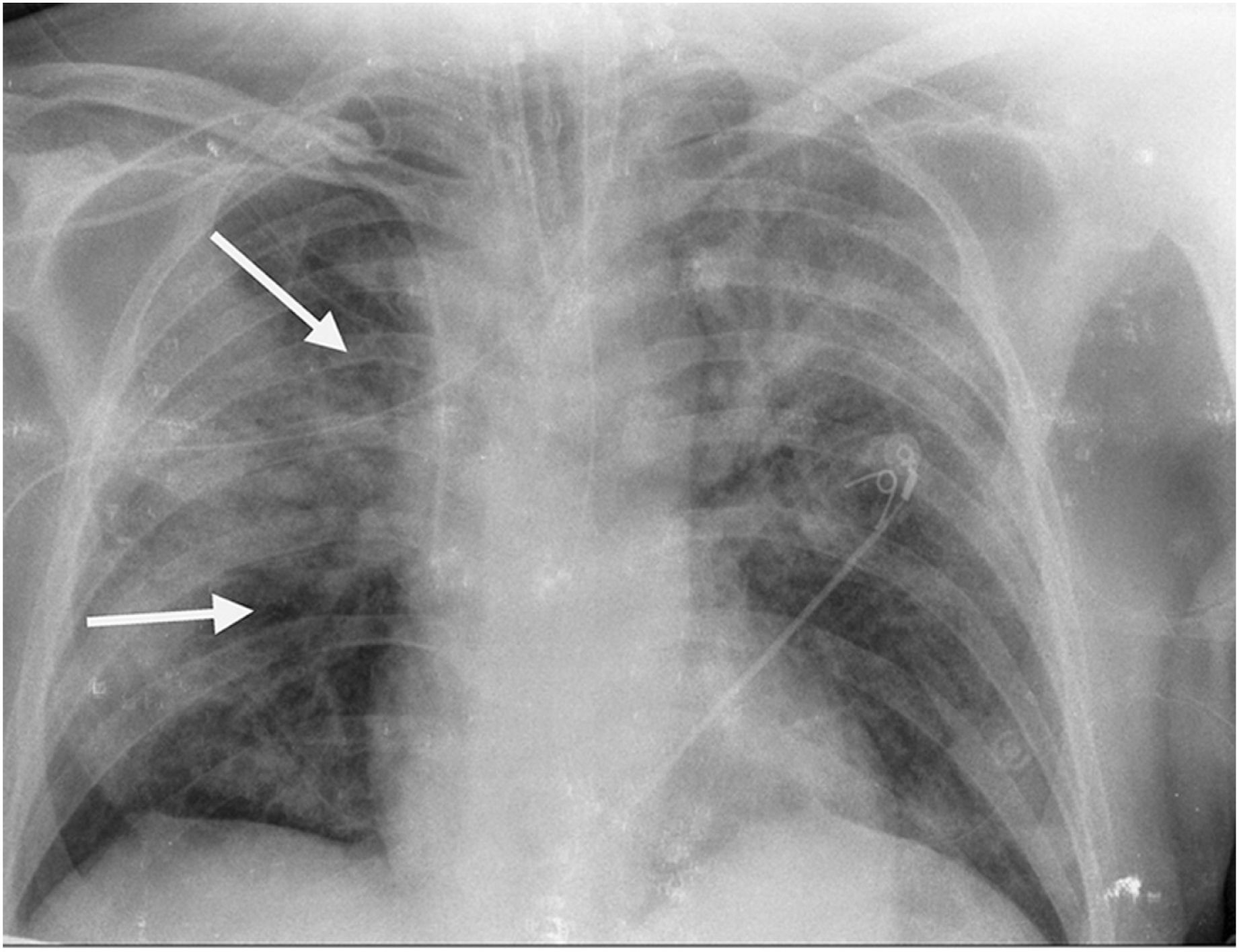
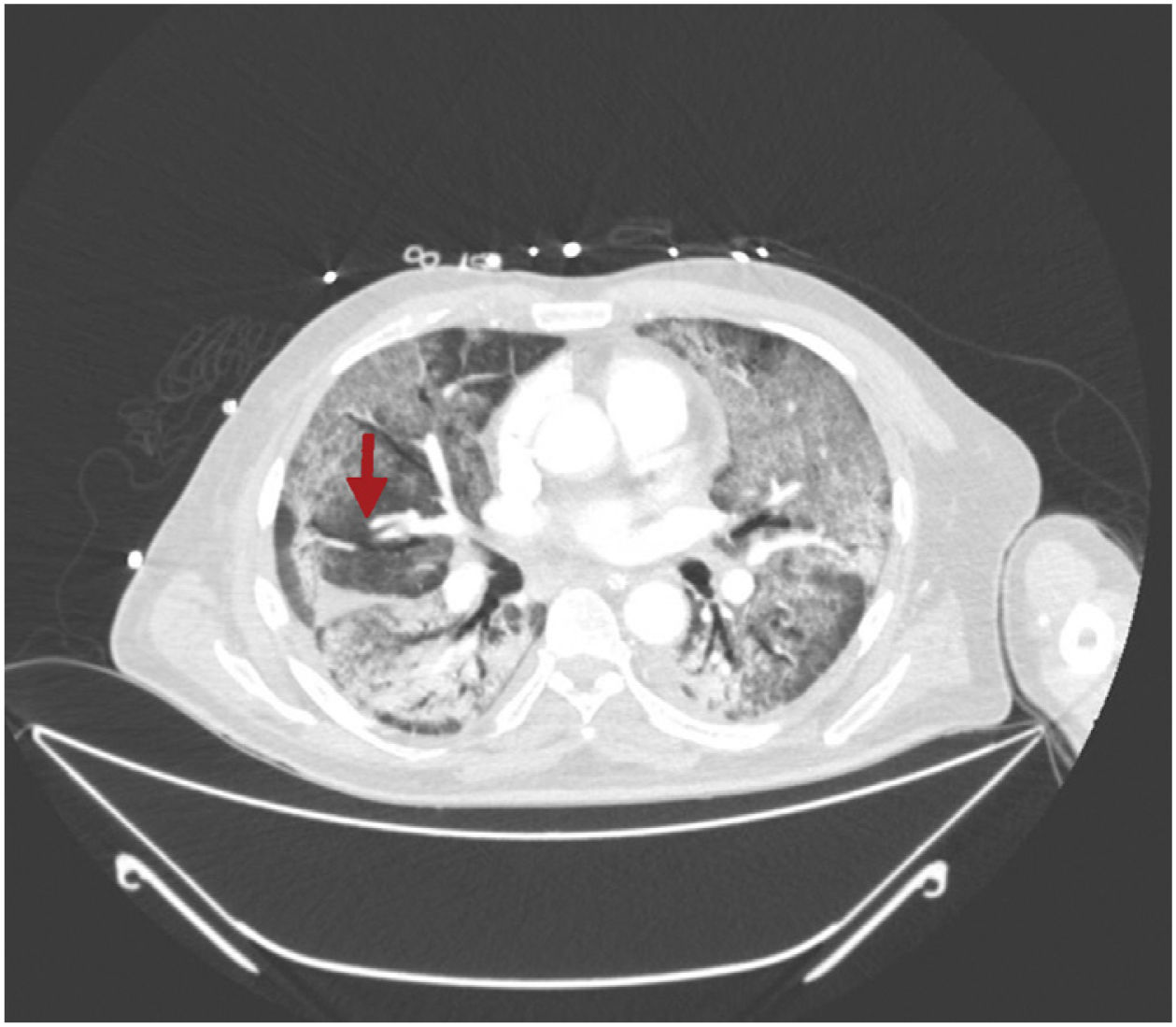
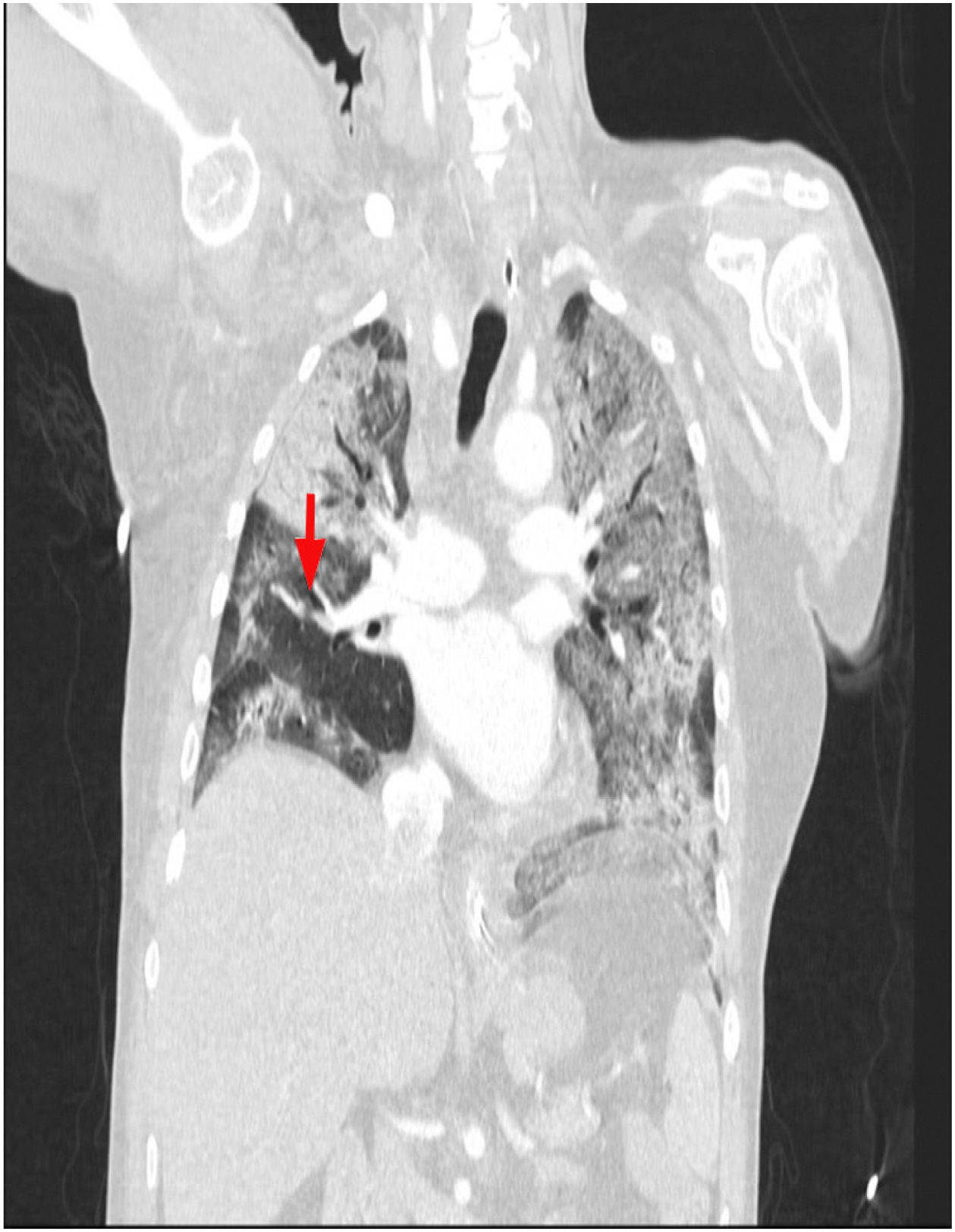
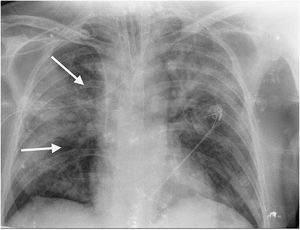
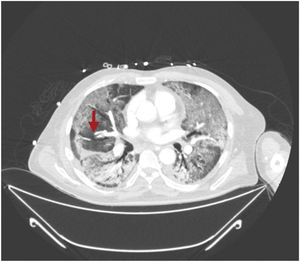
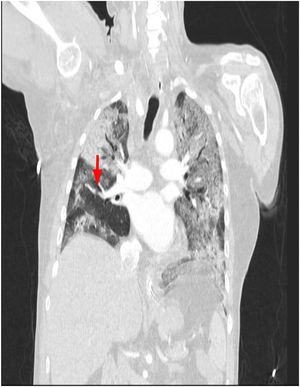
This is the case of a 64-year-old man with a past medical history of hypertension admitted to the ICU with a diagnosis of severe ARDS due to COVID-19-related bilateral pneumonia. The thoracic x-ray reveals a bilateral alveolar-interstitial pattern with damage to the right lung, especially the mid field (Fig. 1, pointer arrows). The blood test results show very high D-dimer levels (28970ng/mL) and due to suspected PTE, a thoracic echocardiography is performed that reveals the presence of RV pressure overload with positive McConnell sign. Following the echocardiographic findings, anticoagulant therapy with low-molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin 1mg/kg/every 12h) is initiated. A thoracic CCTA was performed for diagnostic confirmation purposes that revealed the presence of a repletion defect in the artery of the medial lobe lateral segment (arrows in Figs. 2 and 3) in the PTE setting. Also, the presence of diffuse bilateral damage and extensive areas of cobblestone pattern in a viral infectious process setting (Figs. 2 and 3). The patient remained on anticoagulant therapy until hospital discharge without any associated bleeding complications.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más