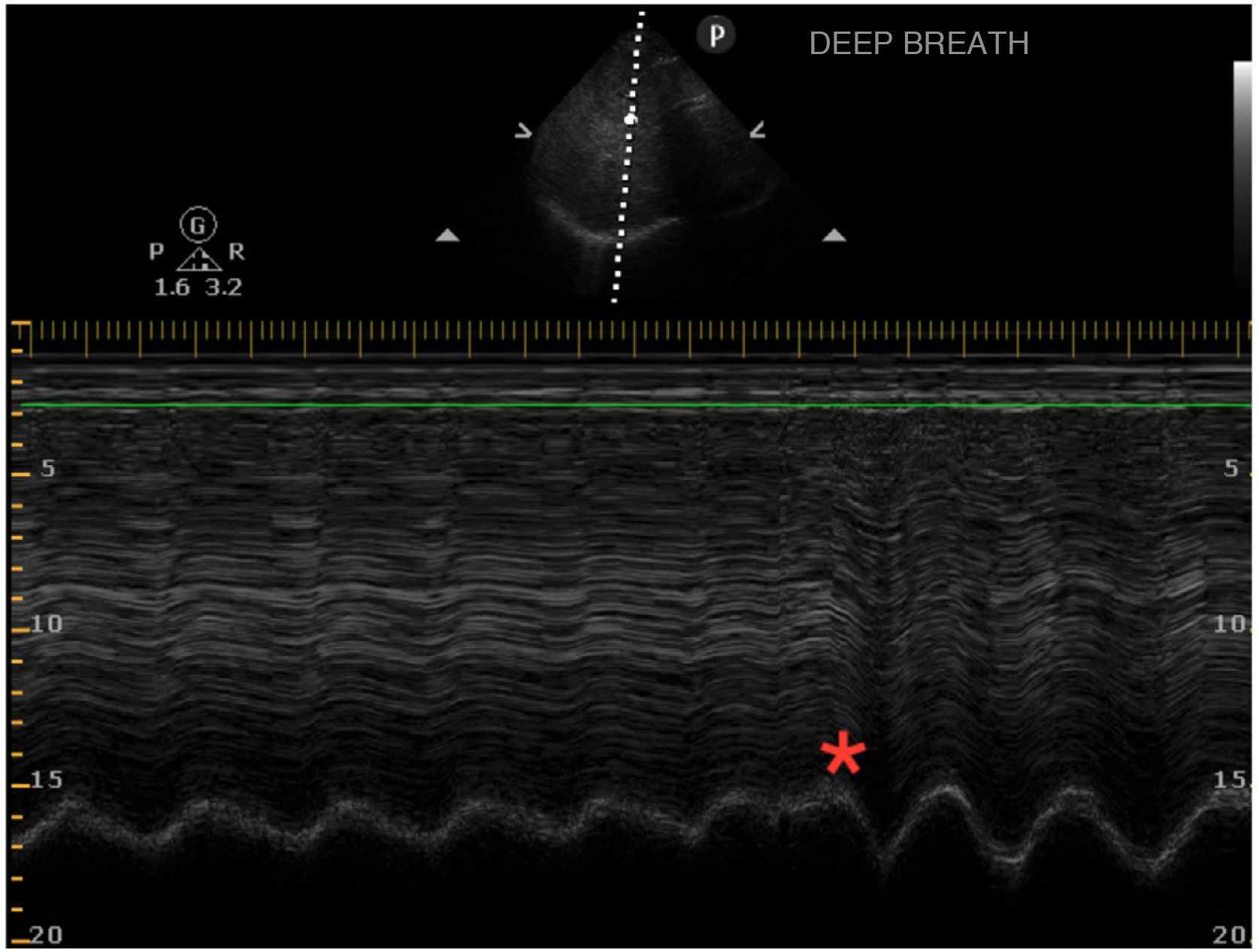
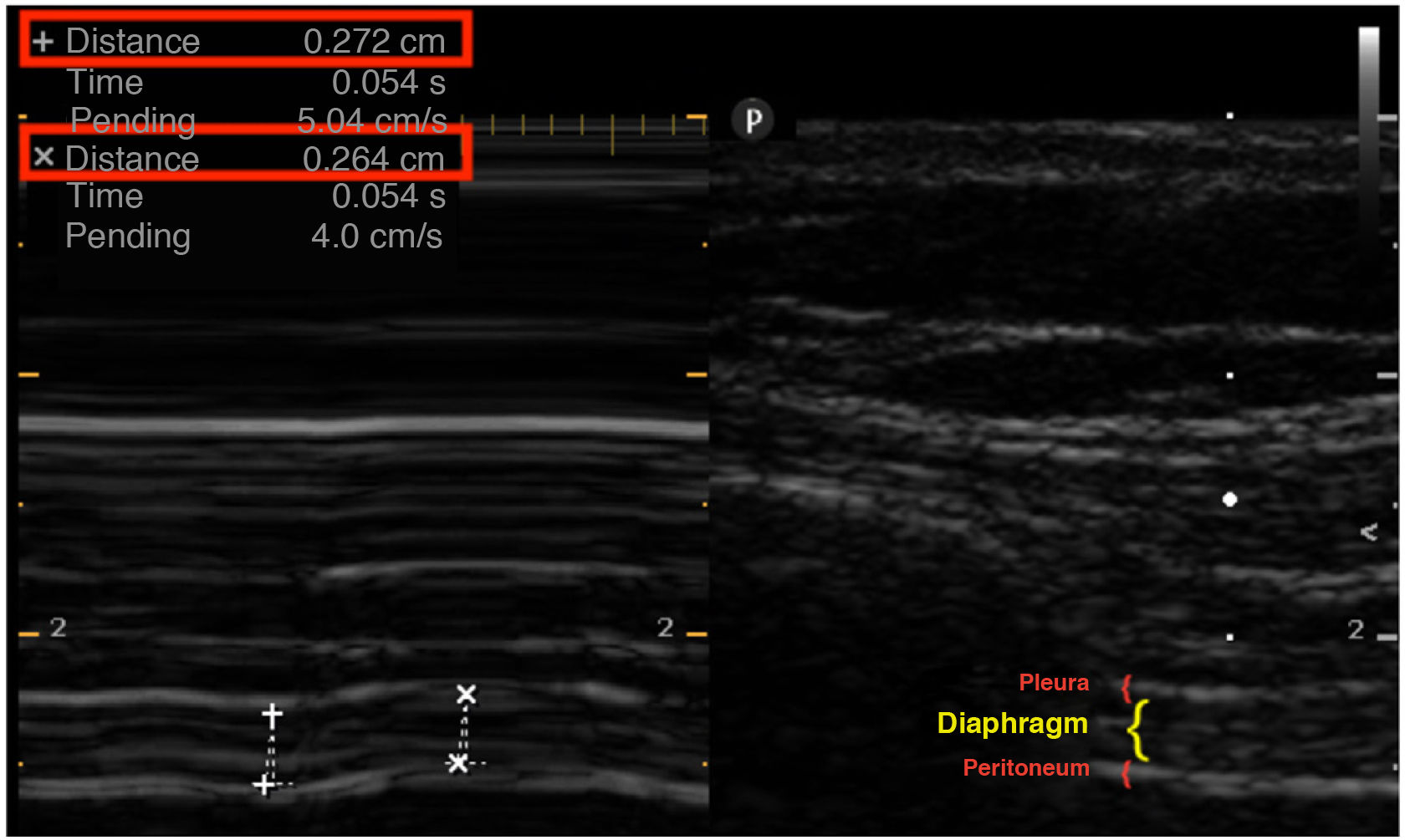
This is the case of a 66-year-old man admitted to the ICU due to COVID-19 after high-flow nasal oxygen failure at the conventional hospital ward setting. Non-invasive support (non-invasive ventilation) is initiated with the following parameters: BiPAP mode with IPAP of 12, EPAP of 9, and a FiO2 of 100% with a tidal volume of approximately 350−450 mL (6.25−8 mL/kg of ideal weight) with respiratory rate dropping from 30 to 23 breaths/min. The diaphragmatic ultrasound performed at admission reveals the presence of a regular diaphragmatic excursion of 2 cm. The patient is asked to take a deep breath (*). Inverted diaphragm motion occurs that triggers the use of accessory muscles. M mode is used. Diaphragmatic thickening of only 3% is reported. Nor the pressure or the volume change dramatically. Twenty-four hours later, failed later non-invasive ventilation is confirmed followed by the need for intubation. Figs. 1 and 2.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more