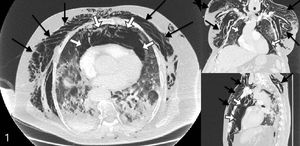
A 77-year-old man was admitted for moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, with PCR confirmed SARS-Cov-2 infection. Protective ventilation strategy included: tidal volume of 6mL/kg (ideal body weight), Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) titration with plateau pressure inferior to 28cmH2O, neuromuscular blockers, and prone position. At day 5 of ventilation, we observed acute chest and collar subcutaneous emphysema associated with bradycardia at 47bpm. Chest CT scan revealed diffuse pneumomediastinum (white arrows) with diffuse subcutaneous emphysema (black arrows) (Fig. 1). There was no pneumothorax and no evidence for tracheal or esophageal perforation. No intervention was required. Pneumomediastinum are observed in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Whether or not this complication is related to the mechanical ventilation or to the COVID-19 pathogeny per se remains an unanswered question.
The authors thank the patient, whom relative gave full written permission for this report.