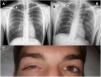
A 27-year-old man was admitted for a first episode of spontaneous apical right pneumothorax (chest X-ray, Fig. 1A). The patient reported no relevant medical history except cannabis use. We inserted an 8.5 French pigtail catheter in the pleural space (Monaldi position). No adverse events occurred during pleural drainage (local anesthesia). Chest X-ray assessed the correct chest tube position and complete lung re-expansion (Fig. 1B). 24&#¿;h after chest drain insertion, the patient presented ipsilateral palpebral ptosis with enophthalmos and myosis occurred (Fig. 1C): a pathognomonic triad defines Horner’s syndrome. A brain and cervical magnetic resonance angiography and a chest computed tomography did not reveal any lesion to explain Horner’s syndrome. The right pleural drain was removed as soon as pulmonary re-expansion. At hospital discharge, the patient suffered from persistent right myosis and ptosis.
Exceptional Horner’s syndrome cases could occur after a central or peripheral sympathetic pathway lesion (stellate ganglion) due to a chest tube.