Describir las secuelas al mes del alta hospitalaria en pacientes que precisaron ingreso en Cuidados Intensivos por neumonía grave COVID-19 y analizar las diferencias entre los que recibieron terapia exclusivamente con oxigenoterapia con alto flujo con respecto a los que precisaron ventilación mecánica invasiva (VMI).
DiseñoEstudio de cohorte, prospectivo y observacional.
ÁmbitoConsulta multidisciplinar pos Cuidados Intensivos.
Pacientes o participantesPacientes que superaron el ingreso en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) por neumonía grave COVID-19 desde abril 2020 hasta octubre 2021.
IntervencionesInclusión en el programa multidisciplinar pos UCI.
Variables de interés principalesSecuelas motoras, sensitivas, psicológicas/psiquiátricas, respiratorias y nutricionales tras el ingreso hospitalario.
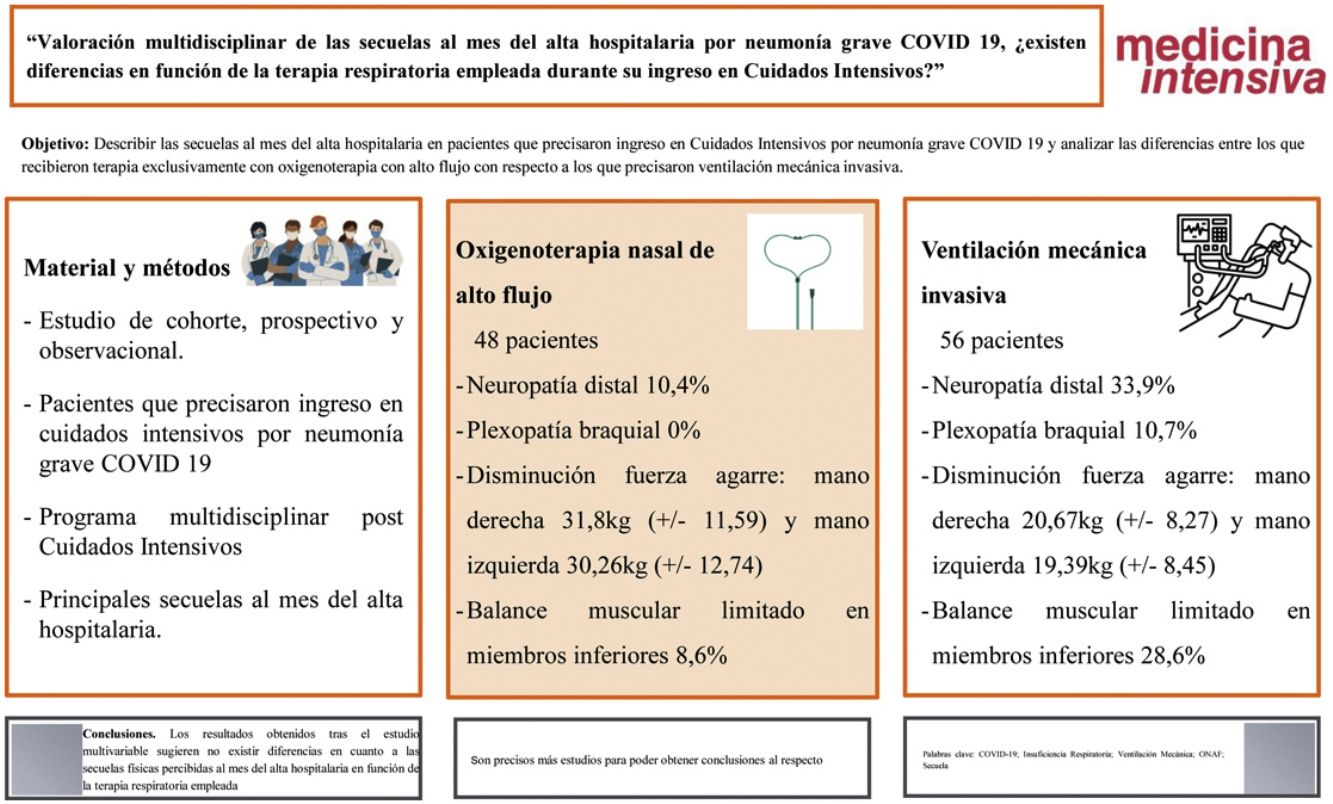
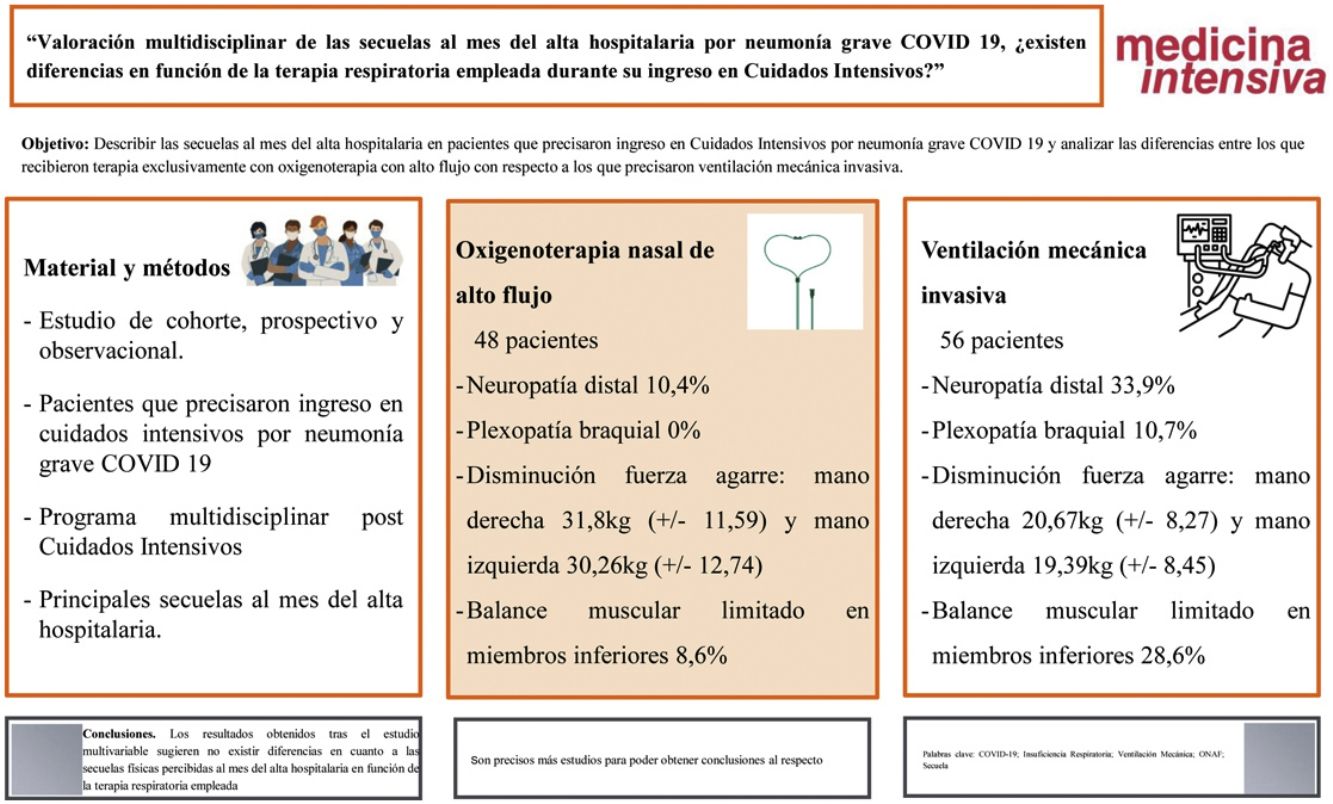
ResultadosSe incluyeron 104 pacientes. 48 pacientes recibieron oxigenoterapia nasal de alto flujo (ONAF) y 56 VMI. Las principales secuelas encontradas fueron la neuropatía distal (33,9% VMI vs. 10,4% ONAF); plexopatía braquial (10,7% VMI vs. 0% ONAF); disminución de fuerza de agarre: mano derecha 20,67 kg (± 8,27) en VMI vs. 31,8 kg (± 11,59) en ONAF y mano izquierda 19,39 kg (± 8,45) en VMI vs. 30,26 kg (± 12,74) en ONAF; y balance muscular limitado en miembros inferiores (28,6% VMI vs. 8,6% ONAF). Las diferencias observadas entre ambos grupos no alcanzaron significación estadística en el estudio multivariable.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos tras el estudio multivariable sugieren no existir diferencias en cuanto a las secuelas físicas percibidas al mes del alta hospitalaria en función de la terapia respiratoria empleada, ya fuera ONAF o ventilación mecánica prolongada, si bien son precisos más estudios para poder obtener conclusiones al respecto.
To describe the sequelae one month after hospital discharge in patients who required admission to intensive care for severe COVID-19 pneumonia and to analyze the differences between those who received therapy exclusively with high-flow oxygen therapy compared to those who required invasive mechanical ventilation.
DesignCohort, prospective and observational study.
SettingPost-intensive care multidisciplinary program.
Patients or participantsPatients who survived admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) for severe COVID-19 pneumonia from April 2020 to October 2021.
InterventionsInclusion in the post-ICU multidisciplinary program.
Main variables of interestMotor, sensory, psychological/psychiatric, respiratory and nutritional sequelae after hospital admission.
ResultsOne hundred and four patients were included. 48 patients received high-flow nasal oxygen therapy (ONAF) and 56 invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV). The main sequelae found were distal neuropathy (33.9% IMV vs. 10.4% ONAF); brachial plexopathy (10.7% IMV vs. 0% ONAF); decrease in grip strength: right hand 20.67 kg (± 8.27) in VMI vs. 31.8 kg (± 11.59) in ONAF and left hand 19.39 kg (± 8.45) in VMI vs. 30.26 kg (± 12.74) in ONAF; and limited muscle balance in the lower limbs (28.6% VMI vs. 8.6% ONAF). The differences observed between both groups did not reach statistical significance in the multivariable study.
ConclusionsThe results obtained after the multivariate study suggest that there are no differences in the perceived physical sequelae one month after hospital discharge depending on the respiratory therapy used, whether it was high-flow nasal oxygen therapy or prolonged mechanical ventilation, although more studies are needed to be able to draw conclusions.
La enfermedad por coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) se trata de una enfermedad relativamente nueva en nuestro medio, habiendo sido notificada por primera vez en Wuhan (China), en diciembre de 2019, declarándose el 11 de marzo de 2020 como pandemia por parte de la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) por los alarmantes niveles de propagación y gravedad.
La aparición de esta nueva enfermedad y el aumento exponencial de pacientes que precisaron ingreso en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) por hipoxemia grave secundaria a neumonía bilateral, no sólo colapsaron las UCI1 sino que multiplicaron los pacientes con secuelas más o menos invalidantes provocadas por la estancia prolongada en la UCI, el distrés respiratorio, la terapia agresiva (incluyendo maniobras de prono)2 y las derivadas del virus. Hasta el momento, se han realizado una docena de estudios que evalúan aspectos como el deterioro cognitivo3, secuelas motoras con impacto en la calidad de vida diaria4 (dolor o malestar, ansiedad o depresión, cuidado personal y actividad habitual), nivel de fatiga percibido5, intolerancia al ejercicio, disnea de moderados esfuerzos, astenia, así como limitaciones en la capacidad física y su influencia sobre la salud psicológica6,7, haciendo necesario el abordaje multidisciplinar de estos pacientes por la complejidad de los mismos.
Esta nueva realidad ha motivado que en algunos hospitales se hayan creado distintas herramientas para el seguimiento de estos pacientes tan complejos, habiéndose creado para ello circuitos específicos en distintos hospitales, así como la especial implicación desde el Grupo Ítaca (grupo de colaboración y trabajo para la prevención, diagnóstico, seguimiento y tratamiento de pacientes con síndrome pos Cuidados Intensivos [SPCI]) lanzando el estudio CORONAPICS a nivel nacional para describir las características del SPCI en supervivientes de la pandemia COVID-19, entre otros objetivos.
Nuestro estudio pretende abordar las secuelas al mes del alta hospitalaria de los pacientes con neumonía bilateral grave por COVID-19, desde un punto multidisciplinar, por parte de Medicina Intensiva, Medicina Física y Rehabilitación, Endocrinología y Nutrición, Salud Mental y Neumología. Los estudios existentes hasta el momento8 incluyen a los supervivientes por COVID-19 tras ingreso en Cuidados Intensivos sin hacer distinción en cuanto a la terapia respiratoria empleada durante su ingreso, por lo que se pretende analizar si existen diferencias entre los pacientes que recibieron oxigenoterapia con alto flujo exclusivamente, o aquellos que precisaron escalar a VMI.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio prospectivo observacional de los pacientes que precisaron ingreso en la UCI del Hospital Virgen de la Victoria de Málaga desde abril del año 2020 hasta octubre de 2021 por neumonía grave por COVID-19. Los pacientes ingresados en UCI fueron todos aquellos pacientes susceptibles de medidas agresivas, con necesidad de oxígeno mayor a 15 lpm y PaO2/FiO2 < 200.
Se incluyeron en el estudio los pacientes supervivientes, siendo citados en el circuito de Atención Multidisciplinar Pos COVID, donde fueron valorados en «consulta de acto único» por Medicina Física y Rehabilitación, Endocrinología, Neumología, Salud Mental y Medicina Intensiva.
Se excluyeron los pacientes que fueron remitidos desde otros hospitales, al tratarse nuestro centro del Hospital de referencia del área Costa del Sol y de la Serranía de Ronda, así como los pacientes extranjeros por la dificultad para la realización del seguimiento de los mismos.
En la primera visita, correspondiente al mes del alta hospitalaria, se incluyeron los siguientes registros:
- •
Historia clínica detallando calidad de vida previa, independencia para las actividades básicas de la vida diaria, necesidad de ayuda para la marcha, cansancio, hábito de ejercicio físico, dolor y debilidad.
- •
Recogida de información acerca del ingreso: días de ingreso en UCI y hospitalario, terapia respiratoria empleada, días de VMI, tratamiento administrado, días de relajante muscular y ciclos de prono.
- ∘
Secuelas: otorrinolaringológicas (ORL), psicológicas/psiquiátricas, consumo de benzodiacepinas y antidepresivos, oxigenoterapia al alta, disnea (escala de MRCm), espirometría, kilos de peso perdidos tras el ingreso hospitalario, masa celular corporal (BCM) y masa celular corporal indexada (BCMI).
- ∘
Exploración: Balance articular global y balance muscular global (MRC modificada). Fuerza de agarre con dinamómetro de mano. Presiones musculares respiratorias: presión inspiratoria máxima (Pimax) y presión espiratoria máxima (Pemax). Test de marcha seis minutos
- ∘
Escalas/cuestionarios de calidad de vida: escala FACIT-F, escala EuroQol-5D, escala Barthel. Test de evaluación cognitiva de Montreal (MoCA)
Una vez valorados los pacientes y si presentaban algún tipo de déficit, se les indicaba la posibilidad de realizar un programa de rehabilitación integral, presencial o domiciliario (fig. 1) en función de las siguientes características:
Las indicaciones para realizar un programa de rehabilitación presencial fueron:
- •
Pacientes COVID-19 con PCR negativa, con capacidad de deambulación independiente, estables, que presentan disnea de moderados – grandes esfuerzos y/o cansancio con esfuerzos moderados, frágiles con SPPB<10 y/o necesidad de O2.
- •
Buen nivel cognitivo y capacidad de colaboración.
Las indicaciones para realizar un programa de rehabilitación domiciliario fueron:
- •
Pacientes frágiles sin necesidad de O2.
- •
Pacientes que no podían acudir a un programa de rehabilitación presencial.
El estudio se realizó de acuerdo con la Declaración de Helsinki y los principios de Buena Práctica Clínica y fue aprobado por el Comité de Ética Institucional del HVV (proyecto POSTUCI21 - 1654-N-21).
La identidad de los sujetos es confidencial, identificando cada sujeto mediante números que permitieron realizar el emparejamiento de los datos entre las distintas consultas, llevándose a cabo la realización de una base de datos desde donde poder extrapolar los datos y obtener las conclusiones del presente estudio. Los pacientes incluidos en el estudio proporcionaron su consentimiento informado para la utilización de sus datos con carácter anónimo, sabiendo que se trata de un estudio descriptivo en cuanto a sus características basales, autorizando a su seguimiento a largo plazo. Los pacientes podrán revocar el consentimiento informado para la participación en este estudio en el momento en el que así lo estimen oportuno. Únicamente un paciente que no quiso participar en el estudio no deseando firmar el consentimiento informado para el análisis de los resultados obtenidos en consulta.
Análisis estadísticoLas características demográficas de los pacientes se expresaron como media y desviación estándar para las variables continuas y valores absolutos junto con porcentajes para las variables categóricas.
Los participantes se clasificaron en dos grupos de acuerdo con la terapia respiratoria empleada durante su ingreso en la UCI: ONAF o VMI. El análisis descriptivo de las características sociodemográficas y clínicas de los pacientes, se realizó el test de X2 para la igualdad de medias y la prueba de Levene de calidad de varianzas en las variables cuantitativas y la prueba de X2 en las variables cualitativas, aplicando la prueba exacta de Fisher cuando se requirió, para valorar si existía alguna diferencia estadísticamente significativa entre las variables estudiadas y el tipo de terapia respiratoria empleada, con un nivel de confianza de 95%.
Mediante un modelo de regresión logística binomial, se ha realizado el análisis multivariable para evaluar los predictores de plexopatía braquial, balance muscular limitado en miembros inferiores y neuropatía distal. Se introdujeron en el análisis multivariable las variables en las que se observó asociación estadística en el univariante.
Todos los análisis estadísticos de la base de datos se han realizado con el programa estadístico IBM SPSS Statistics V.24 (IBM). Se ha considerado estadísticamente significativo p < 0,05.
ResultadosUn total de 360 pacientes fueron ingresados en la UCI del Hospital Virgen de las Victoria desde abril del año 2020 hasta octubre de 2021. Se incluyeron en la consulta multidisciplinar pos COVID 104 pacientes. Respecto a los 256 pacientes restantes, 127 pacientes fallecieron durante su ingreso hospitalario, 74 pacientes no cumplieron los criterios de inclusión: 28 fueron trasladados desde otros hospitales, 45 pacientes se trataban de pacientes extranjeros y únicamente un paciente no deseó participar en el seguimiento y 55 pacientes perdieron el seguimiento tras el alta hospitalaria.
Las características sociodemográficas y clínicas de los pacientes en función de la terapia respiratoria empleada: ONAF o VMI se muestra en la tabla 1. De los 56 pacientes que recibieron VMI, 29 pacientes fueron intubados directamente al ingreso, 14 en las primeras 24 horas de ingreso, siete a las 48 horas de ingreso y seis pasado ese tiempo. La terapia respiratoria empleada previamente a la intubación orotraqueal fue en todos los casos ONAF. Hubo diferencia estadísticamente significativa (p < 0,001) en el número de días de ingreso en UCI, con una media de 8,97 (DE 3,86) en pacientes con ONAF vs. 32,82 (DE 21,03) en pacientes con VMI y en el número de días de ingreso hospitalario, con una media de 24,12 (DE 16,72) ONAF vs. 67,23 (DE 59,06) VMI.
Características sociodemográficas basales y clínicas en pacientes COVID-19 en función de la terapia respiratoria empleada: oxigenoterapia nasal de alto flujo o ventilación mecánica invasiva
| ONAF | VMI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 48 | n = 56 | ||
| Edad, media (DE) | 56,43 (15,83) | 59,16 (10,45) | 0,312 |
| Mayores 60 años, n (%) | 23 (47,9) | 31 (55,4) | 0,449 |
| Género | 0,512 | ||
| Hombre, n (%) | 36 (75) | 45 (80,4) | |
| Mujer, n (%) | 12 (25) | 11 (19,6) | |
| Comorbilidad, n (%) | |||
| Hipertensión arterial | 22 (45,8) | 28 (50) | 0,672 |
| Diabetes | 12 (25) | 17 (30,4) | 0,544 |
| Dislipemia | 14 (29,2) | 8 (32,1) | 0,743 |
| Hábito tabáquico, n (%) | 0,250 | ||
| No fumador | 22 (45,8) | 32 (57,1) | |
| Fumador | 3 (6,3) | 1 (1,8) | |
| Ex-fumador | 23 (47,9) | 23 (41,1) | |
| Antecedentes respiratorios, n (%) | 8 (16,7) | 15 (26,8) | 0,669 |
| EPOC | 1 (2,1) | 2 (3,6) | |
| Asma | 3 (6,3) | 6 (10,7) | |
| SAOS | 4 (8,3) | 7 (12,5) | |
| Enfermedad renal, n (%) | 1 (2,1) | 1 (1,8) | 0,712 |
| Antecedentes cardiológicos, n (%) | 6 (12,5) | 5 (8,9) | 0,555 |
| Cardiopatía isquémica | 2 (4,2) | 3 (5,4) | |
| Arritmias | 2 (4,2) | 1 (1,8) | |
| Valvulopatías | 1 (2,1) | 1 (1,8) | |
| Otros | 1 (2,1) | 0 (0) | |
| Antecedentes ortopédicos, n (%) | 3 (6,3) | 5 (8,9) | 0,447 |
| Fracturas previas | 1 (2,1) | 3 (5,4) | |
| Artritis | 1 (2,1) | 0 (0) | |
| Mialgias | 0 (0) | 1 (1,8) | |
| Artrosis | 1 (2,1) | 1 (1,8) | |
| IMC, n (%) | 0,326 | ||
| Normal (18,5-24,9) | 5 (10,4) | 2 (3,6) | |
| Sobrepeso (25-29,9) | 13 (27,1) | 18 (32,1) | |
| Obesidad 1 (30-34,9) | 12 (25) | 20 (35,7) | |
| Obesidad 2 (35-39,9) | 11 (22,9) | 7 (12,5) | |
| Obesidad mórbida (> 40) | 7 (14,6) | 9 (16,1) | |
| IMC, media (DE) | 32,85 (6,87) | 33,05 (7,10) | 0,885 |
| Escala APACHE, media (DE) | 8,18 (3,17) | 9,07 (4,41) | 0,284 |
n: número de pacientes; DE: desviación estándar; EPOC: enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica; SAOS: síndrome de apnea obstructiva del sueño; IMC: índice de masa corporal.
La escala APACHE II obtuvo resultados similares en ambos grupos de estudio, con una media de 8,18 (DE 3,17) en ONAF vs. 9,07 (DE 4,41) en VMI.
Los síntomas presentes al mes del alta hospitalaria se describen en la tabla 2, encontrando diferencias entre ambas terapias de soporte respiratorio en cuanto a las secuelas ORL encontrando casos de afonía, granuloma glótico, estenosis traqueal, hipoacusia y fístula traqueostoma en el grupo de VMI.
Síntomas detectados al mes del alta hospitalaria
| ONAF | VMI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 48 | n = 56 | ||
| Peso perdido pos UCI (kg), media (DE) | 8,54 (4,59) | 13,64 (8,78) | < 0,001 |
| BCM (kg), media (DE) | 31,96 (8,74) | 26,87 (6,84) | 0,007 |
| BCMI (kg/m2), media (DE) | 11,16 (2,83) | 9,20 (2,15) | 0,001 |
| ORL, n (%) | 1 (2,1) | 22 (39,3) | 0,001 |
| Alteraciones psicológicas/psiquiátricas, n (%) | 17 (35,42) | 23 (41,07) | 0,350 |
| Insomnio, n (%) | 11 (22,91) | 16 (28,57) | 0,512 |
| Consumo benzodiacepinas, n (%) | 11 (22,91) | 19 (33,93) | 0,217 |
| Consumo antidepresivos, n (%) | 10 (20,83) | 18 (32,14) | 0,195 |
| Disnea mMRC, n (%) | 0,267 | ||
| Grado 0 | 19 (39,6) | 18 (32,1) | |
| Grado 1 | 18 (37,5) | 15 (26,8) | |
| Grado 2 | 8 (16,7) | 17 (30,4) | |
| Grado 3 | 3 (6,3) | 6 (10,7) | |
| Oxigenoterapia domiciliaria, n (%) al alta hospitalaria | 22 (45,8) | 17 (30,4) | 0,104 |
| Balance articular, n (%) normal | 31 (88,6) | 35 (71,4) | 0,059 |
| Balance muscular, n (%) normal | 27 (77,1) | 24 (49) | 0,009 |
| Procesos dolorosos, n (%) | 14 (29,2) | 22 (39,3) | 0,633 |
| Plexopatía braquial, n (%) | 0 (0) | 6 (10,7) | 0,024 |
| Neuropatía distal, n (%) | 5 (10,4) | 19 (33,9) | 0,005 |
| Pie equino, n (%) | 2 (4,3) | 6 (10,71) | 0,260 |
| Ayuda, n (%) | |||
| Sin ayuda | 43 (89,6) | 42 (75) | |
| Bastón/andador | 3 (6,3) | 13 (23,2) | |
| Silla de ruedas | 2 (4,2) | 1 (1,8) | 0,055 |
| MOCA, media (DE) | 19,5 (10,31) | 20,52 (8,77) | 0,741 |
| Fatiga/cansancio, n (%) | 34 (70,8) | 45 (84,9) | 0,087 |
BCM: masa corporal total; BCMI: masa corporal total indexada; ORL: otorrinolaringológicas; mMRC: escala de disnea modificada del Medical Research Council; MoCA: evaluación cognitiva de Montreal.
Las secuelas físicas presentes en la consulta de Rehabilitación con diferencias significativas fueron la neuropatía distal (p = 0,005) y la limitación del balance muscular en miembros inferiores (p = 0,024). La plexopatía braquial se describió únicamente en los pacientes que precisaron VMI (p = 0,024). No se encontraron diferencias en los procesos dolorosos estudiados (cervicobraquialgia, neuropático, lumbociática, síndrome facetario, entesopatía múltiple y meralgia parestésica).
En la primera consulta realizada por parte de Rehabilitación (tabla 3), se realizó el test de la marcha, la medición de la Pimax y Pemax y la dinamometría de mano. Los hombres obtuvieron mejores resultados (p = 0,010) en la Pimax en el grupo de ONAF con una media de 112,10 cm H2O (DE 33,04 cmH2O), en comparación con con 89,81 cmH2O (DE 34,71 cmH2O) en el subgrupo de VMI. El test de prensión isométrica mediante el dinamómetro de mano mostró disminución de fuerza de agarre con una media en mano derecha de 20,67 kg (± 8,27) en VMI vs. 31,8 kg (± 11,59) en ONAF, y una media en mano izquierda de 19,39 kg (± 8,45) en VMI vs. 30,26 kg (± 12,74) en ONAF.
Pruebas funcionales: Rehabilitación. Test de la marcha y dinamómetro de mano. Pruebas funcionales respiratorias: Espirometría y presiones respiratorias
| ONAF | VMI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test de la marcha, n (%) | n = 16 | n = 30 | 0,220 |
| Distancia normal | 12 (75) | 17 (56,7) | |
| Distancia < 350 m | 4 (25) | 13 (43,3) | |
| Paradas, n (%) | n = 30 | n = 30 | 0,83 |
| 0 | 14 (87,5) | 26 (86,7) | |
| 1 | 1 (6,3) | 3 (10) | |
| 2 ó más | 1 (6,3) | 1 (3,3) | |
| Oxígeno, n (%) | 1 (6,3) | 2 (6,7) | 0,726 |
| Dinamómetro de mano (kg), media (DE) | n = 35 | n = 46 | |
| Mano D (kg) | 31,8 (11,59) | 20,67 (8,27) | <0,001 |
| Mano I (kg) | 30,26 (12,74) | 19,39 (8,45) | <0,001 |
| Espirometría | N = 32 | N = 34 | |
| FVC (%), media (DE) | 85,57 (17,61) | 90,80 (27,49) | 0,389 |
| FEV1, media (DE) | 87,31 (17,99) | 89,03 (20,22) | 0,724 |
| FEV1/FVC, media (DE) | 82,34 (8,43) | 84,16 (15,26) | 0,549 |
| Presiones respiratorias | |||
| Hombres | n = 28 | n = 38 | |
| Pimax, media (DE) | 112,10 (33,04) | 89,81 (34,71) | 0,010 |
| Pemax, media (DE) | 107 (27,38) | 97,07 (28,34) | 0,166 |
| Mujeres | n = 9 | n = 8 | |
| Pimax, media (DE) | 76,22 (45,88) | 62,25 (19,52) | 0,423 |
| Pemax, media (DE) | 72,66 (19,15) | 74,12 (25,82) | 0,898 |
FVC: capacidad vital forzada; FEV1: Volumen Espirado Máximo en el primer segundo de la espiración forzada; FEV1/FVC; Pimax: presión inspiratoria máxima; Pemax: presión espiratoria máxima.
De los 104 pacientes a los que se realizó el seguimiento en la consulta multidisciplinar pos UCI, no precisaron rehabilitación un total de 23 pacientes. Respecto a los 81 pacientes restantes, 36,54% precisaron rehabilitación grupal y 41,35% domiciliaria (p = 0,056).
Otras escalas realizadas fueron: el índice de Barthel con 95,28 puntos (DE 14,44 puntos) en ONAF y 89,12 (DE 20,70 puntos) en VMI; la escala EQ-5D con diferencia estadísticamente significativa en cuanto a la calidad de vida percibida a los seis meses entre los subgrupos estudiados (p = 0,004), sin existir diferencia en la primera revisión (p = 0,301) ni en el resto de los aspectos valorados en la escala; y la escala FACIT a los seis meses (p = 0,099).
Tras el análisis multivariable (tabla 4) para evaluar los factores de riesgo asociados con la plexopatía braquial, balance muscular limitado en miembros inferiores y neuropatía distal, no se encontró asociación estadísticamente significativa.
Análisis multivariable factores de riesgo asociados a plexopatía braquial (A), balance muscular limitado miembros inferiores (B) y neuropatía distal (C)
| Plexopatía braquial | ||
|---|---|---|
| OR (IC 95%) | p | |
| Kilos perdidos UCI | 1,046 (0,953-1,147) | 0,344 |
| Pronos | 1,175 (0,779-1,771) | 0,443 |
| Balance muscular limitado en miembros inferiores | ||
|---|---|---|
| OR (IC 95%) | p | |
| Edad | 1,045 (0,977-1,117) | 0,199 |
| BCMI | 0,803 (0,570-1,130) | 0,208 |
| Días ingreso UCI | 0,986 (0,943-1,030) | 0,515 |
| Pronos | 1,248 (0,888-1,755) | 0,202 |
| ONAF/VMI | 2,417 (0,334-17,504) | 0,385 |
| Neuropatía distal | ||
|---|---|---|
| OR (IC 95%) | p | |
| Traqueostomía | 7,988 (0,923-69,107) | 0,059 |
| Kilos perdidos UCI | 1,088 (0,988-1,198) | 0,088 |
| Días ingreso UCI | 0,850 (0,701-1,031) | 0,100 |
| Días ingreso hospitalario | 1,016 (0,995-1,037) | 0,127 |
| Días VM | 1,126 (0,949-1,336) | 0,174 |
| Pronos | 1,153 (0,819-1,624) | 0,415 |
En nuestro estudio no se aprecian diferencias estadísticamente significativas en cuanto a las secuelas físicas percibidas tras el alta hospitalaria en función de la terapia respiratoria empleada, ya fuera ONAF o VMI prolongada, sin encontrar diferencias tampoco entre los pacientes que precisaron rehabilitación. Aun sin existir diferencias significativas, más del doble de pacientes del grupo de VMI precisaron rehabilitación grupal con respecto a los pacientes que requirieron ONAF, pudiendo generar incertidumbre acerca de los resultados. El protocolo de rehabilitación domiciliaria fue igual al presencial salvo por la supervisión por parte de un fisioterapeuta, aspecto que hizo más individualizado el tratamiento, al mismo tiempo que el paciente se comprometía a acudir al mismo, teniendo una actitud positiva hacia el programa con una buena adherencia. En el programa domiciliario, no hubo supervisión y ha dependido fundamentalmente de la concienciación que tuviera el paciente para asumir esta terapia.
Desde el punto de vista respiratorio, prácticamente el doble de pacientes dentro del grupo de VMI describió disnea grado 2-3 mMRC. Llama la atención la ausencia de significación en cuanto a la necesidad de oxigenoterapia al alta, sin observar un menor porcentaje dentro del grupo de ONAF con respecto a VMI. Estos datos resultan interesantes e invitan a la formulación de hipótesis al respecto, en cuanto a la duración del distrés y el tiempo de reparación pulmonar. El hecho de que pacientes que fueron tratados con alto flujo9 no presenten diferencias significativas con respecto a la VMI plantea dos hipótesis fundamentalmente: menor tiempo de ingreso en Cuidados Intensivos y menor tiempo de ingreso hospitalario total, pasando los últimos días del distrés en domicilio; y una segunda hipótesis que defiende que el apoyo no invasivo conlleva riesgo de lesión pulmonar autoinfligida por el paciente afectando negativamente a los síntomas percibidos10,11.
Se ha realizado este estudio con el interés de estudiar las posibles diferencias en cuanto a las secuelas de los pacientes en función de la terapia respiratoria empleada durante su ingreso en Cuidados Intensivos, al existir escaso número de estudios que hayan realizado una comparación directa entre ambos grupos y no existir hasta la fecha recomendaciones respecto al momento óptimo de inicio de la oxigenoterapia nasal de alto flujo (ONAF) y sus posibles efectos12,13. En los estudios encontrados, los supervivientes de UCI tenían puntuaciones de disnea y función pulmonar similares a los pacientes que no precisaron ingreso en UCI, pese a presentar peores resultados en la tomografía computarizada (TC) y rendimiento menor en las actividades habituales14. En cuanto a las pruebas respiratorias funcionales mediante la Pimax y Pemax, así como el volumen ventilatorio máximo han sido estudiados en distintos perfiles de pacientes, existiendo correlación entre la fuerza de prensión manual como determinante de la fuerza de los músculos periféricos y la fuerza de los músculos pulmonares en comparación con pacientes sanos15. Nuestro estudio ha encontrado16 diferencias significativas en el número de días de ingreso en Cuidados Intensivos y hospitalario en función de la terapia respiratoria que precisaron durante su ingreso (p < 0,001), sin encontrar diferencia a nivel de las pruebas respiratorias realizadas, como la espirometría (FVC, FEV1 y FEV1/FVC). Únicamente se encontraron diferencias significativas en la Pimax en los varones estudiados.
El SPCI17–19 presenta niveles clínicamente significativos de síntomas depresivos, ansiedad y síntomas de estrés postraumático20, habiendo sido acuñado el término síndrome pos COVID-19, síndrome pos COVID-19 persistente (PPCS) o COVID prolongado21. Existen estudios acerca de la calidad de vida o secuelas tras el alta hospitalaria, en neumonía por COVID-19 no crítico22 examinando el impacto de la misma en la función pulmonar, calidad de vida relacionada con la salud y disnea percibida. La aparición de deterioro cognitivo en infección leve sintomática por COVID-19, evaluado mediante el test de MOCA, está descrita, si bien se desconoce la patogenia de esta complicación3. En cuanto al impacto en la calidad de vida diaria, evaluada mediante la escala EQ-5D-5L, se han encontrado diferencias4 en pacientes supervivientes de UCI con respecto a casos leves o moderados. Otros estudios23 muestran alteración en movilidad, autocuidado, dolor, ansiedad o depresión, actividad habitual en ambos grupos, con una ligera diferencia en el dolor en el grupo de la UCI.
La rehabilitación es fundamental en el seguimiento multidisciplinar de los pacientes tras el alta hospitalaria24 para la recuperación de enfermedades graves asociadas con el COVID-19, optimizar su independencia y facilitar la reintegración en la comunidad, por lo que debe promoverse una rehabilitación temprana25–27. Nuestro estudio muestra asociación entre VMI y plexopatía braquial, neuropatía distal y balance muscular limitado en miembros inferiores. No obstante, tras el análisis multivariable no se observaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas.
Desde el punto de vista nutricional, encontramos diferencias significativas en BCM y BCMI28 en pacientes que precisaron VMI, si bien los resultados parecen guardar relación con un mayor número de días de ingreso en UCI e ingreso hospitalario, habiendo contribuido con peores resultados nutricionales en estos pacientes.
Las principales limitaciones de este estudio han sido el pequeño tamaño muestral además del hecho de que no todos los pacientes fueron valorados por todos los especialistas incluidos en el programa multidisciplinar, habiendo realizado determinadas pruebas, como la espirometría, en los pacientes con peor evolución desde el punto de vista respiratorio al alta hospitalaria.
Se excluyeron del estudio, lamentablemente, un alto número de pacientes dado que nuestro hospital es referente de otras áreas sanitarias, por lo que del total de pacientes que sobrevivieron, se excluyeron 74 pacientes al pertenecer a otros hospitales o tratarse de pacientes extranjeros que volvieron a sus países de origen. Además se perdieron 55 pacientes que no fueron incluidos en el estudio al no disponer de datos acerca de sus secuelas al mes del alta hospitalaria, probablemente producto del cierre de agendas de la consulta pos COVID en la tercera ola, en enero 2021.
Otro factor a tener en cuenta en el estudio es la medicación administrada durante su ingreso, sin existir diferencia en cuanto a dexametasona y tocilizumab, si la observamos con lopinavir/ritonavir e hidrocloroquina, administrados fundamentalmente en los pacientes con VMI. Este hecho podría generar sesgos, si bien estos fármacos a fecha de 4 de julio de 2020 fueron desaconsejados en su uso por la OMS aceptando la recomendación del Grupo directivo internacional del ensayo Solidarity, por la que la reducción de la mortalidad en enfermos COVID-19 no justificaba su uso. Esto mismo ocurrió con el interferón beta-1A, existiendo evidencia y datos que demostraron la no disminución de mortalidad y/o de necesidad de VM29. Por tanto, no consideramos que su utilización en los pacientes seleccionados de la primera ola haya podido generar sesgos entre ambos grupos.
Es preciso el seguimiento a largo plazo y aumentar el tamaño muestral para caracterizar mejor las consecuencias de la COVID-19.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos tras el estudio multivariable sugieren no existir diferencias estadísticamente significativas en cuanto a las secuelas físicas percibidas tras el alta hospitalaria en función de la terapia respiratoria empleada, ya fuera ONAF o ventilación mecánica prolongada, si bien son precisos más estudios para poder obtener conclusiones al respecto.
Contribución de los autoresLa consulta multidisciplinar ha estado constituida por los servicios de Medicina Intensiva, Medicina Fïsica y Rehabilitación, Endocrinología y Nutrición, Salud Mental y Neumología. La contribución por parte de los distintos servicios citados ha estado representada por el Dr. José M. García Almeida como médico especialista en Endocrinología y Nutrición; la Dra. Elma Avanesi-Molina como médico especialista en Salud Mental; la Dra. Eva Cabrera-César como médico especialista en Neumología, la Dra. Pilar Martínez-López como médico especialista en Medicina Intensiva y Adela M. Gómez-González como especialista en Medicina Física y Rehabilitación. El artículo ha sido dirigido por las Dras. Pilar Martínez-López y Adela M. Gómez-González, como principales creadoras de la consulta pos COVID-19, con la colaboración de la directora médica hospitalaria, la Dras. Maria A. Estecha-Foncea. La elaboración del proyecto, búsqueda bibliográfica, discusión y conclusiones ha sido realizada por la Dra. Ana M. Sánchez-García, con la revisión externa por parte del Dr. Pedro L. Sánchez-Fernández, Manuel F. Jiménez-Navarro y la Dra. María A. Estecha-Foncea. Han contribuido en la recogida de datos los Dres. Nicolás Zamboshi, Carolina Rueda-Molina, Victoria Doncel-Abad, Ana I. Molina- Ramos, Imad Ben-Abdellatif, Marina Gordillo-Resina y Esteban Pérez-Mesa. Las encuestas telefónicas fueron realizadas por las Dras. Maria Nieto-González, Pilar Nuevo-Ortega y Carmen Reina-Artacho. El análisis estadístico de los datos fue realizado por los doctores Jorge Rodriguez-Capitán y Rafael J. Jiménez-López. El autor de correspondencia es el Dr. Manuel F. Jiménez-Navarro, perteneciente al Instituto de Investigación Biomédica de Málaga (IBIMA), Universidad de Málaga (UMA).
Conflicto de interesesLos autores declaran no tener ningún conflicto de intereses.