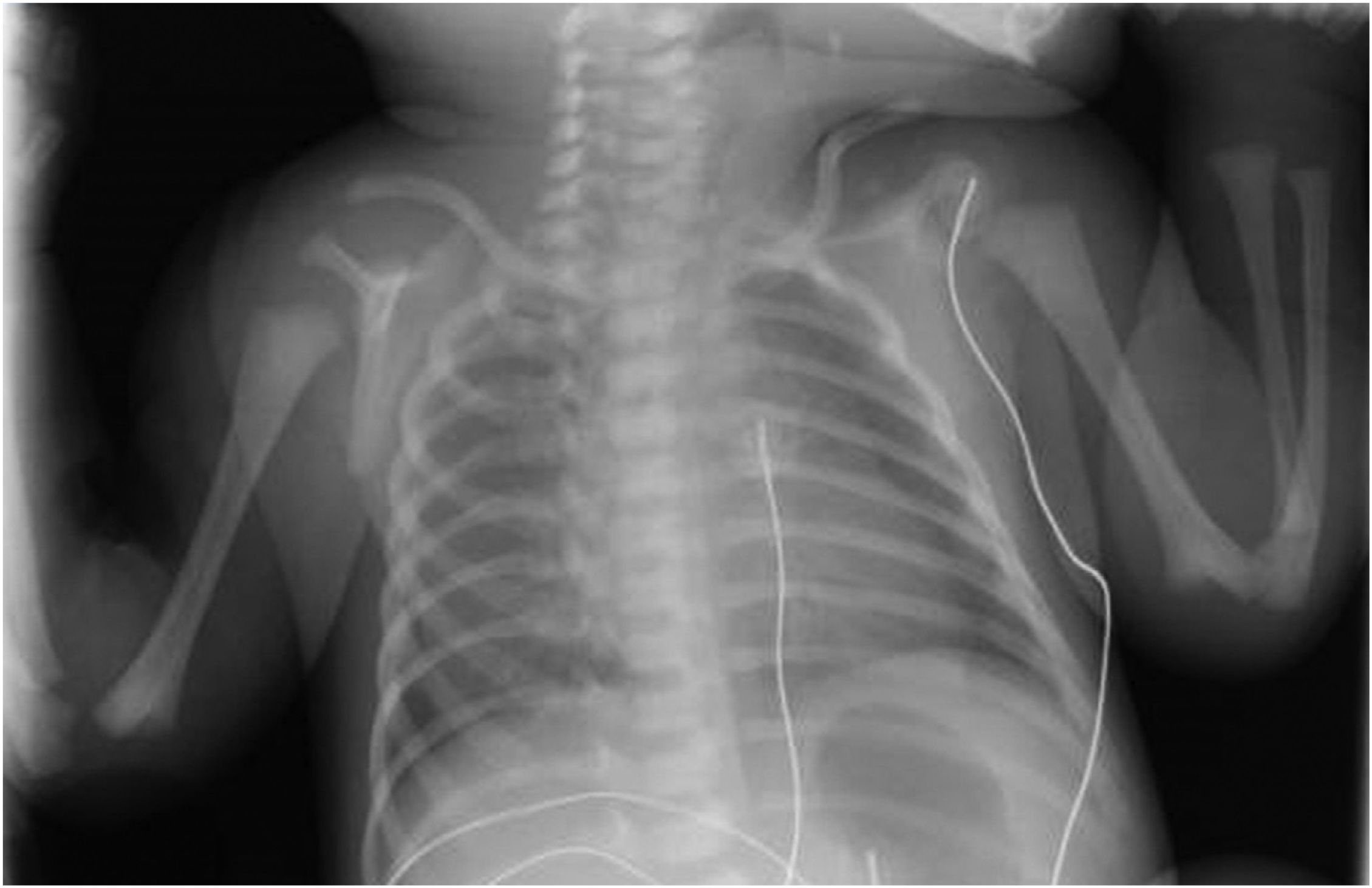
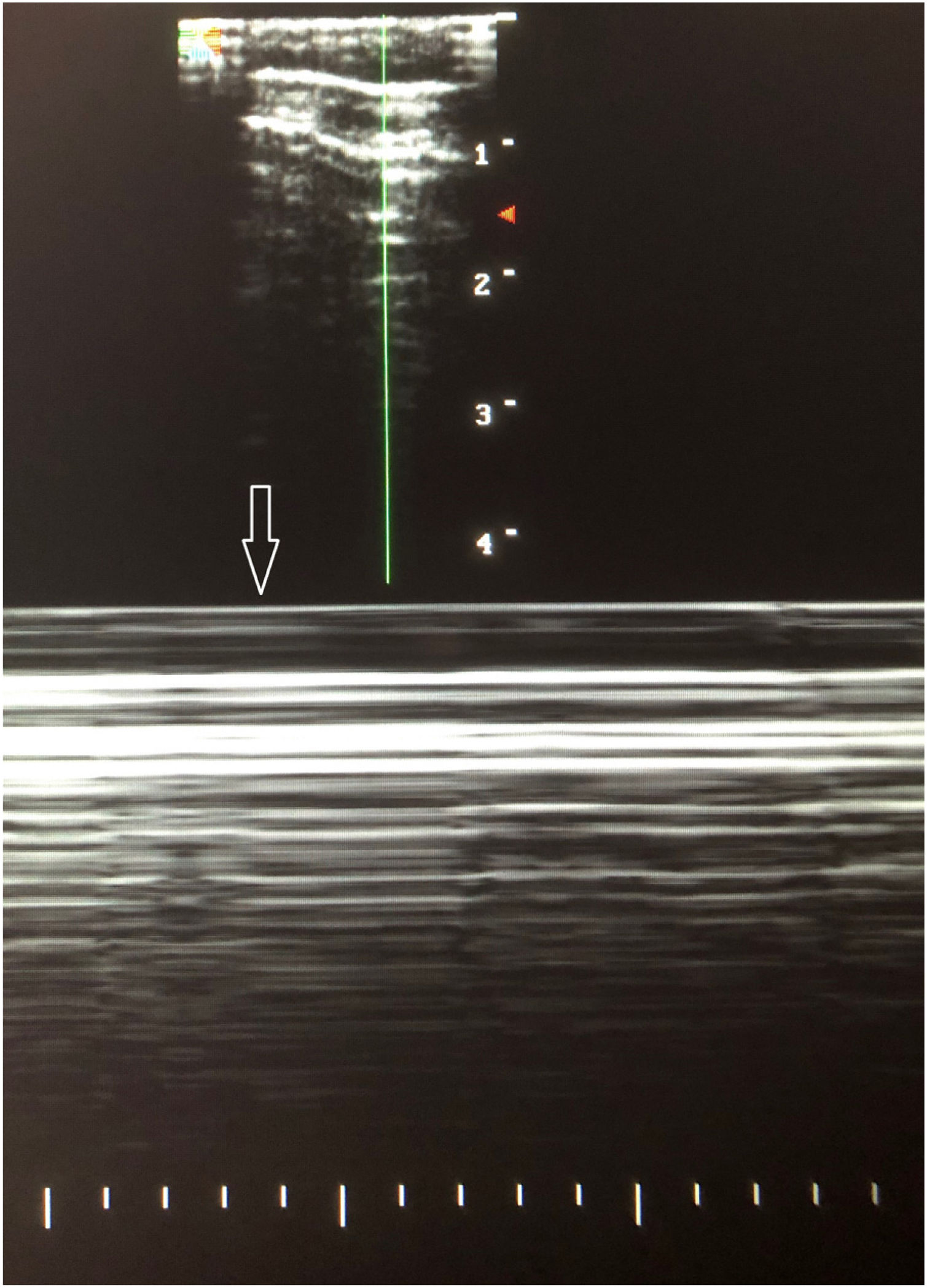
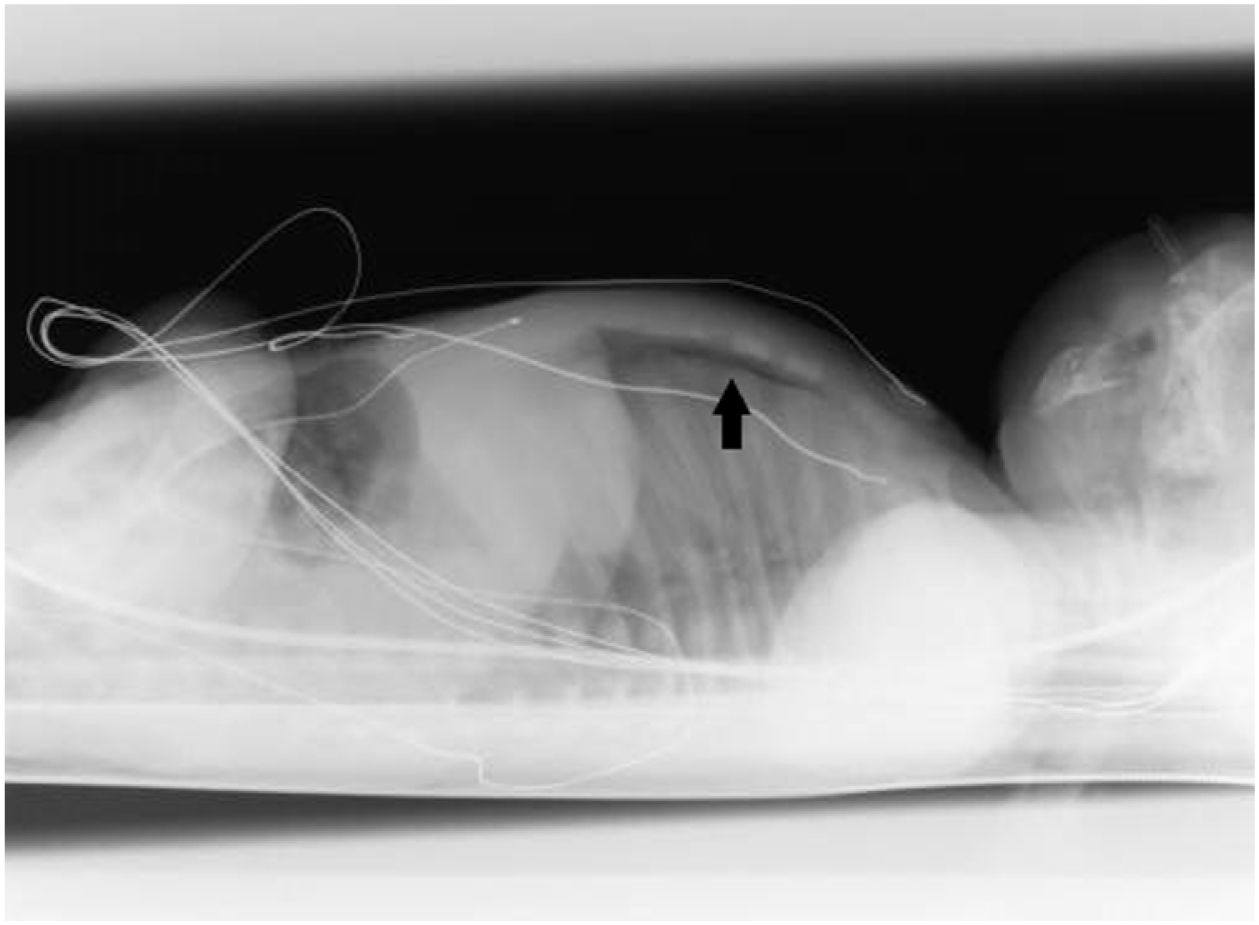
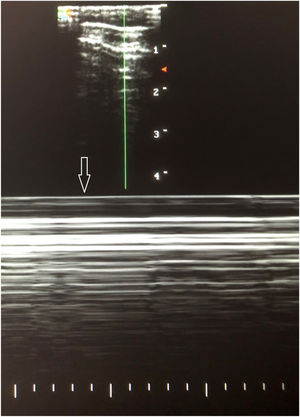
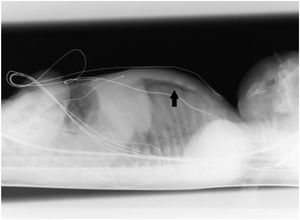
This is the case of a new-born baby who, in his 10th minute of life, starts showing signs of respiratory distress that decreases after admission to the neonatology unit after the administration of oxygen therapy through nasal cannula. Physical examination: bilateral hypoventilation without any other pathological findings. Posterior-anterior chest x-ray is performed without any pathological findings being reported (Fig. 1), which is why it was decided to perform a pulmonary ultrasound that reveals the presence of bilateral anterior pneumothorax (Fig. 2). The ultrasound shows no lung sliding with lung point sign in B mode in the anterior axillary line and the «bar code» or «stratosphere» sign in M mode (arrow) suggestive of no lung sliding. For educational reasons, it was decided to perform a lateral chest x-ray with horizontal beam lateral view, and the finding was confirmed (Fig. 3, black arrow). Patient progression was good and oxygen therapy was removed 2 days after admission. Since then, serial ultrasound follow-ups have been conducted that have confirmed the spontaneous resolution of the disease.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more