To evaluate if there is an association between obesity and mortality in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) in adult patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
DesignSystematic review with meta-analysis.
ScopeICU.
Data sourceA search was made in MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL and Global Health databases without language restriction, until February 21, 2017.
Selection of studiesStudies that reported mortality in the ICU in obese versus non-obese patients who received IMV were included.
Main variablesMortality in the ICU.
Results2163 articles were found, of which 14 studies were included. No statistically significant differences were found between obese and non-obese patients with respect to the variable mortality in the ICU (OR: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.81–1.10, P=.45).
ConclusionNo relationship was found between the subgroup of obese adult patients receiving IMV and the mortality variable in the ICU.
Evaluar si existe asociación entre obesidad y mortalidad en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) en pacientes adultos que reciben ventilación mecánica invasiva.
DiseñoRevisión sistemática con metaanálisis.
ÁmbitoUCI.
Fuente de datosSe realizó una búsqueda en las bases de datos MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL y Global Health sin restricción de lenguaje, hasta el 21 de febrero del año 2017.
Selección de estudiosSe incluyeron estudios que informaron mortalidad en UCI en pacientes obesos versus no obesos que recibieron VMI.
Variables principalMortalidad en UCI.
ResultadosSe hallaron 2.163 artículos, de los cuales se incluyeron 14 estudios. No se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los pacientes obesos y no obesos respecto a la variable mortalidad en UCI (odds ratio: 0,94; intervalo de confianza del 95%: 0,81-1,10; p=0,45).
ConclusiónNo se halló relación entre el subgrupo de pacientes adultos obesos que reciben VMI y la variable mortalidad en UCI.
Obesity is a multifactor chronic disease1 defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as an abnormal or excessive accumulation of fat.2 Actually, it is a public health problem worldwide.3
Due to the growing prevalence and frequent association with other diseases and conditions, obese patients are often hospitalized in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) where Invasive Mechanical Ventilation (IMV) is one of the most widely used therapeutic options.4,5 Regardless of the cause for admission, this subgroup of critically ill patients is challenging per se due to their higher morbimortality.6 Controversial results have been found among the various studies that have analyzed the association between obesity and mortality at the ICU setting.4,7–13
Bercault et al. reported that obesity and IMV are independent risk factors of mortality at the ICU mortality setting (odds ratio [OR] 2.1; 95% confidence interval: 1.2–3.6, P=.007)4 while Solh et al. found this association in the subgroup of patients with morbid obesity.7 Similarly, Goulenok et al. found that a high body mass index (BMI) is a prognostic factor of mortality in critically ill patients.8
In the studies conducted by O’Brien et al., Tremblay, and Frat et al. no correlation between obesity and mortality was found.9,10,12 Similarly, Anzueto et al. analyzed time variables such as days on IMV, length of the ICU and hospital stays and they did not find any significant differences among the different categories of the BMI.11 However, O’Brien et al. reported lower mortality rates.13
To this day, 7 systematic reviews (SR) that analyzed the correlation between obesity and mortality at the ICU setting have been found showing various results.14–20 Hogue et al. and Oliveros et al. did not establish any correlations between such variables in critically ill patients.14,15 However, Falagas et al. reported higher mortality rates in subjects with infections,16 and other authors have described lower mortality rates in septic patients,18 patients with pneumonia,17 and critically ill patients.20
The meta-analyses that study this issue reported statistical heterogeneity and did not take the clinical or methodological characteristics of each of the studies included into consideration. This means that some SRs showed methodological heterogeneity because their meta-analysis considered retrospective and prospective studies together without making any differences among different designs.14,15,17,18,20 Regarding clinical heterogeneity, some studies used different ways to stratify the BMI including low-body-weight patients in the analysis.20 Other studies analyzed specific subgroups of patients such as patients with pneumonia,17 sepsis, and septic shock.18 Lastly, some of the studies published did not discriminate between patients who received IMV and those who did not.14,15
Therefore, none of the aforementioned studies has emphasized the impact BMI has on mortality at the ICU setting in obese patients who need IMV. For this reason, we believe it is very important to analyze this subgroup of patients.
The hypothesis of our study is that obese adult patients who need IMV have higher mortality rates at the ICU setting compared to non-obese patients.
The goal of this SR was to assess whether there is a correlation between obesity (BMI≥30kg/m2) and mortality at the ICU setting in adult patients on IMV.
Patients and methodSearch strategy: a systematic review (SR) was conducted of the medical literature available according to the following checklist: Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies Epidemiology (MOOSE).21 The registry took place at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) back in March 27, 2017 with code# crd42017059983.22
The search was conducted by an experienced librarian who reviewed the following databases: MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, and OVID (Global Health) without language restriction until February 2017. A specific strategy was established for every particular database (annex 1 of the supplementary data).
The data published on gray literature on Google®, GreyNet International, Open Grey, and New York Academy of Medicine Grey Literature Report were reviewed too.
A manual search of the article references identified as relevant was conducted. The lead author of the studies reviewed identified as relevant was contacted over the e-mail. When no answer was received or his answer was not consistent with the primary and secondary outcome variables, the study was eliminated since data could not be analyzed.
Selection of studies and data miningFour reviewers grouped in pairs identified the studies and conducted an independent examination of the titles and abstracts identified through electronic searches. The complete versions of all potentially relevant studies were recovered. When no agreement was reached between the authors of the pair, a third reviewer from the team of researchers was added to the mix to solve discrepancies.
Inclusion criteriaThe primary studies that met the following criteria were included:
- –
Comparison between obese patients (BMI≥30kg/m2) versus non-obese patients (BMI<30kg/m2).
- –
Mortality at the ICU setting reported as the outcome variable.
- –
Present a population that requires IMV during the ICU stay.
- –
Studies that analyzed the same patient database. Of these, the study whose sample had the smallest size was excluded.
- –
Studies duplicated in several databases.
- –
Studies conducted in neonatal or pediatric ICUs.
- –
Mortality at the ICU setting.
- –
Duration of IMV: days elapsed since ventilatory support was prescribed until extubation, and lack of ventilatory support for 48h after weaning from ventilatory support.23
- –
ICU stay: days elapsed since admission until discharge or death.
- –
Hospital stay: days elapsed since admission until discharge or death at the hospital.
Four reviewers grouped in pairs scored the methodological quality of each study included usinfg the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. This scale is a tool used to assess the quality of the observational studies of SRs and meta-analyses.24 Disagreements were solved by consensus.
On the other hand, 2 independent reviewers assessed the quality of the evidence of the primary variables using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation (GRADE)25 and the GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GDT) software. These variables were stratified from low to high quality. Reviewers solved disagreements by consensus.
Data synthesis and statistical analysisThe following data from every study were collected: information on the author, year of publication, type of study, results, and other significant characteristics. In order to estimate mortality at the ICU setting, the number of events was registered over the total number of patients. The mean and standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR) of the studies that provided information on the duration of IMV and ICU and hospital stay were registered for every BMI category using the criteria established by the WHO.2 This classification—used and recognized worlwide—considers obese subjects those with BMI≥30kg/m2.
The correlation between obesity and mortality at the ICU setting was expressed using the OR with a 95%CI.
In order to conduct the meta-analysis, the presence of 3 or more studies that met the inclusion criteria was established as a prerequisite.
Statistical heterogeneity was calculated using the chi-square test and the I2 values. According to the latter, heterogeneity was classified as low (<30%), moderate (30–70%), and high (>70%).
First, 2 sensitivity analyses were conducted based on the type of study design, and prospective and retrospective studies were assessed in isolation. No thorough analysis was conducted of the latter due to their limitations in the registry of the variables and associated biases. On the other hand, the prospective studies that categorized the BMI were analyzed and the low-body-weight subgroup (BMI<18.5kg/m2) was excluded due to its higher mortality rate.
The mortality variable at the ICU setting was analyzed using the fixed effect estimator. In the presence of clinical and methodological heterogeneity the random effect estimator was used. These values were expressed using the forest plot for the variables analyzed. Publication bias was assessed using Begg's test, Egger's test, and the corresponding funnel plot was designed.
P values≤.05 were considered statistically significant.
The analysis of data was conducted using the RevMan software (Review Manager) version 5.3.5 developed by the Cochrane Group, Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 5.3.5. Copenhaguen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014 y el software STATA versión 13 (StataCorp. 2013. Stata Statistical Software: Release 13. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP.).
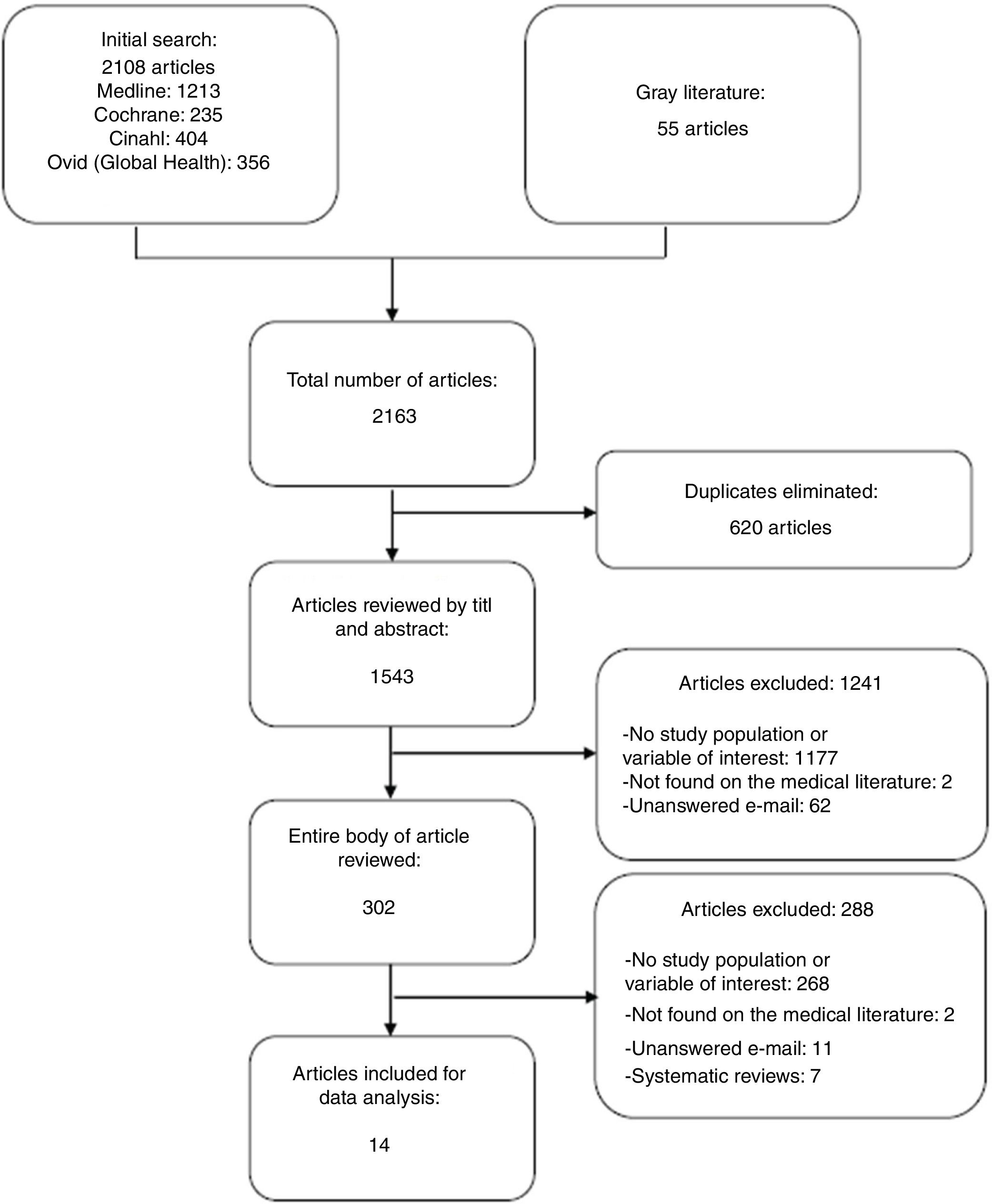
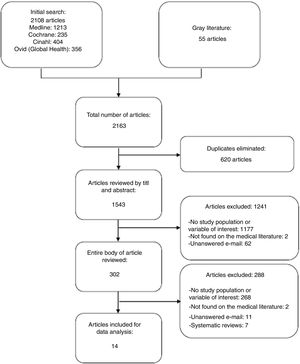
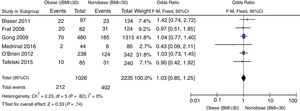
ResultsThe initial search identified 2163 studies out of which 1543 were reviewed by title and abstract considering that 36 of these came from the manual search. The entire body of 302 articles was assessed, of which 14 met the inclusion criteria for data analysis (Fig. 1).
Reasons for excluding articles (Fig. 1):
- –
Studies that did not provide any information on the variables of interest, whether primary or secondary, because the analysis of data would have been impossible.
- –
Studies not found on the medical literature after reviewing different sources of access to scientific literature.
- –
Studies whose lead authors were contacted over the e-mail and who did not respond or had not analyzed the study variables.
- –
All SRs considered secondary studies. However, the references were analyzed to have more information.
Table 1 of the annex (supplementary data) shows the data considered relevant from all the studies included.
Regarding the design of the studies analyzed, 6 were prospective and 8 were retrospective studies. Seven of these were conducted in Europe, 2 in North America, and 1 in Asia. In total, 89031 patients who required IMV were included of which 6702 (7.5%) showed BMI≥30kg/m2. Regarding diagnosis at the ICU admission, subjects with acute lung injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, abdominal hypertension, closed trauma, respiratory failure, and septic shock were included. However, none of the studies included the reason for initiating IMV.
Obesity was categorized different depending on the study. Three studies26–28 used the criteria suggested by the WHO,2 213,29 followed the recommendations established by the National Institutes of Health (NIH),1 1 study followed the modified NIH recommendations,30 and 6 other studies31–36 registered it as a dichotomic variable using BMI≥30kg/m2 as a cut-off value for obesity. However, Frat et al. only considered severe obesity for their analysis (BMI≥35kg/m2).12
Regarding the demographic variables, in the studies where the entire population required IMV, males27,33,35,37 were the predominant sex. Regarding age, 3 studies27,35,36 used the same statistical estimator (mean±SD). Sasabuchi et al.27 reported that obese patients were younger, similar to what Gong et al.36 reported in morbid obese patients (BMI≥40kg/m2). However, Lam et al. did not any find statistically significant inter-group differences.35
Regarding severity at the ICU admission, the most widely used scoring system was the Simplified Acute Physiologic II (SAPS II)12,26,28,29,33,35 followed by the Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA), the Acute Physiologic and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II,26,33,35 and the APACHE III34,36).
Taking into consideration the studies that used the SAPS II, O’Brien et al. were the only ones to find statistically significant differences in the chances of survival in the subgroup of severely obese patients.13 Among the studies that used the APACHE II score, only Sakr al. observed that the group of severely obese patients showed less severity at admission compared to normal-body-weight patients.29 However, this score was obtained for the entire population of patients regardless of their IMV needs. On the other hand, none of the studies that provided information on severity through the SOFA,12,26,33,35 and the APACHE III scores34,36 found statistically significant inter-group differences.
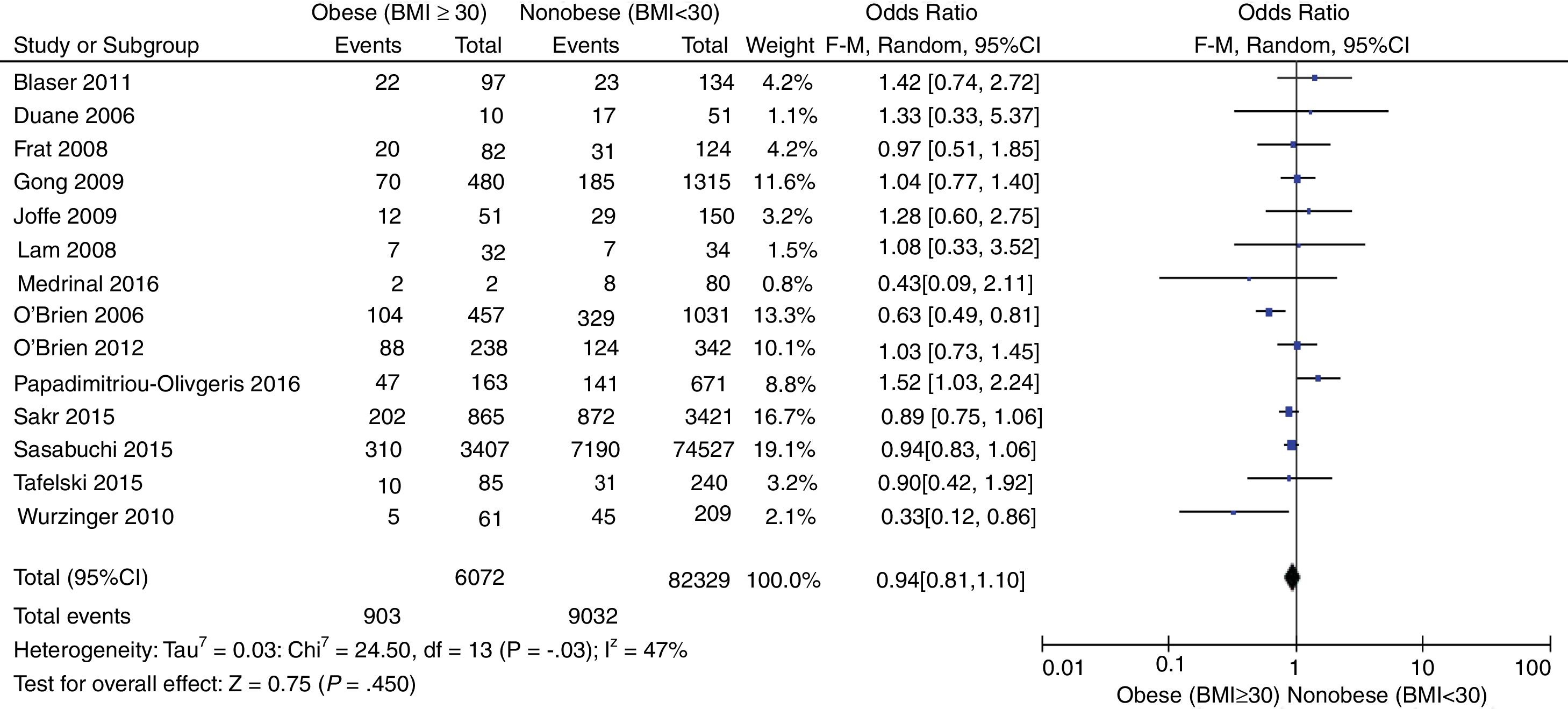
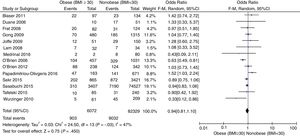
Mortality at the Intensive Care UnitFig. 2 shows the distribution of all studies included regarding mortality at the ICU setting. No statistically significant differences were found between obese and nonobese patients [OR, 0.94 (95%CI, 0.81–1.10; P=.45)] expressed through a random effects model. Moderate statistical heterogeneity found (I2=47).
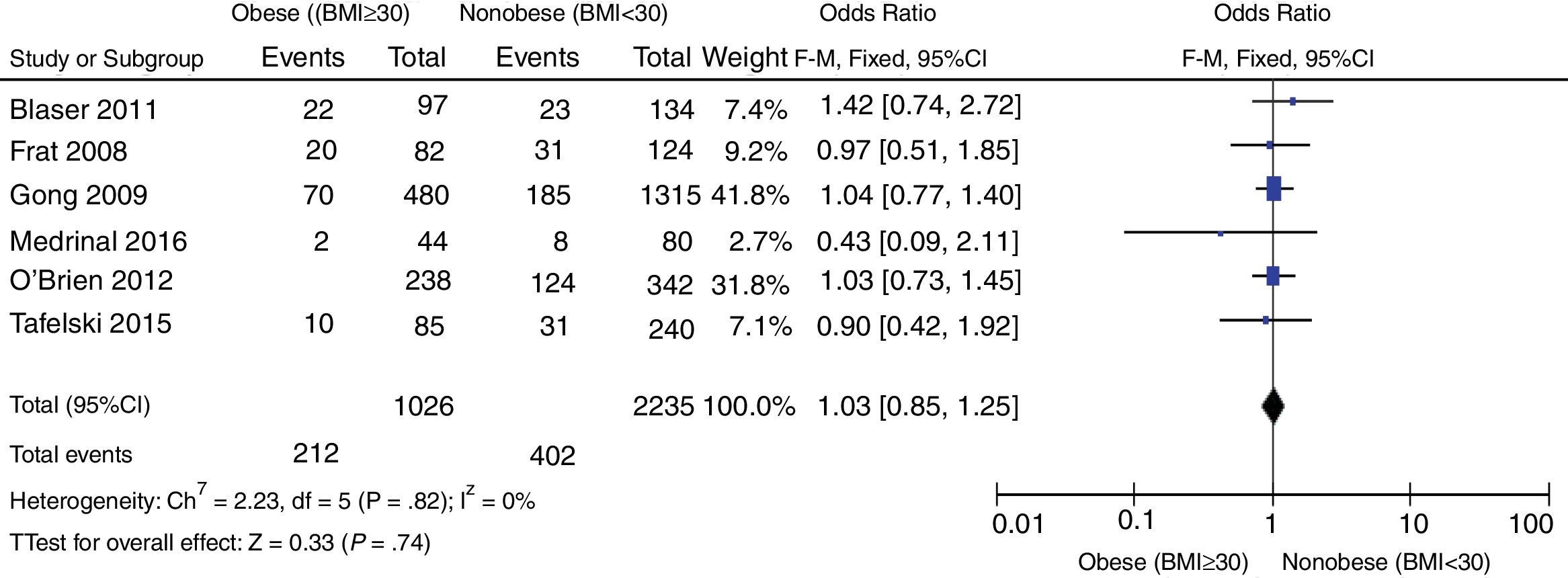
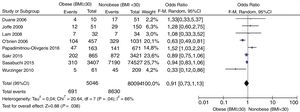
The forest plot shown in Fig. 3 shows the sensitivity analysis based on the study design that included prospective studies. There were no statistically significant differences regarding mortality at the ICU setting between obese and nonobese patients [OR 1.03 (95%CI, 0.85–1.25; P=.74)] expressed through a random effects model. No statistical heterogeneity found (I2=0).
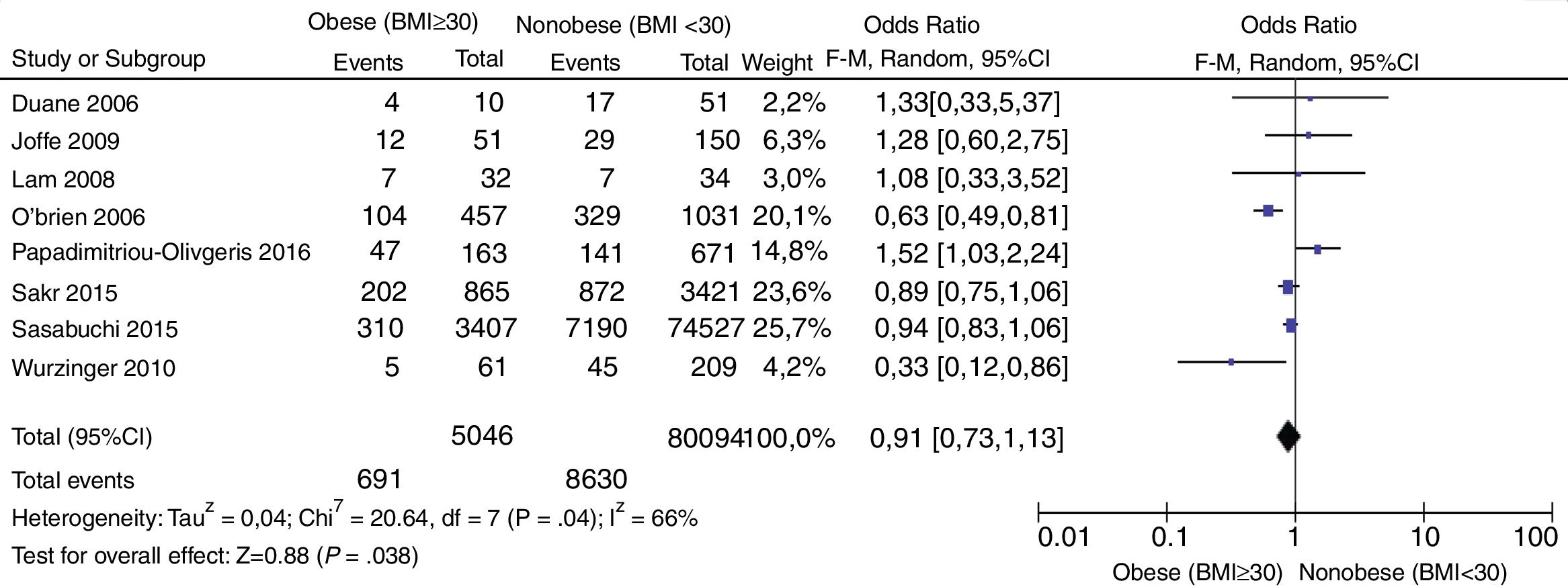
The forest plot shown in Fig. 4 performed a second sensitivity analysis including all retrospective studies. [OR, 0.91 (95%CI, 073–1.13; P=.38)] expressed through a random effects model with no statistically significant inter-group differences. Statistical heterogeneity found (I2=66%).
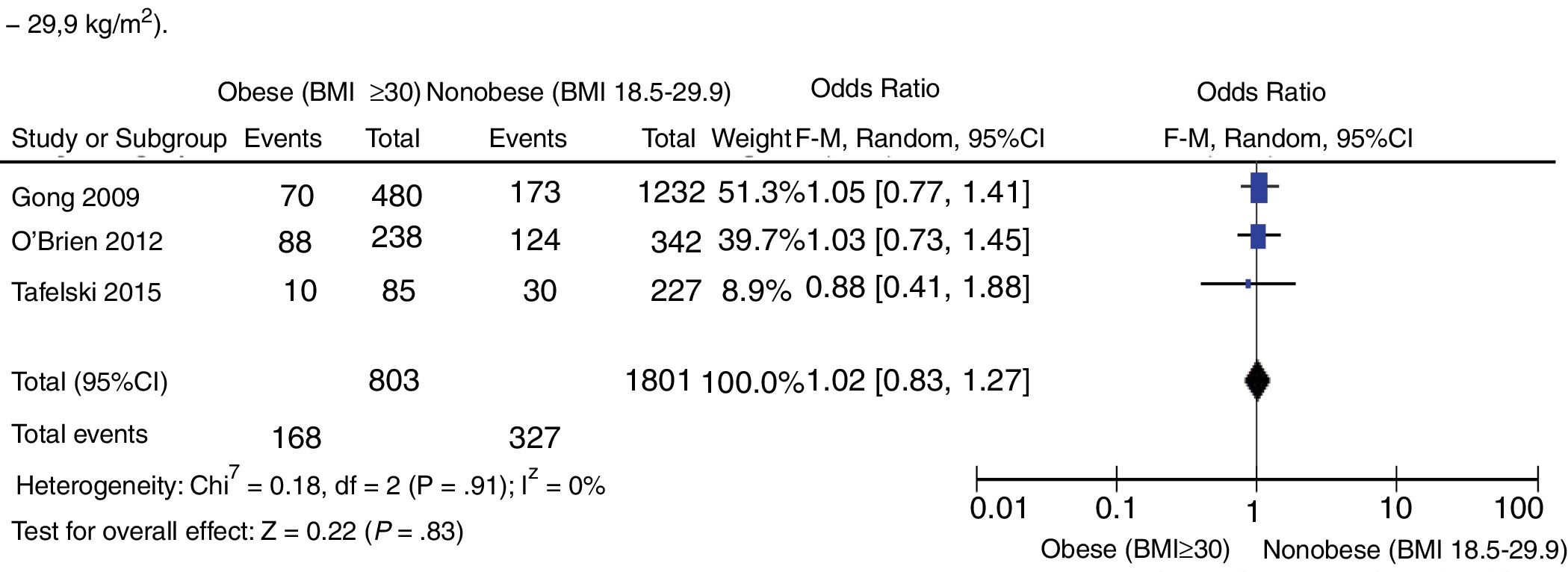
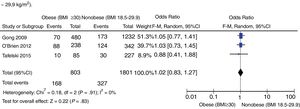
Lastly, a third sensitivity analysis of prospective studies was conducted that eliminated those that included low-body-weight patients (Fig. 5) [OR, 1.02 (95%CI, 0.83–1.27; P=.82) expressed through a random effects model with no statistically significant inter-group differences. No statistical heterogeneity found (I2=0).
Time variablesDuration of invasive mechanical ventilationThe duration of IMV has been reported by 5 studies. Duane et al. reported on the mean duration of IMV (in days) and found no statistically significant differences (P=.72).32
Similarly, Frat et al.,12 Tafelski et al.,31 and Gong et al.36 reported on the median duration of IMV (in days) to find no statistically significant differences either: P=.28, P=.374, and P=.6, respectively. The first 2 authors reported on this variable as days on IMV while Gong et al. reported it as IMV-free days.
Stay at the Intensive Care UnitEight studies reported on this variable. Duane et al., O’Brien et al., and Lam et al. reported it and expressed it as mean±SD but found no statistically significant differences between the subgroups of obese and nonobese patients.13,32,35
Frat et al., Sakr et al., Tafelski et al., and Sasabuchi et al. reported it in days and expressed it as median (RIQ), but found no statistically significant differences either.12,27,29,31. However, Sasabuchi et al. also drew a comparison between patients with and without need for IMV and obtained a value of 4 days (2–8) versus 1 (1–3), respectively, which was a statistically significant difference (P=.01).27
Lastly, Gong et al. also reported on this variable in days (median) in the following terms: normal-body-weight subgroup, 13 days (7–23); overweight, 10 days (6–19); obese, 15.5 days (7–26.5); severely obese, 13 days (9–26), and found statistically significant differences (P=.02) in the category of obese subjects.36
Hospital stayFive studies reported on this variable. O’Brien et al. and Duane et al. reported it and expressed it as mean days and found no statistically inter-group significant differences.13,32
Other authors reported on this variable in days and expressed it as median. Lam et al. found no statistically significant inter-group differences (P=.75),35 but Gong et al. found 18 days (6–34) in the low-body-weight subgroup, 20 days (10–55) in the normal-body-weight subgroup, 16 days (9–39) in the overweight group, 27 days (12–27) in the obese group, and 28 days (12–60) in severely obese subjects obtaining statistical significance for obese and severely obese groups (P=.007).36 Lastly, Sasabuchi et al. found no statistically significant inter-group differences and longer hospital stays compared to the subgroup of patients who did not require IMV (P=.001).27
Assessment of methodological qualityThe Newcastle-Ottawa scale was used to assess methodological quality in 3 domains: the selection of study groups, group comparability, and quality exposing information (for case studies and controls) or results (for cohort studies).24
As Table 2 of the annex (supplementary data) shows, the prospective study that scored the highest points was the study conducted by Gong et al.,36 and the retrospective design studies that scored the most points were the studies conducted by O’Brien et al.,13 Lam et al.,35 Sasabuchi et al.,27 and Wurzinger et al. (annex, Table 3).28 The main flaws found in prospective studies were the presence of result of interest at the beginning of the study and the lack of proper cohort follow-up. The main flaws found in retrospective studies were the lack of non-response rate.
Assessment of the quality of evidenceThe GRADE score25 was used to assess the 14 studies included in this SR. This score reported low quality of evidence for the mortality variable at the ICU setting (annex, Table 4).
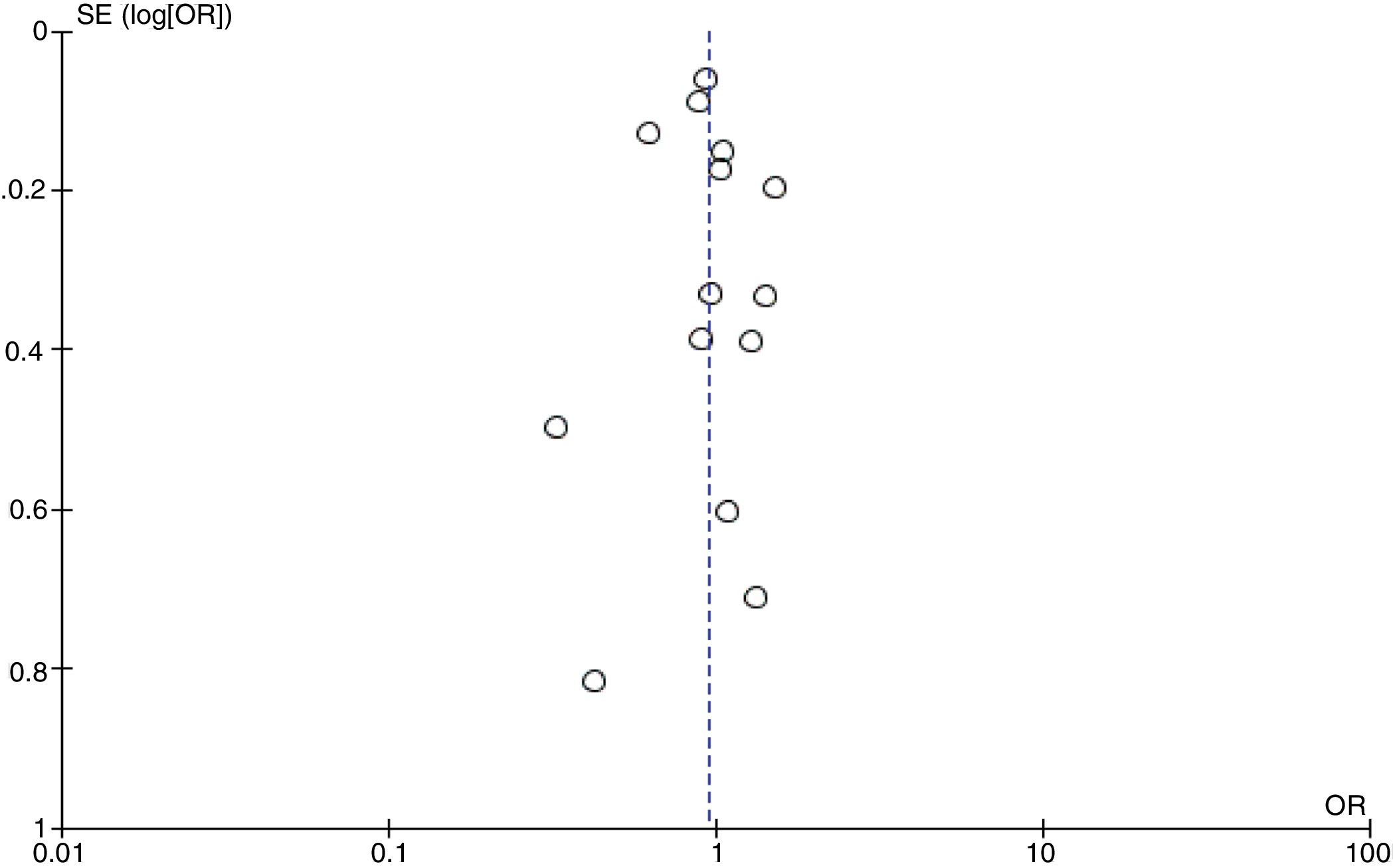
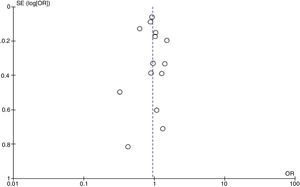
Publication biasThe funnel plot visual inspection assessed mortality at the ICU setting showing no asymmetry (Fig. 6), which was consistent with the results obtained in Begg's test=.956 (P=.35) and Egger's test=.876 (P=.45) without statistically significant differences.
DiscussionThe objective of this study was to describe the correlation between the mortality variable at the ICU setting and obese patients requiring IMV. Unlike the reviewed medical literature, this SR focused exclusively on this critical population and found no statistically significant differences between this subgroup mortality and nonobese subjects.
The lack of a statistically significant association between the obesity variable and mortality at the ICU setting is consistent with the studies conducted by Hogue et al.,14 and Oliveros et al.15 However, these authors did not include in their population subjects requiring IMV only.
Contrary to the findings of this SR, Cai et al. and Pepper et al. reported on the lower mortality rate of obese patients.17,18. If we analyze the results from their studies, we will see statistical heterogeneity added to the fact that not all the patients included received IMV. Similarly, Akinnusi et al. concluded that subjects with grade i and ii obesity also had lower mortality rates maybe due to a probable protective effect.20 However, this conclusion is consistent with the results found on in-hospital mortality and not with ICU mortality (that does not show any statistically significant inter-group differences).
On the other hand, the SR of the study conducted by Falagas et al. reported higher mortality rates in the subgroup of obese patients.16 The authors based their conclusion on the results from 2 out of the 5 studies included. However, this statement is not backed with a meta-analysis.
In our SR, the meta-analysis of time variables could not be conducted for several reasons: lack of registry in certain studies; different methodological designs; different statistical estimators12,31,32,36,37 and incorrect use of these estimators32; and lack of response from the authors contacted, among others.
Regarding the BMI, not all studies categorized it the same way: some conducted data mining26,28 while in others the measurement method35 was not specified or was conducted after IMV.30 We should mention here that only O’Brien et al. took into consideration the patient's dry weight.30 This BMI measurement bias may have impacted our analysis, but we did not have any tools available to limit the effects of this impact.
When conducting the meta-analyse of the mortality variable in the ICU setting from all the studies included, we saw clinical, statistical, and methodological heterogeneity. For this reason, it was decided to conduct a sensitivity analysis excluding retrospective studies to restrict the limitations seen when measuring weight, height, and categorizing BMI. As a result, both groups had the same risk of mortality at the ICU setting.
To reduce clinical heterogeneity, a second sensitivity analysis was conducted and the prospective studies that analyzed the low-body-weight subgroup (BMI<18.5kg/m2) were excluded since evidence shows that this subgroup has higher mortality rates.29 As in the aforementioned analysis, the result showed no differences regarding mortality between obese and nonobese patients receiving IMV in the ICU setting.
As it is the case with other reviews14,17 the Newcastle-Ottawa scale24 was the tool of choice to assess the quality of observational studies.14 However, the lack of rigorous manuals makes the interpretation of this tool by the user a difficult task.38
On the other hand, the quality of evidence was assessed using the GRADE score25 since it is mandatory for new reviews and is applied on nonrandomized trials such as those included in this review. The 14 studies included were analyzed for the main result variable and the quality of evidence found was low.
The quality of evidence of time variables was not assessed using this scale since they were not meta-analyzed.
LimitationsThe subgroup comparison of normal-body-weight subjects (BMI 18.5–24.99kg/m2) versus obese subjects (BMI≥30kg/m2) was not possible because not all primary studies stratified it this way. Also, because the author we contacted over the e-mail did not get back to us.
We could not conduct a meta-regression analysis to assess how mortality behaves in both groups. Also, we did not assess the influence of the variables that may be confounding factors such as age, underlying conditions, reason for IMV or severity of patients at the ICU admission. The problem here was that not all studies described these data and those that described them did it in a different way.
Regarding the tool used to assess the study methodological quality, no recommendation advocates for its reliability or validity. It does not stratify studies based on methodological quality either.
ConclusionThis SR found no correlation between the subgroup of obese adult patients who received IMV and mortality at the ICU setting.
The studies included did not allow us to analyze the demographic and time variables because of the different ways the authors expressed such variables and the low quality of evidence available.
We believe it is essential to achieve consensus in future studies to have a more operative registry of such variables so that the conclusions drawn can be more solid.
Conflict of interestNone of the aforementioned authors declared any conflicts of interest whatsoever.
We wish to thank the Kinesiology Unit and Intensive Therapy Unit at the Hospital General de Agudos Parmenio T. Piñero.
Reference search advisor: Lic. Daniel Comandé.
Please cite this article as: Tocalini P, Vicente A, Amoza RL, García Reid C, Cura AJ, Tozzi WA, et al. Asociación entre obesidad y mortalidad en pacientes adultos que reciben ventilación mecánica invasiva: una revisión sistemática y metaanálisis. Med Intensiva. 2020;44:18–26.