Oversedation has adverse effects on critically ill patients. The Analgosedation and Delirium Committee of the FEPIMCTI (Pan-American and Iberian Federation of Critical Care Medicine and Intensive Care) conducted a cross-sectional study through a survey addressed to ICU physicians: PANDEMIC (Pan-American and Iberian Study on the Management of Analgosedation and Delirium in Critical Care [fepImCti]).
HypothesisWorsening of these practices in the course of the pandemic and that continued afterwards, with further oversedation.
ObjectivesPerception of analgosedation and delirium practices in Pan-American and Iberian ICUs before, during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, and factors associated with persistent oversedation after the pandemic.
Of the 1008 respondents, 25% perceived oversedation after the pandemic (95%CI 22.4–27.8). This perception was higher in South America (35.8%, P < .001). Main risk factor: habit acquired during the pandemic (adjusted OR [aOR] 3.16, 95%CI 2.24–4.45, P < .001). Main protective factor: delirium monitoring before the pandemic (aOR 0.70, 95%CI 0.50−0.98, P = .038).
The factors identified in this study provide a basis for targeting future interventions.
La sobresedación tiene consecuencias negativas en pacientes críticos. Desde el Comité de Analgosedación y Delirium de la FEPIMCTI (Federación Panamericana e Ibérica de Medicina Crítica y Terapia Intensiva) diseñamos estudio transversal mediante encuesta dirigida a médicos/as de UCI: PANDEMIC [estudio Panamericano e Ibérico sobre manejo de ANalgosedación y DEliriuM en Cuidados Críticos (fepImCti)].
HipótesisEmpeoramiento de dichas prácticas durante la pandemia que persistieron tras ella, con mayor sobresedación.
ObjetivosPercepción de prácticas de analgosedación y delirium en las UCI de la región Panamericana e Ibérica, antes, durante y después de la pandemia COVID-19 y factores asociados a persistencia sobresedación post-pandemia.
De los 1008 encuestados, 25% informó percepción de sobresedación tras la pandemia (IC95% 22.4%–27.8%), mayor en Sudamérica (35.8%, P < .001). Principal factor riesgo: hábito adquirido durante la pandemia (OR ajustado [aOR] 3.16, IC95% 2.24–4.45, P < .001). Principal factor protector: monitorización delirium (aOR 0.70, IC95% 0.50−0.98, P = .038) previo a la pandemia.
Estos factores identificados en el estudio ofrecen una base para dirigir intervenciones futuras.
Sedation is a common practice in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), though its overuse (doses higher than those needed by the patient) leads to oversedation with adverse effects such as increase duration of mechanical ventilation (MV), prolonged ICU stay, and delirium.1,2 To minimize these adverse effects, the eCASH (early Comfort using Analgesia, minimal Sedatives and maximal Humane care) approach emphasizes early patient comfort, minimizing sedative use and promoting humane care.3–5 The goal is to keep the patient awake, to minimize sedation and keep it as short as possible, and to avoid the use of benzodiazepines to improve the outcomes in the ICU.6–8 Campaigns have been proposed to prevent oversedation in the ICU, to ensure patient comfort without compromising safety, and to improve the efficiency of bed management.2
Chamorro et al. recommended not to “turn off the brain” unless absolutely necessary, and for the shortest time possible, to avoid oversedation and its adverse effects.9 A decrease in brain activity can alter neurotransmitter balance, increasing neuronal apoptosis and cerebral inflammation, which in turn can induce patient delirium and cognitive impairment. Thus, objective monitoring of the level of sedation is essential in patients requiring deep sedation.
Deep sedation is a risk factor for the development of delirium during hospital admission.10 Delirium, characterized by acute and fluctuating alterations in consciousness and the thinking process, is a common problem in the ICU, affecting up to 80% of all patients undergoing MV.11–13 It is associated with a number of adverse effects including a prolongation of MV, increased mortality, long-term cognitive impairment, and an increased risk of functional disability.14 Furthermore, patients who have received infusions of sedatives and opioids for prolonged periods are at a risk for iatrogenic withdrawal syndrome in the ICU and its associated problems.15
Against this background, the analgosedation and delirium guidelines of the American Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and the Pan-American and Iberian Federation of Critical Care Medicine and Intensive Care (FEPIMCTI) provide recommendations for the optimal management of analgosedation and delirium in critically ill patients.16,17 The ABCDEF bundle of measures, developed by the SCCM (A: Assess, prevent and manage pain; B: Withdraw sedation and perform spontaneous breathing tests; C: Choice of analgesia and sedation; D: Assess, prevent and manage delirium; E: Early mobility and exercise; F: Family engagement and empowerment), provides an operational framework for implementing such recommendations, with ample evidence of their positive impact upon the outcomes of critical patients.18,19 Despite the familiarity of these measures, their adoption is limited, and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further complicated their implementation, with a negative impact upon analgosedation practices.20–25
Based on the hypothesis that there was a worsening of these practices during the pandemic, with increased oversedation, and that such poor practices persisted after the pandemic, the present study was conducted to assess ICU physician’s perceptions of analgosedation and delirium practices in the Pan-American and Iberian setting before, during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, and to identify the factors associated with persistent oversedation after the pandemic.
Patients and methodsStudy designA cross-sectional observational study involving a survey administered to physicians working in an adult ICU was conducted. An ad hoc questionnaire was developed for the study (see the Supplementary material).
The questionnaire was published online in a private password-protected server with access restricted to the principal investigators (Microsoft™ Forms; see Supplementary material).
Survey target populationThe survey was targeted to healthcare professionals working in the adult ICUs of the region at the time of the study and also during the pandemic.
Distribution of the survey and invitation to participateThe invitation to participate was made iteratively through the online dissemination channels of the FEPIMCTI and its member societies, with the collaboration of the national coordinators. The survey was distributed by e-mail with the attached electronic link to the Microsoft™ Forms platform.
Sample sizeThe literature on sedation practices during the COVID-19 pandemic is limited. According to some reports and a previous study, it was estimated that the study would require 864 participants.26,27 This sample size provided a 1.5% power with a two-sided 95% confidence interval to detect an estimated 10% incidence of perceived poorer sedation practices following the COVID-19 pandemic. The decision was made to increase the sample size by 15% (total of 1000 participants) to compensate for potential data loss.
Analytical strategyA descriptive analysis was used to characterize the study sample by calculating the mean, standard deviation (SD), median and frequency. The 95% confidence interval (95%CI) was calculated for point estimates. Statistical significance was considered for P < .05. The inferential analysis in turn was based on the Student t-test and Mann-Whitney U test for the comparison of means, and the Fisher exact test for qualitative variables. The odds ratio (OR) was estimated to assess associations including the 95%CI. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify the relevant explanatory variables and control for confounding factors. Variables showing potential associations (P < .15) were entered in the multivariate model. The diagnostic ability was estimated from the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and goodness of fit was calculated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow statistic. The analyses were performed using the STATA® version 16.1 statistical package (StataCorp LP, 1996–2020).
Ethical particularsThe present study was evaluated and approved by the Red Municipal de Bioética Clínica y Social of the city of Córdoba (Argentina) and complies with the National Law on Personal Data Protection 25.326 (Republic of Argentina) for safeguarding the identity and data of the participants, and guaranteeing complete anonymity and confidentiality of the information. Informed consent was obtained from all the participants after receiving an explanation of the aims of the study and the time required to complete it.
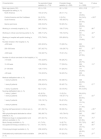
ResultsSociodemographic characteristics of the participants and study sitesSociodemographic data are presented in Table 1, and the distribution of countries to which the participants belonged is shown in Fig. 1, in order of perceived persistence of oversedation after the pandemic. This perception was greater among the professionals working in South America (35.8%), followed by the Iberian Peninsula (19.3%) and North America (15.5%).
Sociodemographic characteristics of the study participants and centers.
| Characteristics | No persistent deep sedation (n = 719) | Persistent deep sedation (n = 252) | Total (n = 1008) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years, SD) | 43.3 ± 10.8 | 42.1 ± 10.8 | 43.0 ± 10.8 | .17 1 |
| Geographical setting (n, %) | ||||
| North America | 153 (21.3%) | 28 (11.1%) | 181 (18.6%) | |
| Central America and the Caribbean | 24 (3.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 24 (2.4%) | <.0012 |
| South America | 296 (41.2%) | 165 (65.5%) | 461 (47.5%) | |
| Iberian peninsula | 246 (34.2%) | 59 (23.4%) | 342 (33.9%) | |
| Working in university hospital (n, %) | 547 (78.6%) | 190 (77.9%) | 737 (78.4%) | .86 2 |
| Working in critical care training center (n, %) | 396 (71.2%) | 155 (74.5%) | 551 (72.1%) | .42 2 |
| Working in hospital with public funding (n, %) | 572 (79.6%) | 203 (80.6%) | 775 (79.8%) | .79 2 |
| Number of beds in the hospital (n, %) | ||||
| <200 beds | 220 (20.6%) | 73 (29.0%) | 293 (30.2%) | |
| 200–500 beds | 307 (42.7%) | 100 (39.7%) | 407 (41.9%) | .37 2 |
| >500 beds | 192 (26.7%) | 79 (31.4%) | 271 (27.9%) | |
| Number of critical care beds in the hospital (n, %) | ||||
| <10 beds | 164 (22.8%) | 66 (26.2%) | 230 (23.7%) | |
| 10−20 beds | 279 (38.8%) | 77 (30.6%) | 356 (36.7%) | .13 2 |
| 21–30 beds | 126 (17.5%) | 51 (20.2%) | 177 (18.2%) | |
| >30 beds | 150 (20.9%) | 58 (23.0%) | 208 (21.4%) | |
| Medical staff/patient ratio (n, %) | ||||
| 1 every 4 patients | 258 (46.4%) | 80 (38.5%) | 338 (44.2%) | |
| 1 every 8 patients | 236 (42.4%) | 95 (45.7%) | 331 (43.3%) | .07 2 |
| 1 every 12 patients | 62 (11.2%) | 33 (15.9%) | 95 (12.4%) | |
| Nursing staff/patient ratio (n, %) | ||||
| 1 every 1 patient | 45 (6.3%) | 13 (5.2%) | 58 (6.0%) | |
| 1 every 2 patients | 473 (65.8%) | 144 (57.1%) | 617 (63.5%) | .02 2 |
| 1 every 3 patients | 130 (18.1%) | 55 (21.8%) | 185 (19.1%) | |
| 1 every 4 patients | 71 (9.9%) | 40 (15.9%) | 111 (11.4%) | |
| Nursing staff specialized in critical care (n, %) | 281 (39.1%) | 99 (39.3%) | 380 (39.1%) | >.99 2 |
| With physiotherapist dedicated to critical patients (n, %) | 382 (68.7%) | 163 (78.4%) | 545 (71.3%) | .009 1 |
| Reference drugs in analgosedation and delirium available (n, %) | 231 (32.1%) | 78 (31.0%) | 309 (31.8%) | .75 2 |
| Music therapy available (n, %) | 41 (7.4%) | 14 (6.7%) | 55 (7.2%) | .88 2 |
| Occupational therapy available (n, %) | 91 (16.4%) | 47 (22.6%) | 138 (18.1%) | .06 2 |
| Clinical psychologist available (n, %) | 238 (42.8%) | 86 (41.4%) | 324 (42.4%) | .74 2 |
| Dedicated early mobilization team available (n, %) | 204 (36.7%) | 67 (32.2%) | 271 (35.5%) | .27 2 |
IQR: interquartile range; SD: standard deviation.
According to the participants, there was less persistence of oversedation after the pandemic in those units with a higher nurse-to-patient ratio (P = .02) and with physiotherapists assigned to the ICU (P = .009).
Analgosedation practices before the COVID-19 pandemicParticipant’s perceptions of pre-pandemic analgosedation practices are reported in eTable 1 of the Supplementary material.
Targeted analgosedation (P = .001), pain monitoring with the ESCID scale (P = .014), analgesia monitoring by the nursing staff (P = .008), the preference for mild versus deep sedation (P = .007), dynamic and sequential sedation (P = .02), sedation level monitoring (P = .02), the frequency of sedation monitoring (P = .03), and the use of continuous electroencephalography to measure sedation level (P = .006) before the pandemic were associated with less perceived oversedation after the pandemic.
Pharmacotherapy in analgosedation before the COVID-19 pandemicThe most widely used analgesic and sedative drugs before the pandemic are shown in eTable 2. Fentanyl was the most commonly used analgesic for moderate to severe pain (58%), followed by multimodal analgesia (18.4%). Prescription of the latter before the pandemic was associated with a lower perception of persistent patient oversedation after the pandemic (P = .006).
The most commonly used drugs for superficial sedation were dexmedetomidine (39.8%), propofol (35.7%) and midazolam (22.6%), with an association being observed between the use of propofol and less perceived persistent oversedation after the pandemic (P = .007). In contrast, an association was observed between the use of midazolam and the perception of oversedation after the pandemic (P = .001).
The most commonly used drug for deep sedation before the pandemic was midazolam (59.9%), followed by propofol (37.2%).
General non-pharmacological and pharmacological delirium management before the pandemicA total of 44% of the participants reported having delirium management protocols in place, and 75% reported actively assessing delirium before the pandemic, based on validated clinical scales (CAM-ICU and ICDSC) or the clinical impression. Of this 75%, a total of 74.1% used scales, implying that participants measured delirium using validated methods in 47.4% of the cases according to the perception of the participants (eTable3).
Over 70% of the participants reported using some of the measures in the ABCDEF bundle of recommendations for the prevention of delirium before the pandemic, with the association observed between the use of several of these measures and other additional measures and the absence of persistent oversedation after the pandemic (eTable 3).
The drugs most commonly used for the prevention and treatment of delirium were dexmedetomidine (35.5%) and haloperidol (68.2%), respectively (eTable 4).
Changes in analgosedation and delirium management practices during the pandemicOverall, 74.9% of the participants reported a change in analgosedation practices during the pandemic, and 69.9% reported that these changes persisted after the pandemic (Table 2). In turn, 60.1% felt that analgosedation and delirium management practices were worse during the pandemic than before the pandemic. The main reasons for these changes were reported to be work overload (71.9%) and the presence of staff without the necessary training or the necessary experience (70.8%). This latter aspect had a significant impact upon the perception of oversedation after the pandemic (P = .002) (eTable 5).
Changes in analgosedation practices during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
| Characteristics | No persistent deep sedation (n = 719) | Persistent deep sedation (n = 252) | Total (n = 1008) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changes in analgosedation and delirium management practices during pandemic (n, %) | 518 (72.0%) | 209 (82.9%) | 727 (74.9%) | .001 1 |
| Persistence of changes in analgosedation and delirium management practices after pandemic (n, %) | 379 (65.5%) | 181 (81.5%) | 560 (69.9%) | <.001 1 |
| More frequent use of inappropriate deep sedation during pandemic (n, %) | 498 (69.4%) | 244 (96.8%) | 742 (76.5%) | <.001 1 |
| More frequent use of inappropriate NMB during pandemic (n, %) | 498 (69.3%) | 219 (86.9%) | 717 (73.8%) | <.001 1 |
| Persistence of more frequent use of NMB after pandemic (n, %) | 30 (5.1%) | 136 (56.9%) | 166 (20.0%) | <.001 1 |
| Less frequent use of sequential or dynamic sedation during pandemic (n, %) | 437 (60.9%) | 195 (77.4%) | 632 (65.1%) | <.001 1 |
| Persistence of less frequent use of sequential or dynamic sedation after pandemic (n, %) | 57 (10.5%) | 141 (62.1%) | 198 (25.7%) | <.001 1 |
| More frequent use of midazolam during pandemic (n, %) | 430 (60.2%) | 205 (81.7%) | 635 (65.8%) | <.001 1 |
| Persistence of more frequent use of midazolam after pandemic (n, %) | 91 (16.9%) | 146 (64.0%) | 237 (30.9%) | <.001 1 |
| More frequent use of inhaled sedation during pandemic (n, %) | 122 (17.1%) | 44 (17.5%) | 166 (17.2%) | .92 1 |
| Persistence of more frequent use of inhaled sedation after pandemic (n, %) | 88 (26.0%) | 36 (25.2%) | 124 (25.8%) | .91 1 |
| Most common inhaled sedative (n, %) | ||||
| Isoflurane | 74 (43.8%) | 29 55.8%) | 103 (46.6%) | .15 1 |
| Sevoflurane | 95 (56.2%) | 23 (44.2%) | 118 (53.4%) | |
| Reduced monitoring of pain during pandemic (n, %) | 255 (35.5%) | 144 (57.6%) | 399 (41.2%) | <.001 1 |
| Reduced monitoring of sedation during pandemic (n, %) | 211 (29.4%) | 131 (52.4%) | 342 (35.3%) | <.001 1 |
| Reduced monitoring of delirium during pandemic (n, %) | 245 (34.3%) | 142 (57.0%) | 387 (40.2%) | <.001 1 |
NMB: neuromuscular blockade.
The most common changes during the pandemic were an increased use of inappropriate deep sedation and neuromuscular blockade (NMB) (76.5% and 73.8%, respectively), followed by an increased use of midazolam (65.8%) and less sequential or dynamic sedation (65.1%). Less monitoring of pain, sedation and delirium was also reported (41.2%, 35.3% and 40.2%, respectively). In addition, participants reported that more frequent use of midazolam and NMB continued after the pandemic (30.9% and 20%, respectively). All of these changes significantly increased the perception of persistent oversedation after the pandemic (Table 2).
With regard to delirium, 51% of the participants reported less use of delirium prevention measures (ABCDEF bundle and other recommendations) during the pandemic which was associated with the perception of persistent oversedation. In decreasing order of frequency, the defects in applying such measures were: fewer attempts to withdraw sedation (43.7%), failure to prioritize mild sedation (40.1%), no adjustment of ventilatory parameters to avoid asynchronies (38.9%), less monitoring of delirium (31.2%), failure to prioritize non-benzodiazepine drugs (29.5%), lack of adequate analgesia (29.5%) and failure to use reorientation measures (television, clocks, etc.) (25%). All these aspects were associated with a greater perception of persistent oversedation after the pandemic (Table 3).
Changes in the management of delirium during the pandemic.
| Characteristics | No persistent deep sedation (n = 719) | Persistent deep sedation (n = 252) | Total (n = 1008) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced application of measures for the prevention of delirium (n, %) | 333 (46.4%) | 159 (64.4%) | 492 (51.0%) | <.001 1 |
| ABCDEF bundle | ||||
| Reduced guaranteeing of adequate analgesia (n, %) | 184 (26.9%) | 89 (36.9%) | 273 (29.5%) | .004 1 |
| Reduced sedation withdrawal attempts, spontaneous breathing tests and/or mild sedation protocols (n, %) | 283 (41.4%) | 121 (50.2%) | 404 (43.7%) | .02 1 |
| Reduced prioritization of mild sedation (n, %) | 261 (38.2%) | 110 (45.6%) | 371 (40.1%) | .047 1 |
| Reduced selection of non-benzodiazepines (n, %) | 189 (27.6%) | 84 (34.8%) | 273 (29.5%) | .04 1 |
| Reduced sequential and dynamic sedation (n, %) | 162 (23.7%) | 63 (26.1%) | 225 (24.3%) | .49 1 |
| Reduced monitoring of delirium (n, %) | 196 (28.6%) | 93 (38.6%) | 289 (31.2%) | .005 1 |
| Reduced early mobilization and rehabilitation (n, %) | 264 (38.6%) | 96 (39.8%) | 360 (38.9%) | .76 1 |
| Reduced family participation (n, %) | 348 (50.9%) | 110 (45.6%) | 458 (49.5%) | .18 1 |
| Measures beyond the ABCDEF bundle | ||||
| Less adjustment of ventilatory parameters for minimization of asynchronies (n, %) | 248 (36.4%) | 110 (46.0%) | 358 (38.9%) | .01 1 |
| Reduced early mobilization and rehabilitation (n, %) | 293 (43.0%) | 99 (41.4%) | 392 (42.6%) | .70 1 |
| Reduced withdrawal of unnecessary devices (n, %) | 225 (33.0%) | 94 (39.3%) | 319 (34.7%) | .08 1 |
| No avoidance of use of mechanical restraints (n, %) | 188 (27.6%) | 62 (25.9%) | 250 (27.2%) | .67 1 |
| Less facilitation of patient-family-healthcare staff communication (n, %) | 283 (41.6%) | 94 (39.3%) | 377 (41.0%) | .59 1 |
| Less participation of the family and flexibility of visiting hours (n, %) | 271 (39.8%) | 94 (39.3%) | 365 (39.7%) | .94 1 |
| Less avoidance of sensory barriers (n, %) | 151 (22.2%) | 46 (19.2%) | 197 (21.1%) | .36 1 |
| Less use of reorientation measures (n, %) | 185 (27.2%) | 45 (18.8%) | 230 (25.0%) | .01 1 |
| Less preservation of sleep-waking cycle (n, %) | 193 (28.3%) | 61 (25.5%) | 254 (27.6%) | .45 1 |
| Less use of early psychological interventions and neurocognitive stimulation (n, %) | 133 (19.5%) | 49 (20.5%) | 182 (19.8%) | .78 1 |
Overall, 25.9% of the participants felt that the patients were sedated more than necessary after the pandemic (95%CI 22.4%–27.8%) and 12.8% were of the opinion that the analgosedation and delirium management practices were poorer than before the pandemic – this being related to the perception of oversedation (P < .001). Both the persistence of the habits acquired during the pandemic and the presence of untrained staff were significantly correlated with the perception of oversedation after the pandemic (P < .001) (eTable 6).
Multivariate analysisWhen all of the above elements were entered into a multivariate logistic regression analysis, 7 variables retained a statistically significant association with the perception of oversedation after the pandemic. The most significant risk factor identified was the persistence of habits acquired during the pandemic, with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.16 (95%CI 2.24–4.45, P < .001). Other factors were lack of staff training or experience (aOR 1.70, 95%CI 1.16–2.50, P = .007) and the use of midazolam for superficial sedation before the pandemic (aOR 1.47, 95%CI 1.03–2.11, P = .035) (Table 4).
Multiple logistic regression analysis: factors associated with the persistence of oversedation after the COVID-19 pandemic (pseudo R2 = 8.3%).
| Variable | aOR | 95%CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistence of habits acquired during pandemic | 3.16 | 2.24–4.45 | <.001 |
| Staff lacking training or experience | 1.70 | 1.16–2.50 | .007 |
| Use of midazolam for superficial sedation before pandemic | 1.47 | 1.03–2.11 | .035 |
| Medical staff monitoring appearance of delirium before pandemic | 0.70 | 0.50–0.98 | .038 |
| Nursing staff monitoring analgosedation before pandemic | 0.69 | 0.49–0.98 | .038 |
| Guaranteeing of sleep-waking cycle | 0.68 | 0.49–0.96 | .027 |
| Use of targeted analgosedation before pandemic | 0.66 | 0.45–0.98 | .039 |
| Constant (α) | 0.40 | 0.24–0.67 | <.001 |
aOR: adjusted odds ratio; CI: confidence interval.
Likewise, several factors were found to reduce the probability of perceived oversedation after the COVID-19 pandemic. These were the monitoring of delirium by medical staff before the pandemic (aOR 0.70, 95%CI 0.50−0.98, P = .038); analgosedation monitoring by nursing staff before the pandemic (aOR 0.69, 95%CI 0.49−0.98, P = .038); ensuring the sleep-wake cycle before the pandemic (aOR 0.68, 95%CI 0.45−0.96, P = .027); and using a targeted analgosedation strategy before the pandemic (aOR 0.66, 95%CI 0.45−0.98, P = .039).
The full model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of 0.70 (95%CI 0.66−0.74), and showed adequate goodness of fit (Hosmer-Lemeshow P = .59). The full model is shown in Table 4, and the ROC curve is shown in Fig. 2.
DiscussionThe COVID-19 pandemic led to the widespread use of deep sedation strategies in patients with acute respiratory failure requiring MV due to viral pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).28 This practice continued after the pandemic, although 25.9% of respondents considered that the patients were sedated more than necessary during this period. Other studies have reported similar findings. The main risk factor for post-pandemic oversedation, with an OR of 3.1, was found to be the continuation of the deep sedation habits acquired during the pandemic, replacing previous strategies such as the ABCDEF bundle.
The literature highlights the dangers of oversedation, especially when used early, and continuing into the post-pandemic period.29–31 Stephens et al. found early deep sedation in patients undergoing MV for COVID-19 with high benzodiazepine use was associated with increased mortality (aOR 3.44, 95%CI 1.65–7.17, P < .01).26 These authors reported that approximately 70% of the COVID-19 patients undergoing MV received early deep sedation, which was associated with poorer outcomes including fewer ventilator-free days, longer hospital stay and increased mortality.
Additional factors described in other studies, such as the type of hospital (public or private), the number of hospital and ICU beds, or centers with university teaching and critical care training activities, were analyzed but not found to be associated with post-pandemic oversedation in the present study.32–35 In contrast, the nurse-to-patient ratio and the presence of physiotherapists showed a significant association with oversedation, highlighting the importance of ensuring an adequate ratio of health care staff per patient, as reported in previous studies.36
An important and novel observation in our study was the important variability in perceived oversedation among the different geographic regions involved (P < .001). In this regard, 35% of the participants in South America considered that patients were oversedated after the pandemic, compared to 19% in Europe and 15% in North America. These data, which are the first to describe these geographic differences, may reflect a lack of appropriate sedation protocols that prioritize mild sedation, inadequate implementation of the protocols, a lack of adequate monitoring, reduced availability of sedative drugs, and a lack of trained personnel.1
From the pharmacological perspective, global shortages and the need to use the available drugs led to overuse of benzodiazepines and opioids, especially midazolam (19% versus 32%, P = .001), which in turn was associated with post-pandemic oversedation. Oversedation with hypnotic benzodiazepines during the pandemic had a negative impact on patient prognosis, particularly in terms of length of stay and mortality after adjustment for the SOFA score.33–35 The use of benzodiazepines in critically ill patients undergoing MV has been associated with adverse events such as delayed awakening and extubation, prolonged ICU and hospital stay, increased delirium, cognitive impairment and post-ICU syndrome.37–39 Current recommendations emphasize the importance of prioritizing non-benzodiazepine drugs.29,40–44
Another important finding in our study was the association between analgosedation monitoring before the pandemic and the perception of oversedation after the pandemic, which again emphasizes the importance of monitoring in order to ensure adequate management of analgosedation. Analgesia onitoring by the nursing staff (P = .008), the monitoring of the sedation level (P = .02) and its frequency (P = .03), as well as the use of continuous electroencephalography (P = .006) before the pandemic were associated with less oversedation after the pandemic.
These data are consistent with current scientific evidence, which suggests that frequent monitoring of pain and sedation levels using validated scales on a frequent basis is considered to be essential in order to avoid oversedation and adverse events.16 More recently, an expert consensus has recognized the utility of continuous electroencephalography to guide sedation in adult critically ill patients and recommends its use in all patients undergoing deep sedation (whether or not they are undergoing NMB), when clinical assessment is not possible.45
Another important factor in preventing oversedation and adverse events is adherence to the ABCDEF bundle.46 In our study, adherence to the analgosedation protocol before the pandemic was 60%, rising to 80% for targeted analgosedation and to 90% for mild sedation protocols. These figures indicate a high degree of adherence compared with other studies.47–49 These practices in turn were significantly correlated with lower perceptions of oversedation after the pandemic.50–52
Adherence to the ABCDEF bundle varied across geographical settings. In this regard, the literature describes considerable heterogeneity in different studies, generally reporting poor adherence, with many barriers and facilitating factors.52–54 The pandemic exacerbated the challenges, with work overload and a lack of qualified staff being the main barriers.20 In 2019, Carboni Bisso et al. conducted a study to determine the scope and application of these measures in Argentina. The authors found that despite awareness of the bundle of measures, adherence to them was irregular.55 The same group developed a similar questionnaire during the pandemic and found that the conditions of lockdown and work overload were critical in explaining the limitations in applying the ABCDEF bundle. These observations are consistent with our findings, which point to the important workload of the healthcare staff involved, the lack of experience in caring for critical patients, the fear of the isolation measures to avoid infection among the staff, and safety concerns such as self-extubation or orotracheal tube migration.20 In the SAMDS-ICU study, Luz et al. evaluated the use of the bundle of measures before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, and found that many of the practices were not maintained during the pandemic. The main challenges to adherence to the measures were found to be work overload among the health care staff and a reduced presence critical care trained specialists.21
Lastly, the scarce use of validated scales to monitor delirium during the pandemic, and the decrease in preventive measures were associated with greater oversedation after versus before the pandemic (64.4% versus 46.4%, P < .001). Due to the high percentage of delirium diagnosed in COVID-19, with a 50%–60% incidence of hyperactive delirium in some series, we face an important increase in delirium associated with these inadequate sedation practices.13,56 Recently Owen et al., in over 44,000 patients admitted to the ICU in Canada, reported that the adoption of the ABCDEF bundle reduced the incidence of delirium (two-month decrease of 0.34%, 95%CI 0.18−0.50, P < .01) from 33.48% (95%CI 29.64–37.31) in 2017 to 28.74% (95%CI 25.22–32.26) in 2019.57 In our study, the main barriers facing prevention were a lack of family involvement in the care of the patient in the ICU, difficulties in monitoring analgosedation, and the increased benzodiazepine use, as already described in other studies.58,59
Our study has a number of limitations and strengths. Limitations include the subjectivity of the survey and the heterogeneity of analgosedation management in the different geographical settings. Also, we did not consider the professional hierarchy of the survey participants, which may have influenced the perception of medication use. On the other hand, although a considerable sample size was recruited, some of the participating countries showed a lower response rate, which limits the representativeness of our results.
With regard to the strengths of the study, we were able to secure the participation of many of the FEPIMCTI member countries, with local specialists caring for many patients with analgosedation before, during and after the pandemic. This provided relevant information on the factors influencing the changes in analgosedation practices in our setting.
We believe that knowledge of analgosedation and delirium management practices at the regional level is important for the development of local analgosedation and delirium expert committees or workgroups to discuss or endorse strategies for implementing the ABCDEF toolkit and promoting Zero Sedation.
ConclusionsBefore the COVID-19 pandemic, the management of analgosedation was characterized by the predominant use of targeted protocols that favored priority on mild and dynamic sedation in critically ill patients. During the pandemic the percentage of ICU patients receiving deep sedation increased. According to the physicians surveyed, this tendency to use deep sedation continued after the pandemic and was not always justified. The present study found that staff with little to no critical care training or experience, less monitoring of analgosedation, less nursing presence in the ICU, and habits acquired during the pandemic (especially the regular use of benzodiazepines and oversedation) were the main reasons for this perception of the post-pandemic situation. We need to resume socialization and retraining efforts in protocols and bundles of measures for safe patient sedation, and to reduce oversedation in the ICU.
Ethical responsibilitiesThe present study was evaluated and approved by the Red Municipal de Bioética Clínica y Social of the city of Córdoba (Argentina), and abides with the National Law on Personal Data Protection 25.326 (Republic of Argentina) for safeguarding the identity and data of the participants, and guaranteeing full anonymity and confidentiality of the information. Informed consent was obtained from all the participants after receiving an explanation of the aims of the study and the time required to complete it.
RESEARCH CARRIED OUT WITH THE SUPPORT OF: Comité de Analgesia, Sedación y Delirium de la Federación Panamericana e Ibérica de Cuidados Críticos y Terapia Intensiva (FEPIMCTI); URL: https://fepimcti.org/comite-de-expertos/sedacion-y-analgesia/).
Financial supportThe present study has received no partial or total funding, or any type of grant or financial support.