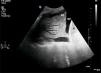
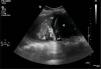
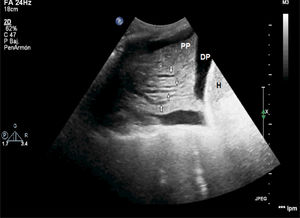
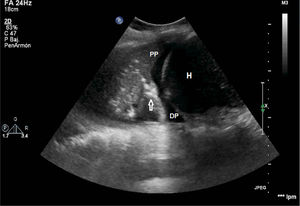
We hereby present two cases of lung ultrasound in two patients admitted to the ICU with respiratory failure due to ARDS who remained on mechanical ventilation for more than seven days. Fig. 1 shows the “fluid bronchogram” sign (arrows) consisting of ramified linear images that correspond to distended bronchi filled with fluid and lack of air over hypoechogenic pulmonary parenchyma and simulate blood vessels but distinguish from them by having a wall (hyperechogenic) and lack of Doppler signal. It suggests pulmonary atelectasis due to central airway obstruction (CAO). Fig. 2 shows pulmonary parenchyma with hyperechogenic dots representative of air inside the bronchus. It is the “air bronchogram” sign. In the appropriate clinical context, it is indicative of infectious lung condensation (mobile bronchogram) or compression atelectasis (static bronchogram).
Please cite this article as: Montero Baladía M, Arroyo Diez M, Badallo Areválo O. Signos básicos en ecografía pulmonar. Broncograma líquido y broncograma aéreo: diferenciación. Med Intensiva. 2018;42:e19.