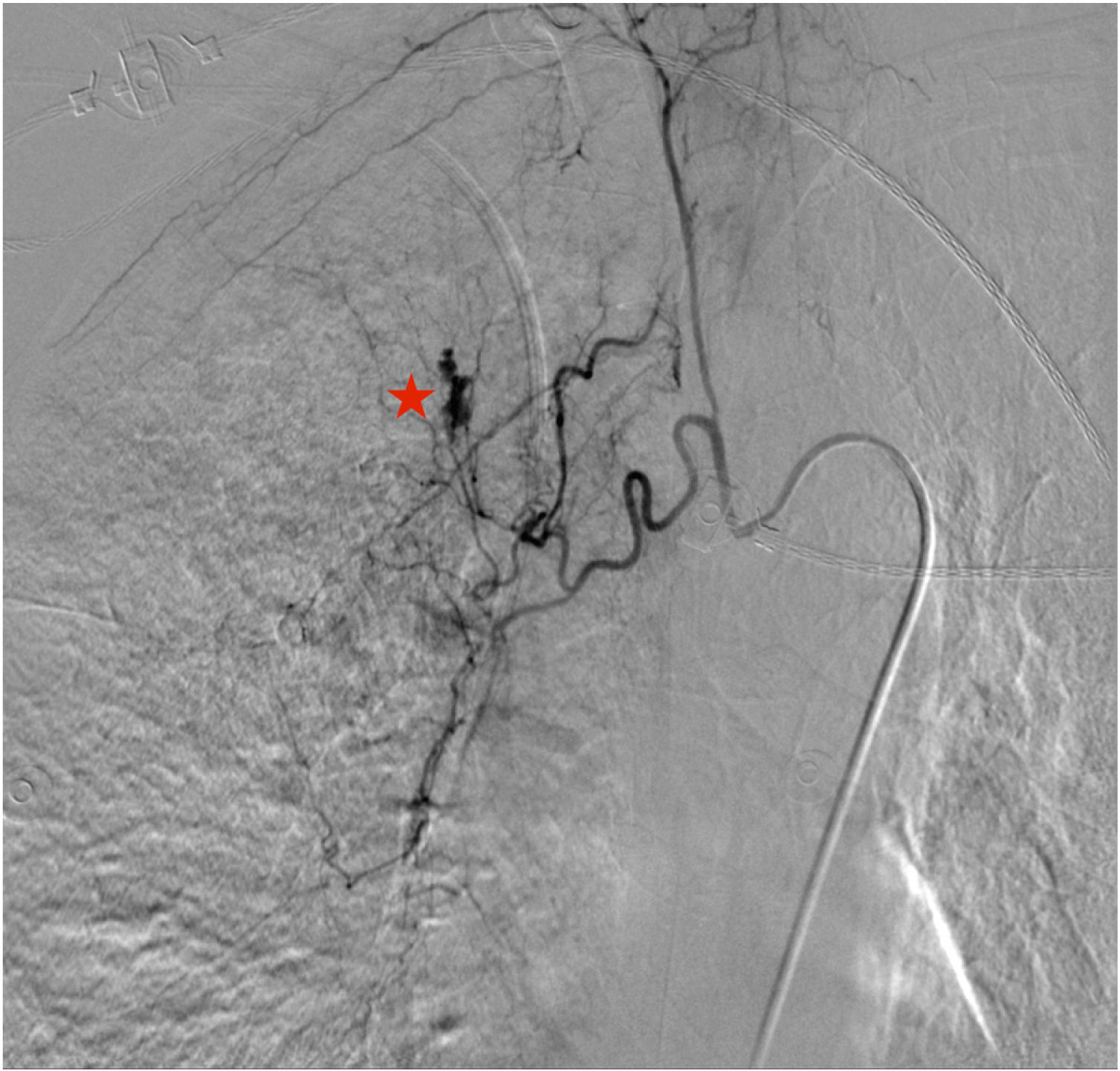
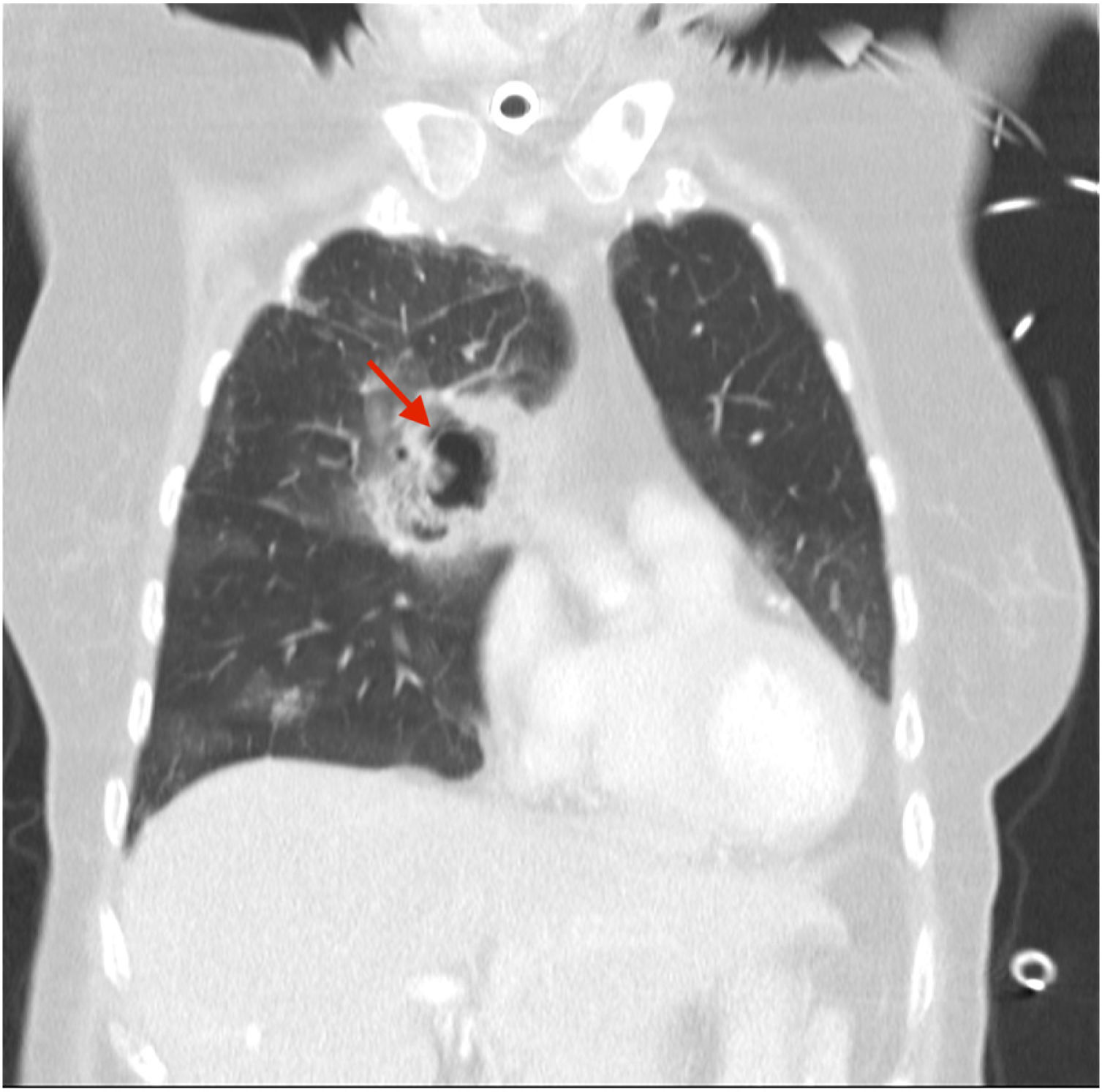
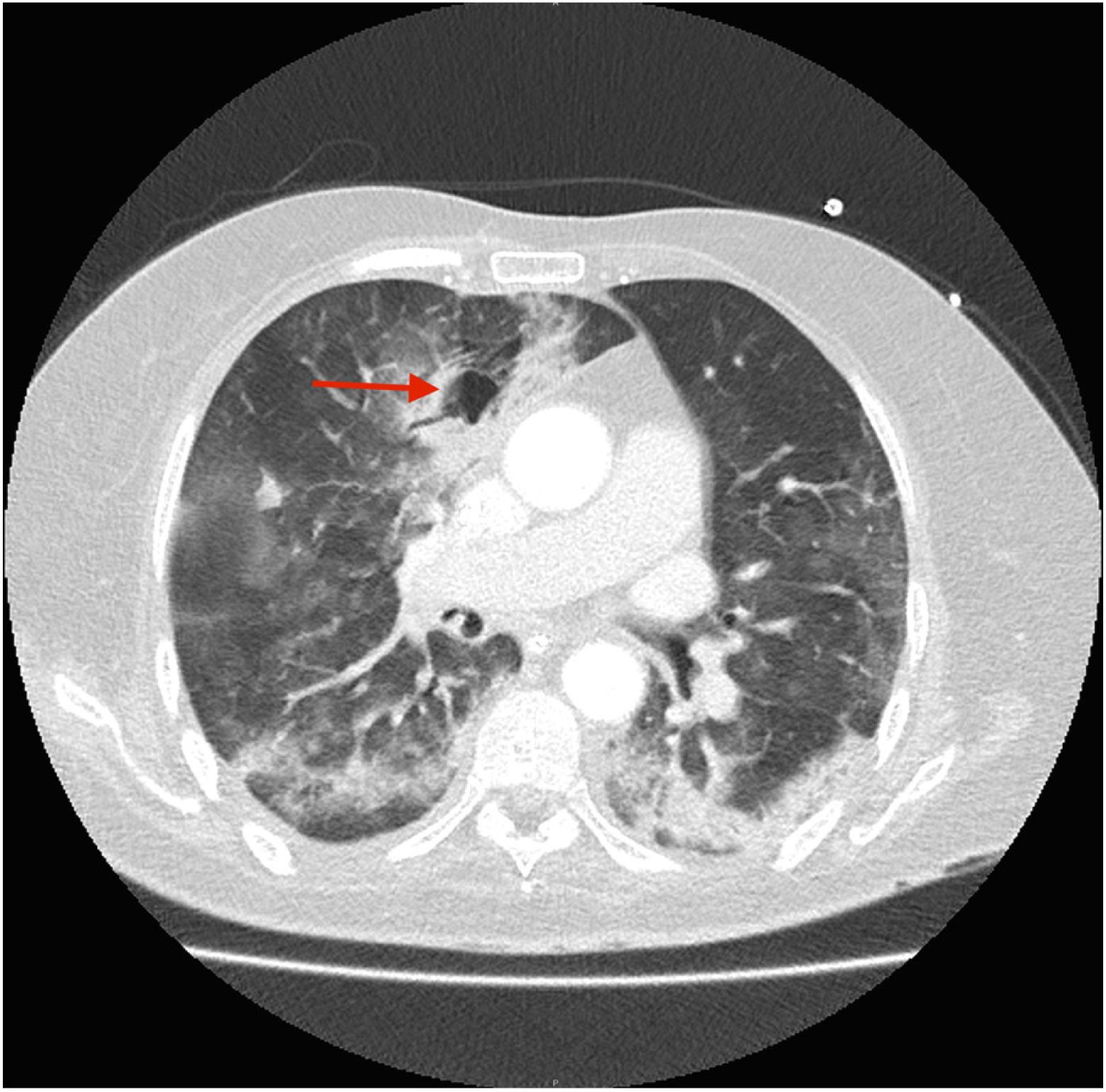
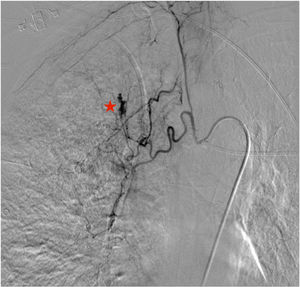
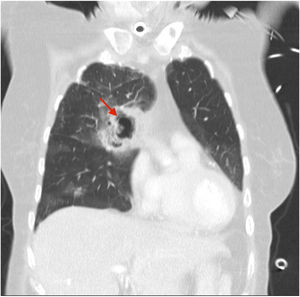
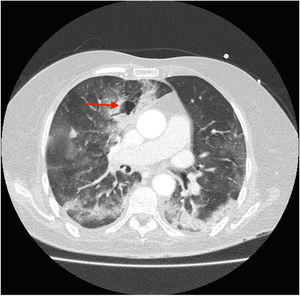
A 70-year-old woman was admitted to our intensive care unit due to COVID-19 pneumonia. She received treatment with remdesivir for five days, two doses of tocilizumab and methylprednisolone (1mg/kg/day). Patient required intubation and tracheostomy due to myopathy. After nineteen days, patient presented a massive hemoptysis. An urgent bronchoscopy evidenced a non-occlusive clot in the right main bronchus and a pulsatile lesion underneath. The pulmonary artery angiography showed a pseudoaneurysm in a right intercostobronchial trunk (Fig. 1) with extravasation of iodinated contrast (red star). Immediate transcatheter exclusion of the pseudoaneurysm was successful. The thoracic CT-scan evidenced the typical COVID-19 pattern with a highly suspicious aspergillus cavity (red arrow) in the right upper lobe pulmonary parenchyma (Figs. 2 and 3). Respiratory secretions cultures were positive for Aspergillus niger so dual antifungal treatment was started. This case illustrates the risk of COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) and related complications.
FundingThis work has not received any type of funding.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.