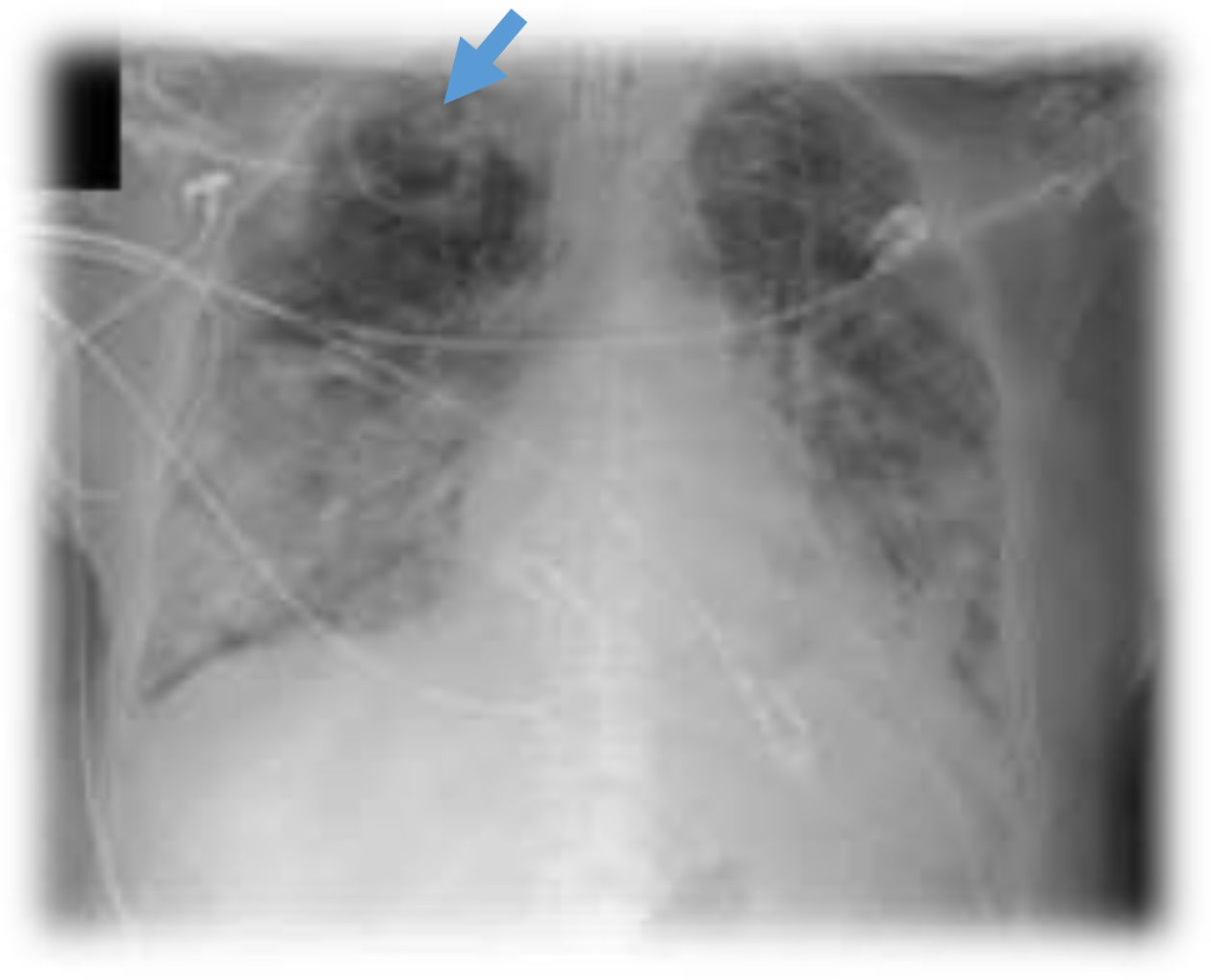
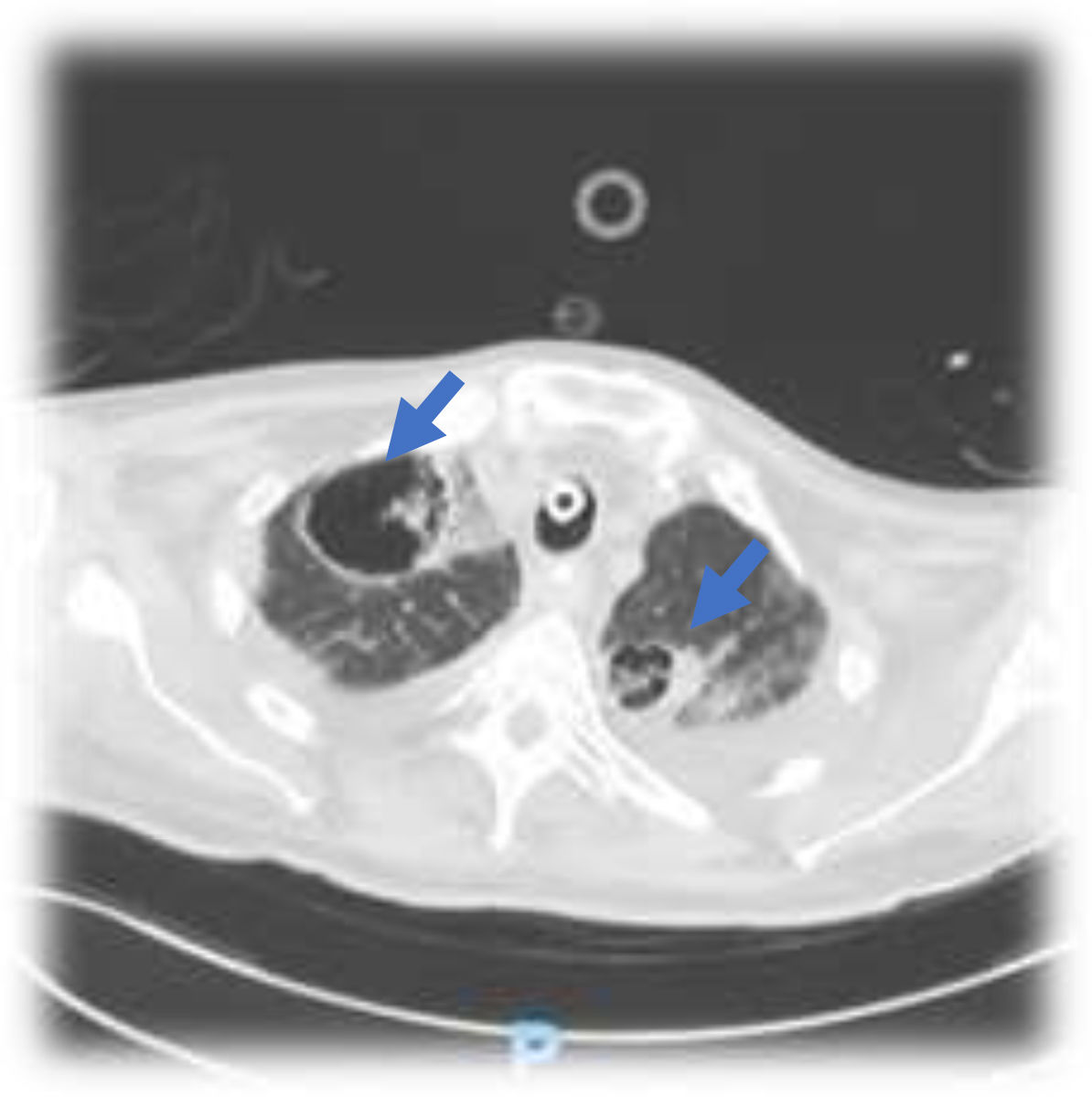
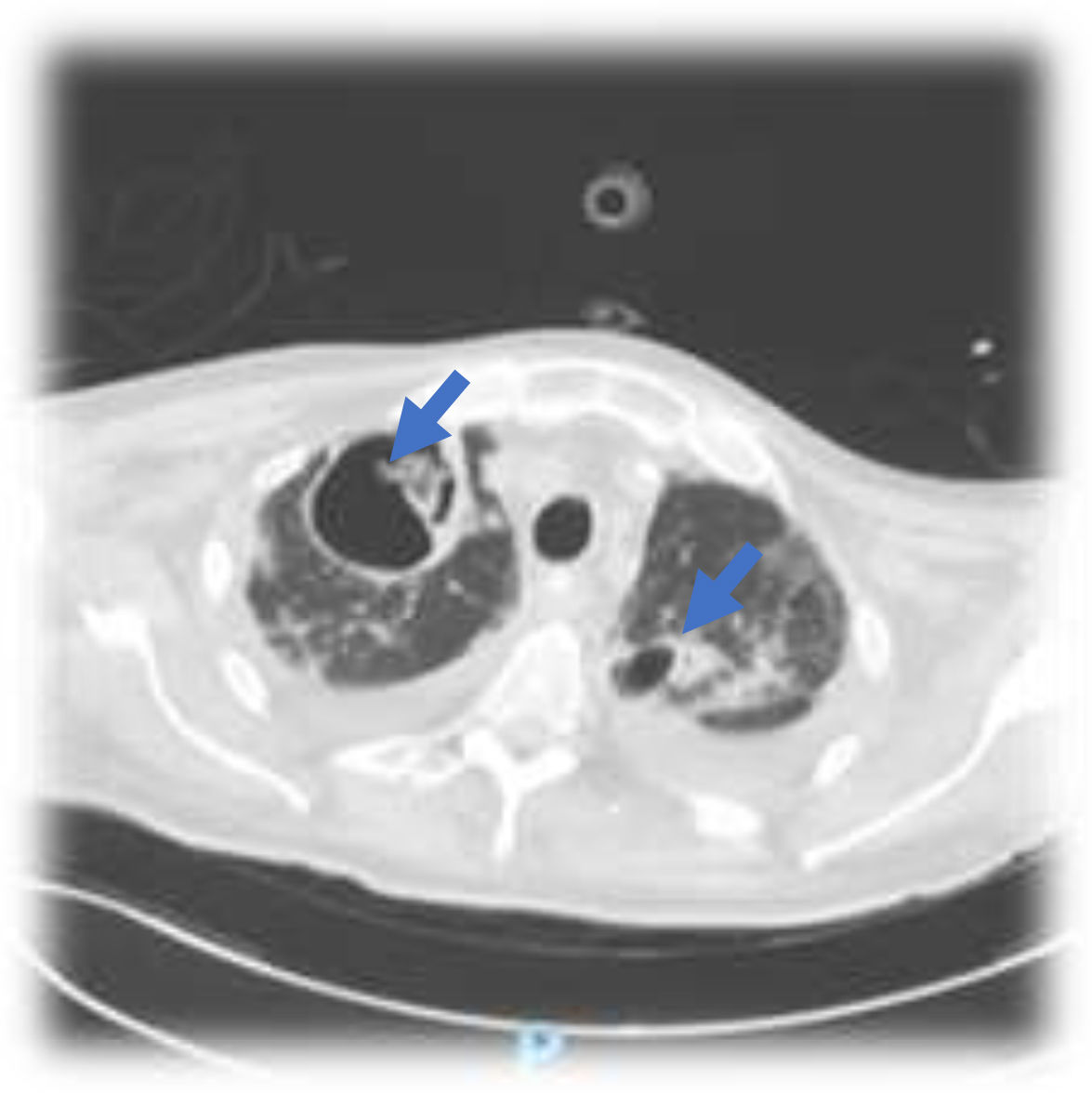
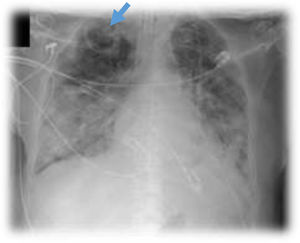
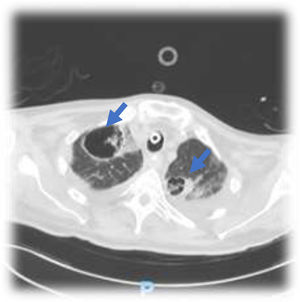
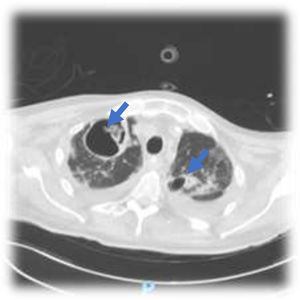
This is the case of a 76-year-old man with a past medical history of anticoagulated AF and mitral prolapse who presents to the hospital with clinical signs consistent with SARS-CoV-2-related pulmonary infection. The patient is diagnosed with bilateral pneumonia with atypical interstitial pattern suggestive of COVID-19 disease.
The patient presented a torpid evolution at the hospital conventional ward with respiratory gradient impairment and need for invasive respiratory support. As part of the medical therapy and with very established selection criteria, interstitial pneumonia with severe respiratory failure was found. The patient was treated with immunosuppressants, tocilizumab, and steroids. The patient showed a bronchial aspirate of Aspergillus fumigatus. The images reveal the presence of cavitatary lesions (aspergillosis) (Figs. 1–3).