Edited by: Juan Antonio Llompart-Pou - Specialist in Intensive Care Medicine, Doctorate in Health Sciences, Universitat Illes Balears. Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Trauma and Neurocritical ICU, Hospital Universitari Son Espases. Palma, Spain
Last update: November 2025
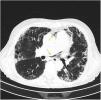
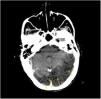
More infoA 72-year-old woman with chronic cough due to severe interstitial lung disease and fibrosis was found in a coma upon awakening. Glasgow Coma Scale score: 3. Gaze deviation to the left. Generalized hypotonia. Anisocoric pupils with right-sided mydriasis. Thoracic CT scan: small left apical pneumothorax and presence of ectopic air in the upper mediastinum (arrows) (Fig. 1). Brain CT scan: presence of numerous air bubbles located in the cerebral sulci (arrows), and cortico-subcortical hypodense areas distributed in bilateral parieto-occipital regions (Fig. 2). An intrapulmonary shunt would be mechanism involved that could explain our case (for the lack of a patent foramen ovale). A sudden increase of intrathoracic pressure due to Valsalva maneuvers, along with the development of pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum in a pathological lung could facilitate the passage of air into the pulmonary veins and from there into the left circulatory system causing cerebral air embolisms.
Ethical considerationsThe patient’s prior written informed consent was obtained to be authorized to use the images in full compliance with the center regulations.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.
FundingNone declared.