The aim of the study was to assess the feasibility and safety of early mobilisation in patients with shock requiring vasoactive drugs in the intensive care unit (ICU).
DesignSystematic review and meta-analysis.
SettingIntensive care unit (ICU).
Patients or participantsAdult patients requiring vasoactive drugs who received early mobilisation in the intensive care unit.
InterventionsA systematic search was conducted using the databases PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Medline Ovid, Science Direct, and CINAHL, including observational studies involving adult patients requiring vasoactive drugs who received early mobilisation. A meta-analysis was performed on the proportion of safety events and the proportion of early mobilisation in patients with high, moderate, and low doses of vasoactive drugs.
Main variables of interestFeasibility, safety events, and the maximum level of activity achieved during early mobilisation.
ResultsThe search yielded 1875 studies, of which 8 were included in the systematic review and 5 in the meta-analysis. The results showed that 64% (95% CI: 34%–95%, p<0.05) of patients were mobilised with low doses of vasoactive drugs, 30% (95% CI: 7%–53%, p<0.05) with moderate doses, and 7% (95% CI: 3%–16%, p 0.17) with high doses. The proportion of adverse events was low, at 2% (95% CI: 1%–4%, p<0.05).
ConclusionsEarly mobilisation in patients with shock and the need for vasoactive drugs is feasible and generally safe. However, there is an emphasis on the need for further high-quality research to confirm these findings.
El objetivo del estudio fue evaluar la viabilidad y seguridad de la movilización temprana en pacientes con shock que requieren drogas vasoactivas en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI).
DiseñoRevisión sistemática y metaanálisis.
ÁmbitoUnidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI).
Pacientes y participantesPacientes adultos que requieren drogas vasoactivas y que recibieron movilización temprana en la unidad de cuidados intensivos.
IntervencionesSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática utilizando las bases de datos PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Medline Ovid, Science Direct y CINAHL, se incluyeron estudios observacionales que involucraban a pacientes adultos que requerían drogas vasoactivas y recibieron movilización temprana. Se realizó un metaanálisis sobre la proporción de eventos de seguridad y la proporción de movilización temprana en pacientes con dosis altas, moderadas y bajas de drogas vasoactivas.
Variables de interés principalesViabilidad, eventos de seguridad y el nivel máximo de actividad alcanzado durante la movilización temprana.
ResultadosLa búsqueda arrojó 1875 estudios, de los cuales 8 fueron incluidos en la revisión sistemática y 5 en el metaanálisis. Los resultados mostraron que el 64% (IC 95%: 34%-95%, p<0.05) de los pacientes fueron movilizados con dosis bajas de drogas vasoactivas, el 30% (IC 95%: 7%-53%, p<0.05) con dosis moderadas y el 7% (IC 95%: 3%-16%, p 0.17) con dosis altas. La proporción de eventos adversos fue baja, del 2% (IC 95%: 1%-4%, p<0.05).
ConclusionesLa movilización temprana en pacientes con shock y necesidad de drogas vasoactivas es viable y generalmente segura. Sin embargo, se enfatiza la necesidad de realizar más investigaciones de alta calidad para confirmar estos hallazgos.
Adult patients admitted to intensive care units (ICU) requiring during long periods invasive ventilatory support, sedation, and neuromuscular blockade will develop neuromuscular, cognitive, and respiratory complications.1 ICU-acquired muscle weakness (ICUAW) is a frequent complication of critical illness, occurring in approximately 50% of ICU patients associated to sedation and prolonged bed rest and is strongly associated with increased morbidity, physical impairment, and short- and long-term mortality.2,3 The consequences of critical illness and therapies administered in the ICU persist beyond hospital discharge and may contribute to poor post-ICU recovery.4–6
Early mobilisation in the ICU appears to be feasible and safe.7–9 The beneficial effects of different early mobilisation strategies are associated with prevention of ICUAW, maintenance of peripheral and respiratory muscle strength, reduction of time on mechanical ventilation and weaning, reduction of ICU and hospital stay, and improvement of patients' quality of life10–13; However, it is important to emphasise that there is significant heterogeneity in the definition of “early mobilization” in different studies.14,15 There is consensus that early mobilisation refers to any form of physical activity within 72hours of ICU admission.14,16,17
Several authors have shown that haemodynamic instability and the use of vasoactive drugs are barriers to the active mobilisation of ICU patients, which can delay the initiation of early mobilization.18–20 Wolfe et al. showed that the use of vasoactive drugs was independently associated with the development of ICU-acquired weakness.21 The aim of this systematic review is to compile the best evidence for the feasibility and safety outcome of early mobilisation in patients with shock and need for vasoactive drugs in the ICU.
MethodsA systematic review was conducted that included prospective and retrospective cohort studies of patient’s ≥18 years with vasoactive drug requirements undergoing early mobilisation in the intensive care unit. The protocol of the systematic review was registered in the CRD42024561501 database of the Prospective International Registry of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), and the systematic review was performed according to the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA).22
The evaluation of methodological quality was performed independently by two investigators; the Newcastle-Ottawa quality assessment scale was used,23 on this scale, scores of seven stars indicate high quality, scores between four and six stars moderate quality, and fewer than four stars poor quality, followed by the kappa coefficient to assess inter-investigator agreement. The certainty of the evidence was evaluated using the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) methodology.24
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with international ethical principles and systematic review guidelines. As it is based on the collection and analysis of data from previously published studies, informed consent from participants was not required. The review was carried out in compliance with research ethics regulations and standards for scientific evidence synthesis.
Eligibility criteriaThis systematic review and meta-analysis included prospective and retrospective cohort studies of ICU patients that analysed early mobilisation and the safety of patients aged ≥18 years receiving any vasoactive drug at any dose in the intensive care unit. The studies had to report the number of sessions conducted with vasoactive drugs, the maximum level of activity achieved, and the safety events associated with early mobilisation (or any of these variables). It was required that the studies be in full text to access the results completely. Studies that included paediatric patients and those that did not include any of the described variables were excluded. There were no restrictions on date or language.
Early mobilisation was defined as any form of physical activity within the first 72hours of ICU admission, including passive mobilisations and the use of assistive technologies such as neuromuscular electrical stimulation.
Search strategyTwo investigators conducted independent systematic literature searches of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Medline Ovid, Science Direct and CINAHL databases published from inception to October 30 2023; discrepancies between the two investigators were resolved with the intervention of a third investigator. The terms “early mobilisation”, “intensive care unit”, “critical illness” “vasoconstrictor agents”, “muscle weakness” “exercise” “physical therapy modalities” and articles in all languages were included, the complete search strategy is described in Supplementary file 1.
Inclusion criteriaProspective or retrospective observational cohort studies analysing early mobilisation or physical rehabilitation and the safety of patients aged ≥18 years receiving any vasoactive drug at any dose in the intensive care unit will be included.
Exclusion criteriaNon-primary studies, those whose unit of analysis was not the patient, case reports, editorials, correspondence and studies that did not report the number of patients who received vasoactive drugs.
Statistical analysisStata 18 software was utilised to conduct a meta-analysis on the proportion of patients undergoing early mobilisation with low, moderate, and high doses of vasoactive drugs, as well as the proportion of reported safety events associated with mobilisation. Confidence intervals of 95% were computed for these proportions. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic, considered present if I2>50%. Random-effects models were employed in cases of heterogeneity; otherwise, a fixed-effects model was applied. Publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots and Begg’s and Egger’s tests.
Data synthesis and extractionA predetermined form was used to extract the following information from the included articles: first author and year of publication, country of the first author, study design, sample size, age, characteristics of included patients, number of patients receiving vasoactive drugs, type and dose of vasoactive drugs, number of mobilisation sessions, maximum level of activity achieved, and safety events.
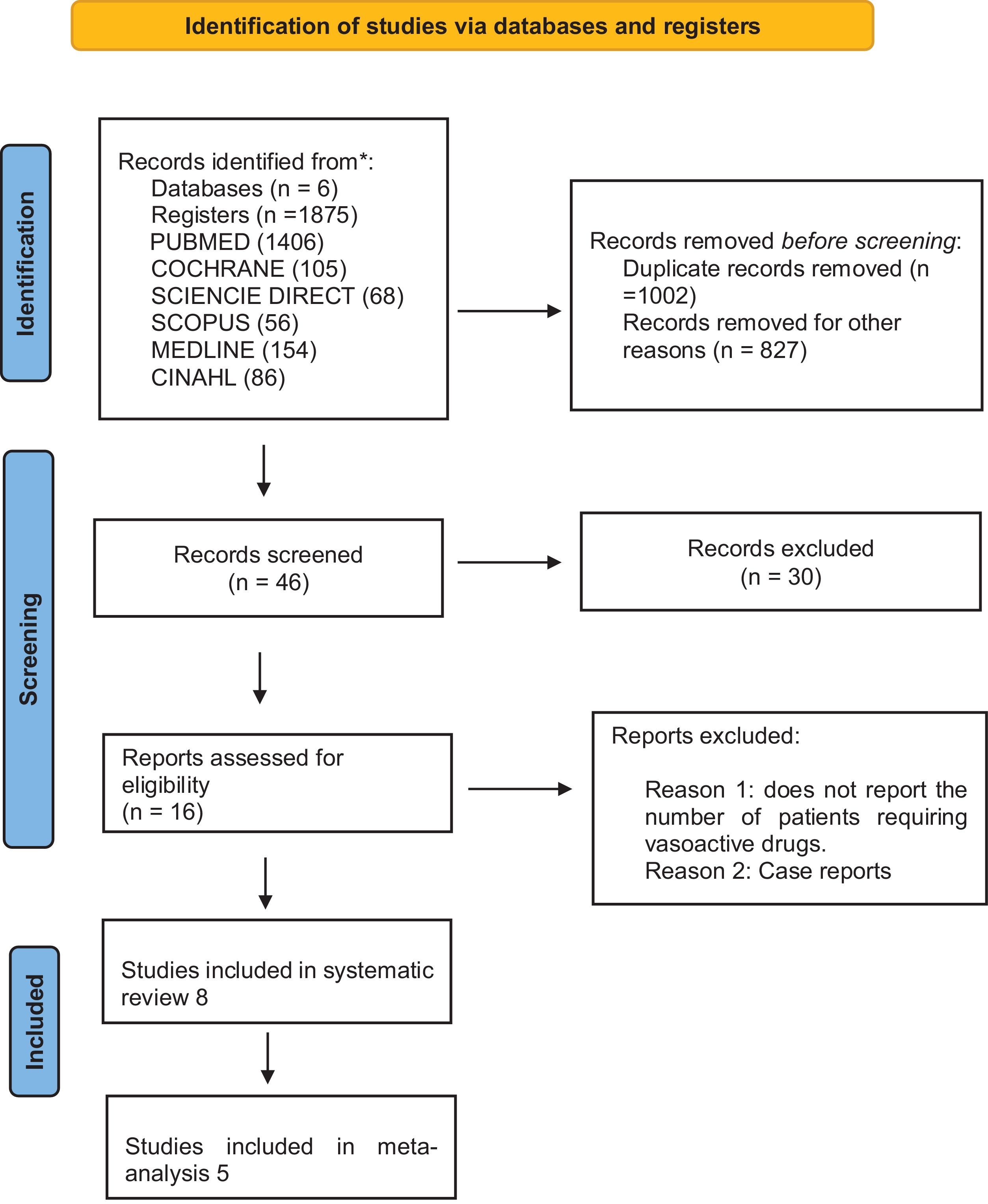
ResultsThe initial search retrieved 1875 articles from seven databases, 1002 duplicates were removed, and 827 articles were excluded based on titles and abstracts, leaving 46 articles; full texts were then reviewed, 30 articles were excluded, and an additional 8 articles were excluded for not reporting the number of patients requiring vasoactive drugs. The systematic review included eight articles, of which five were included in the meta-analysis, totaling 13,143 patients (the detailed PRISMA flow diagram is shown in Fig. 1).
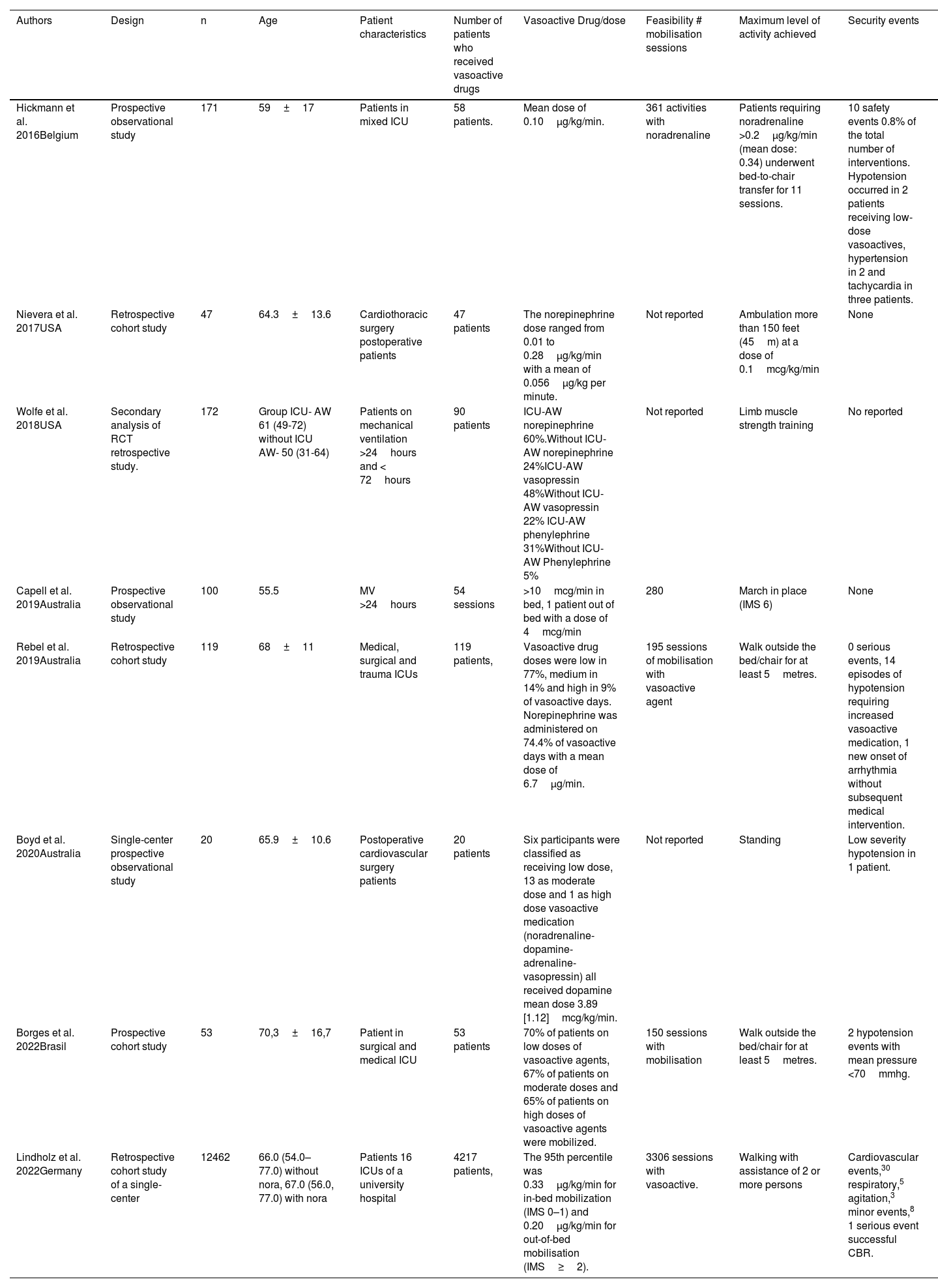
Characteristics of the included studiesThe different characteristics of the studies are listed in Table 1. Four prospective cohort studies,19,25–27 and four retrospective cohort studies21,28–30 were included. The included studies were published between 2016 and 2022 and were conducted in different countries such as Belgium31; USA21,28; Australia19,25,29; Germany30; and Brazil.26 Two studies were performed in postoperative cardiovascular surgery patients25,28; two studies were performed in patients with mechanical ventilation (MV) greater than 24hours19,21; and four studies were performed in mixed ICUs.26,27,29,30 The mean age of study participants was approximately 60+/−3.8 years.
Characteristics of the studies included.
| Authors | Design | n | Age | Patient characteristics | Number of patients who received vasoactive drugs | Vasoactive Drug/dose | Feasibility # mobilisation sessions | Maximum level of activity achieved | Security events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hickmann et al. 2016Belgium | Prospective observational study | 171 | 59±17 | Patients in mixed ICU | 58 patients. | Mean dose of 0.10μg/kg/min. | 361 activities with noradrenaline | Patients requiring noradrenaline >0.2μg/kg/min (mean dose: 0.34) underwent bed-to-chair transfer for 11 sessions. | 10 safety events 0.8% of the total number of interventions. Hypotension occurred in 2 patients receiving low-dose vasoactives, hypertension in 2 and tachycardia in three patients. |
| Nievera et al. 2017USA | Retrospective cohort study | 47 | 64.3±13.6 | Cardiothoracic surgery postoperative patients | 47 patients | The norepinephrine dose ranged from 0.01 to 0.28μg/kg/min with a mean of 0.056μg/kg per minute. | Not reported | Ambulation more than 150 feet (45m) at a dose of 0.1mcg/kg/min | None |
| Wolfe et al. 2018USA | Secondary analysis of RCT retrospective study. | 172 | Group ICU- AW 61 (49-72) without ICU AW- 50 (31-64) | Patients on mechanical ventilation >24hours and < 72hours | 90 patients | ICU-AW norepinephrine 60%.Without ICU-AW norepinephrine 24%ICU-AW vasopressin 48%Without ICU-AW vasopressin 22% ICU-AW phenylephrine 31%Without ICU-AW Phenylephrine 5% | Not reported | Limb muscle strength training | No reported |
| Capell et al. 2019Australia | Prospective observational study | 100 | 55.5 | MV >24hours | 54 sessions | >10mcg/min in bed, 1 patient out of bed with a dose of 4mcg/min | 280 | March in place (IMS 6) | None |
| Rebel et al. 2019Australia | Retrospective cohort study | 119 | 68±11 | Medical, surgical and trauma ICUs | 119 patients, | Vasoactive drug doses were low in 77%, medium in 14% and high in 9% of vasoactive days. Norepinephrine was administered on 74.4% of vasoactive days with a mean dose of 6.7μg/min. | 195 sessions of mobilisation with vasoactive agent | Walk outside the bed/chair for at least 5metres. | 0 serious events, 14 episodes of hypotension requiring increased vasoactive medication, 1 new onset of arrhythmia without subsequent medical intervention. |
| Boyd et al. 2020Australia | Single-center prospective observational study | 20 | 65.9±10.6 | Postoperative cardiovascular surgery patients | 20 patients | Six participants were classified as receiving low dose, 13 as moderate dose and 1 as high dose vasoactive medication (noradrenaline-dopamine-adrenaline-vasopressin) all received dopamine mean dose 3.89 [1.12]mcg/kg/min. | Not reported | Standing | Low severity hypotension in 1 patient. |
| Borges et al. 2022Brasil | Prospective cohort study | 53 | 70,3±16,7 | Patient in surgical and medical ICU | 53 patients | 70% of patients on low doses of vasoactive agents, 67% of patients on moderate doses and 65% of patients on high doses of vasoactive agents were mobilized. | 150 sessions with mobilisation | Walk outside the bed/chair for at least 5metres. | 2 hypotension events with mean pressure <70mmhg. |
| Lindholz et al. 2022Germany | Retrospective cohort study of a single-center | 12462 | 66.0 (54.0– 77.0) without nora, 67.0 (56.0, 77.0) with nora | Patients 16 ICUs of a university hospital | 4217 patients, | The 95th percentile was 0.33μg/kg/min for in-bed mobilization (IMS 0–1) and 0.20μg/kg/min for out-of-bed mobilisation (IMS≥2). | 3306 sessions with vasoactive. | Walking with assistance of 2 or more persons | Cardiovascular events,30 respiratory,5 agitation,3 minor events,8 1 serious event successful CBR. |
MV: Mechanical ventilation; CBR: cardiopulmonary brain resuscitation; MCG/MIN: microgram/minute; μg/kg/min: microgram/kilogram/minute; NORA: noradrenaline; ICUAW: Intensive care unit acquired weakness; IMS: ICU mobility scale; ICU: Intensive Care Unit.
In the included studies, a total of 4604 patients received various vasoactive drugs at different doses, and 4292 sessions of early mobilisation with vasoactive drug infusion were performed. The most commonly used vasoactive drug in the studies was noradrenaline19,21,25–30; additionally, other authors reported the use of vasopressin21,25,26; adrenaline25; phenylephrine21,25; dopamine25; Dobutamine,26 Milrinone.26
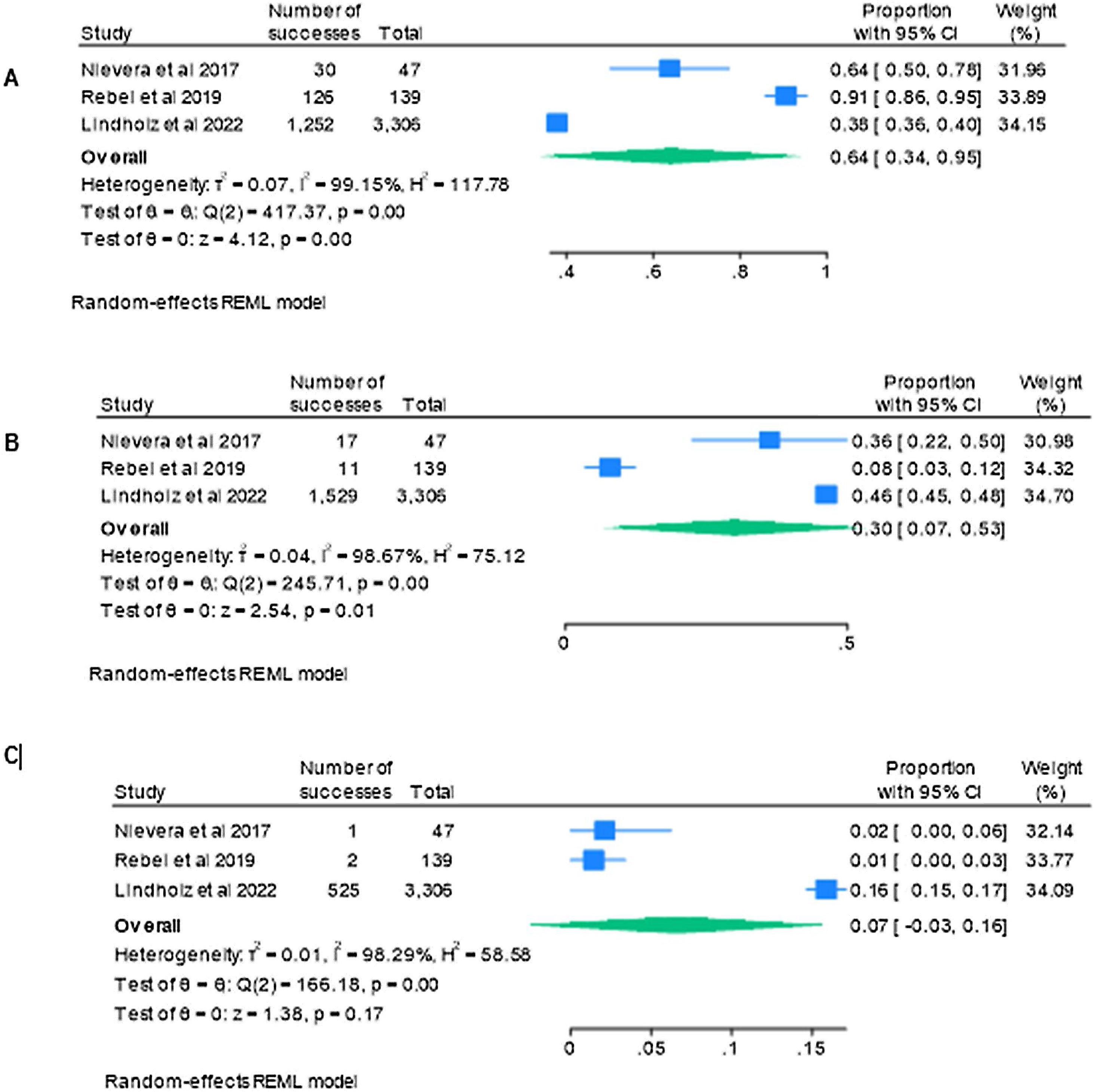
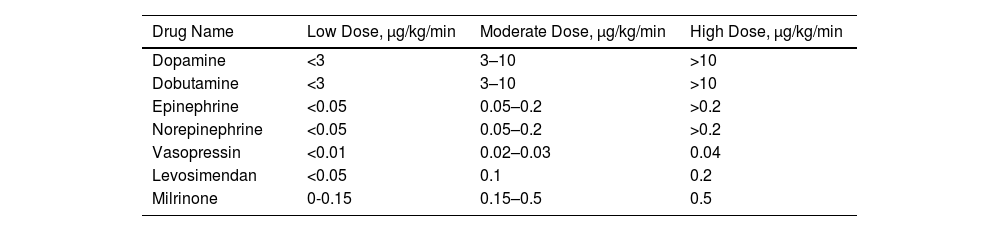
Type of vasoactive drugs and doses usedThree studies reported on early mobilisation performed with different doses of vasoactive drugs.28–30 The proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with low doses of vasoactive drugs was 64% (95% CI 34%–95%) p<0.05 I2 99%; with moderate doses was 30% (95% CI 7%–53%) p<0.05 I2 98%; and with high doses was 7% (95% CI 3%–16%) p 0.17 I2 98% can be seen in Fig. 2. The classification of the most commonly used doses of vasoactive drugs (including inotropics and vasopressors) can be seen in Table 2.
Proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with low, moderate, and high doses of vasoactive drugs.
(A) Proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with low doses. (B) Proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with moderate doses. (B) Proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with high doses.
Vasoactive Drug Dosage Classification From Boyd et al.43
| Drug Name | Low Dose, μg/kg/min | Moderate Dose, μg/kg/min | High Dose, μg/kg/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | <3 | 3–10 | >10 |
| Dobutamine | <3 | 3–10 | >10 |
| Epinephrine | <0.05 | 0.05–0.2 | >0.2 |
| Norepinephrine | <0.05 | 0.05–0.2 | >0.2 |
| Vasopressin | <0.01 | 0.02–0.03 | 0.04 |
| Levosimendan | <0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Milrinone | 0-0.15 | 0.15–0.5 | 0.5 |
μg/kg/min: microgram/kilogram/minute.
All studies included early mobilisation involving exercises assisted by patients. Four studies quantified the level of activity achieved with the ICU mobility scale (IMS).19,26,29,30 In the following studies, the maximum level of activity achieved with vasoactive drug infusion is reported: in the study by Capell et al.,19 the maximum level of activity achieved was exercises out of bed; Nievera et al.,28 achieved active transfer to a chair or ambulation in the first 24 to 72hours after surgery; Boyd et al.,25 performed positional changes and low-level exercises after cardiac surgery; Borges et al.,26 mobilised patients at low intensity (IMS 1 and 2); Wolfe et al.,21 conducted muscle strength training; Hickman et al.,27 reported standing and walking exercises; Rebel et al.,29 reported active mobilisation out of bed, ambulation, and marching in place; finally, Lindholz et al.,30 reported out-of-bed mobilisation as the maximum level of activity achieved.
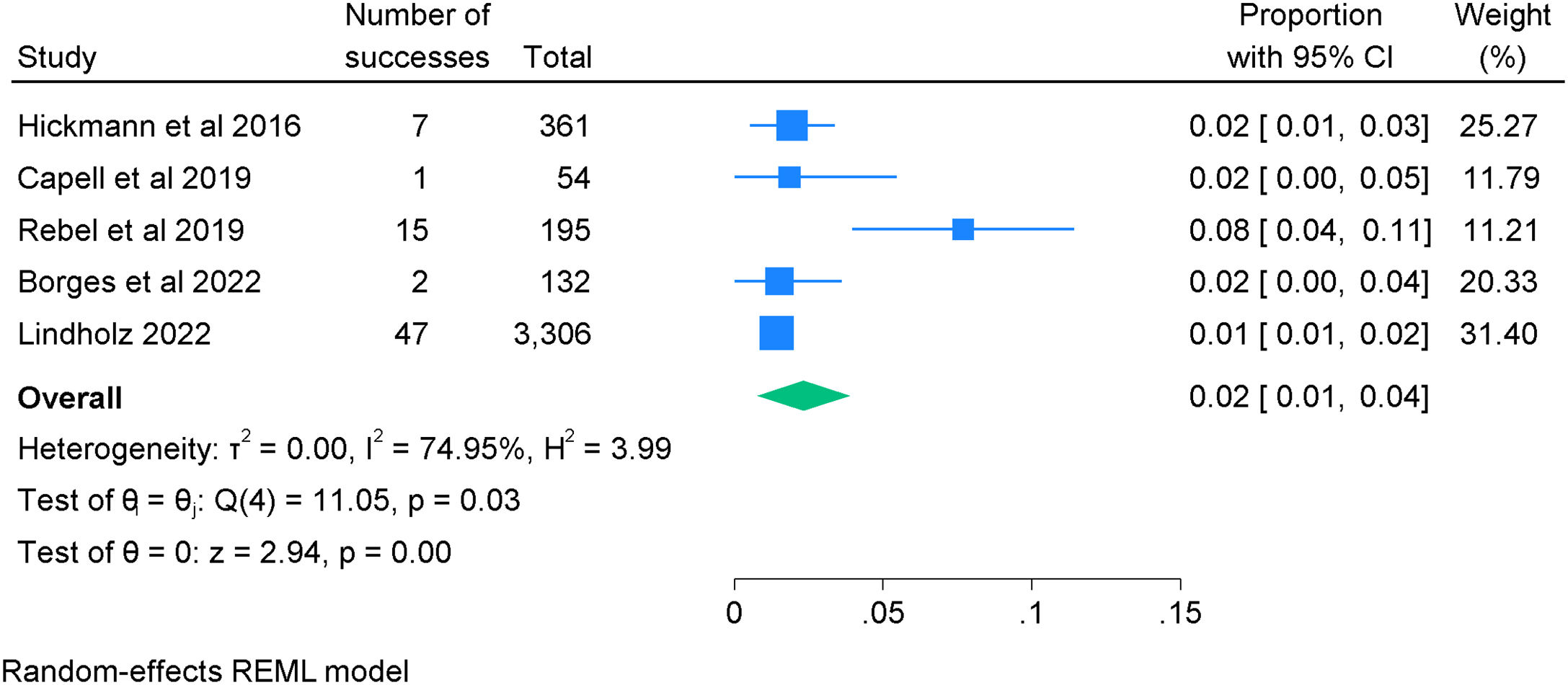
Security eventsFive studies provided information on safety events in patients who underwent early mobilisation with vasoactive drug infusion19,26,27,29,30; The pooled proportion of adverse events from these studies was 2% (95% CI: 1%–4%) p<0.05, I2 74.9% can be seen in Fig. 3. The most reported safety event was hypotension requiring increased vasoactive medications25–27,29,30; arterial hypertension and tachycardia was reported in two studies27,30; arrhythmia without subsequent medical intervention was reported in two studies29,30; In two studies, there were no safety events19,28; and finally, one study reported no safety events.21
Publication biasThere was no significant publication bias in any of the outcomes. The results for publication bias were: proportion of early mobilisation performed in patients with low doses of vasoactive drugs, Egger’s test (p=0.79), Begg’s test (p=1.0); proportion of early mobilisation performed in patients with moderate doses of vasoactive drugs, Egger’s test (p=0.97), Begg’s test (p=1.0); proportion of early mobilisation performed in patients with high doses of vasoactive drugs, Egger’s test (p=0.37), Begg’s test (p=1.0); and proportion of safety events during early mobilisation in patients with vasoactive drug infusion, Egger’s test (p=0.59), Begg’s test (p=0.8). A funnel plot is presented in Additional file.
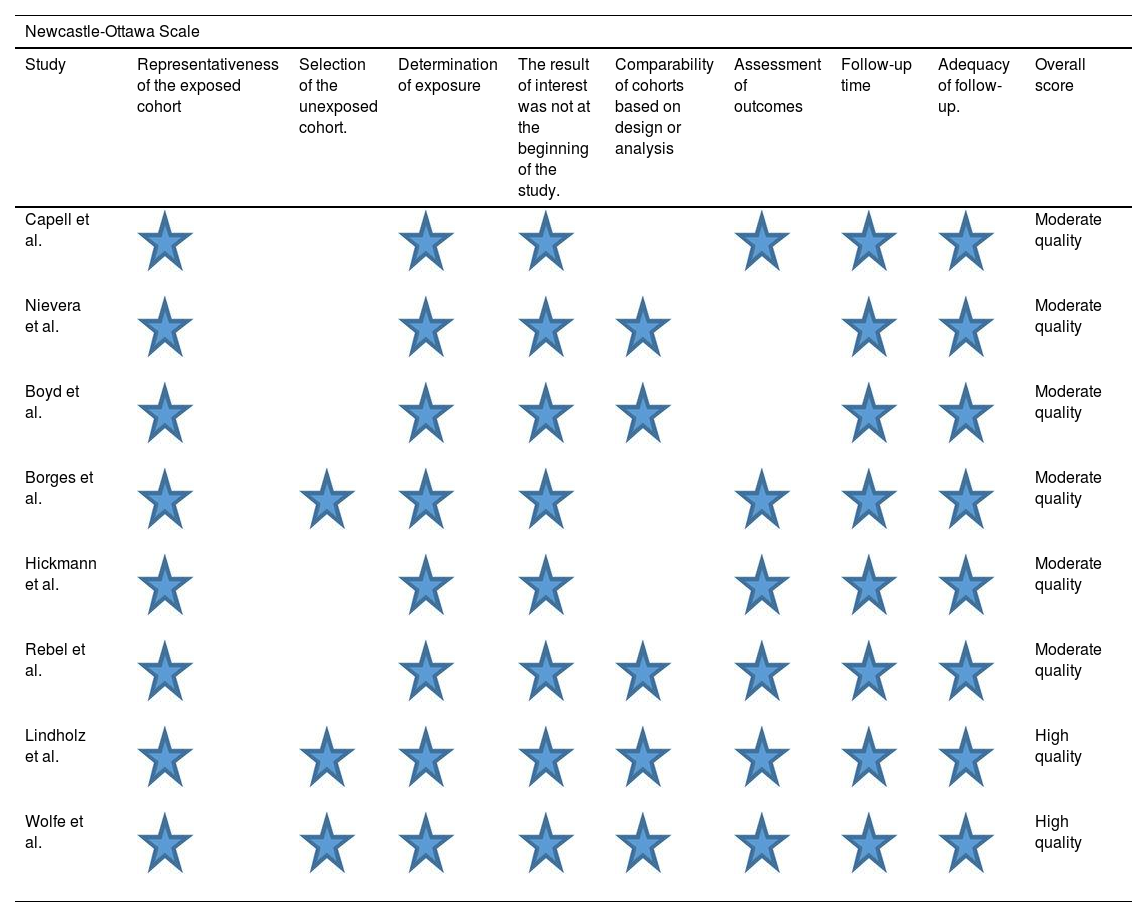
Evaluation of methodological qualityThe results of the quality assessment of the included studies are shown in Table 2. There was agreement among the authors Cohen’s Kappa 0.87 (95% CI 0.74–0.89). There were six studies of moderate quality19,25–29 and two of high quality.21,30 Most studies did not describe the derivation of the unexposed cohort19,25,27–29; in four studies (in some due to their nature) there was no controlled analysis of confounders19,25–27; in two studies there was no clarity on outcome assessment.25,28 Details are described in Table 3. The certainty of the evidence was moderate for the outcomes studied (see Supplementary file).
Results of the quality assessment of the included studies Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
| Newcastle-Ottawa Scale | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Representativeness of the exposed cohort | Selection of the unexposed cohort. | Determination of exposure | The result of interest was not at the beginning of the study. | Comparability of cohorts based on design or analysis | Assessment of outcomes | Follow-up time | Adequacy of follow-up. | Overall score |
| Capell et al. | Moderate quality | ||||||||
| Nievera et al. | Moderate quality | ||||||||
| Boyd et al. | Moderate quality | ||||||||
| Borges et al. | Moderate quality | ||||||||
| Hickmann et al. | Moderate quality | ||||||||
| Rebel et al. | Moderate quality | ||||||||
| Lindholz et al. | High quality | ||||||||
| Wolfe et al. | High quality | ||||||||
Subgroup analyses were conducted for the proportion of safety events and for the proportion of mobilisation in patients with low, moderate, and high-dose vasoactive drug infusion, excluding studies that could cause heterogeneity using the leave-one-out strategy. After excluding the study by Rebel et al.,29 a decrease in the proportion of safety events to 1% (95% CI 1%–2%) was observed p<0.05, and a decrease in heterogeneity to I2 0%. The subgroup analysis for the proportion of mobilisation in patients with low, moderate, and high-dose vasoactive drug infusion did not show a reduction in heterogeneity (see Supplementary file).
DiscussionThis systematic review included 8 studies with a total of 13,143 patients, demonstrating that early mobilisation in most patients with shock requiring vasoactive drugs can be feasible and safe, with a low proportion of safety events, provided that a strict assessment of each patient and their haemodynamic status is carried out to individualise interventions. However, the dosing of vasoactive drugs and the maximum level of activity achieved in relation to dosing are unclear. It is relevant to note that 6 studies are of moderate methodological quality, and the measured outcomes show significant heterogeneity.
Shock is a pathological state that results when the circulation is unable to deliver sufficient oxygen and nutrients to the cells and tissues. The resulting hypoxia, tissue hypoperfusion and cellular dysfunction can lead to multi-organ failure; if this is not treated in a timely and appropriate manner, it can lead to death.31,32 The first step in managing shock is the optimisation of the volume status, along with the restoration of mean arterial pressure (MAP) and organ perfusion.33 The use of catecholamines is considered the cornerstone of hemodynamic treatment of shock; this therapeutic class includes dopamine, epinephrine, noradrenaline and phenylephrine.34 Norepinephrine is the first choice followed by vasopressin or epinephrine in critically ill patients.35 In the included studies, noradrenaline was the most commonly used vasoactive agent in patients undergoing early mobilisation. The included studies do not clearly describe the type of shock presented in the patients; however, they highlight the initial hemodynamic assessment that allows early mobilisation to be initiated in patients receiving vasoactive drugs.
Only one systematic review has been published in recent years,35 which concluded that mobilisation of ICU patients receiving vasoactive drugs appears to be safe, and current studies do not indicate serious safety events associated with mobilisation. Our research included 3 new articles, allowing us to increase the number of patients studied to 13,143 and 4,294 mobilisation sessions with vasoactive drugs; additionally, it is the first study to conduct a meta-analysis of the proportion of safety events and the proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with low, moderate, and high doses of vasoactive drugs. Consistent with the previous study, we demonstrate that early mobilisation in patients with shock and vasoactive drugs can be feasible and safe, provided there is adequate assessment to individualise the intervention.
In contrast to our findings, some studies evidenced that hemodynamic instability and the use of vasoactive drugs were an important barrier to early mobilization.18,36,37
The relationship between the dose of vasoactive drugs and the level of mobility achieved could not be precisely determined due to the heterogeneity of the doses reported in some studies and the lack of information in others. Lindholz et al.,30 concluded that doses of up to 0.20mcg/kg/min for out-of-bed mobilisation (IMS≥2) and doses of up to 0.33mcg/kg/min for in-bed mobilisation (IMS 0–1) appear to be safe; however, given the retrospective nature of the study these findings cannot be generalized; additionally, Rebel et al.29 concluded that patients who received low levels of vasoactive drugs were more likely to mobilise; contrary to this, in another study the authors described that no significant relationship was found between the dose of norepinephrine and the level of activity achieved28; additionally Boyd et al.,25 was able to demonstrate that low level exercise in patients after cardiac surgery who received vasoactive drugs was well tolerated with a low incidence of adverse events and caused significant increases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) by improving cardiac output.
This study shows that the proportion of patients who underwent early mobilisation with the infusion of vasoactive drugs decreased as the dose of vasoactive drugs increased. The proportion decreased from 64% of patients mobilised with low doses to 30% with moderate doses, and to 7% with high doses. This demonstrates that the dosage of vasoactive drugs can be a barrier to mobilisation in the ICU.
The incidence of safety events in patients who underwent early mobilisation and received vasoactive drugs reported in the various included studies was low, and most were of low severity25–27,29,30; the proportion summarised in the meta-analysis was 2%, in agreement with a recent study that evidenced mobilisation in the ICU was associated with less than a 3% likelihood of an adverse event occurring.38 Contrary to these findings, a recent study reported that 61.5% of patients in the early mobilisation group received vasoactive drugs and the incidence of safety events potentially due to mobilisation was 9.2%, concluding that the intervention was associated with safety events.39 It is important to mention that we did not find unified definitions regarding the severity of safety events (serious and minor) in the studies included in this review.
A consensus of 23 experts on safety recommendations for active mobilisation in adults on mechanical ventilation described that it is relevant to perform a rigorous and individualized assessment of the patient’s clinical conditions, the absolute dose of vasoactive drug and the dose change during mobilisation, concluding that the implementation of these recommendations has the potential to maximize early mobilisation and at the same time minimize the risk of adverse safety events; however, there was no consensus regarding the dose of vasoactive drugs (and the combination of these drugs) that would allow safe mobilisation in the ICU.40 Additionally, several authors conclude that vasoactive infusions or mechanical ventilation are not barriers to initiating rehabilitation/mobilisation, provided that patients remain stable with the use of these therapies.41
The duration time of early mobilisation (daily and total) reported in the included studies was very heterogeneous, in agreement with other reviews where they report that such heterogeneity was mainly in the duration and frequency of individual interventions; additionally, the optimal dose for mobilisation remains uncertain.42 This aspect is of great importance in patients receiving vasoactive drugs since the time of intervention could be a determinant of the patient's hemodynamic changes.
We can identify in the limitations of this study the potential biases that each of the studies included in this review may contain, as no randomised trials were included, the heterogeneity found in the meta-analysis results, the low number of studies, and the absence of a common reference value for the dose of vasoactive drugs for safe mobilisation and the highest level of mobility achieved. Among the strengths of this study is the methodological rigor applied in formulating search strategies, selecting studies, data entry, and data analysis, which contributes to the accuracy and reliability of the findings.
The results of this study have implications for clinical practice, as the included studies encompassed a wide variety of patients with diverse characteristics who underwent early mobilisation and received vasoactive drug infusions at different doses. This study is significant because it suggests that early mobilisation in patients receiving vasoactive drugs could be feasible and appears to be safe, provided that a thorough assessment of the patient’s haemodynamic status is conducted to minimise the risk of adverse events associated with the intervention. In this way, the rehabilitation of patients in the ICU is facilitated, and the impacts of ICU-acquired weakness are mitigated. However, given the heterogeneity found in the outcomes measured in the meta-analysis and the quality of some articles, the results should be interpreted with caution.
ConclusionsEarly mobilisation in patients with shock and the need for vasoactive drugs is feasible and appears safe in critically ill ICU patients; however, the reference value of vasoactive drug dosage for safe mobilisation in and out of bed is unclear, more studies of high methodological quality are needed to support the reported findings.
CRediT authorship contribution statementHenry Mauricio Parada-Gereda, Daniel Molano Franco, Joan Ramon Masclans, and Luis Fernando Pardo contributed substantially to the conception and design, data collection, and data analysis and interpretation. Henry Mauricio Parada-Gereda, Daniel Molano Franco, Joan Ramon Masclans, Janneth Milena Avendaño and Luis Fernando Pardo participated in drafting the manuscript or critically reviewed it for important intellectual content. Henry Mauricio Parada-Gereda, Daniel Molano Franco, Joan Ramon Masclans, Janneth Milena Avendaño and Luis Fernando Pardo gave final approval of the version to be published. Each author participated sufficiently in the work to assume public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ informationThe first author of this work is Henry Mauricio Parada-Gereda.
FundingNone.
None.