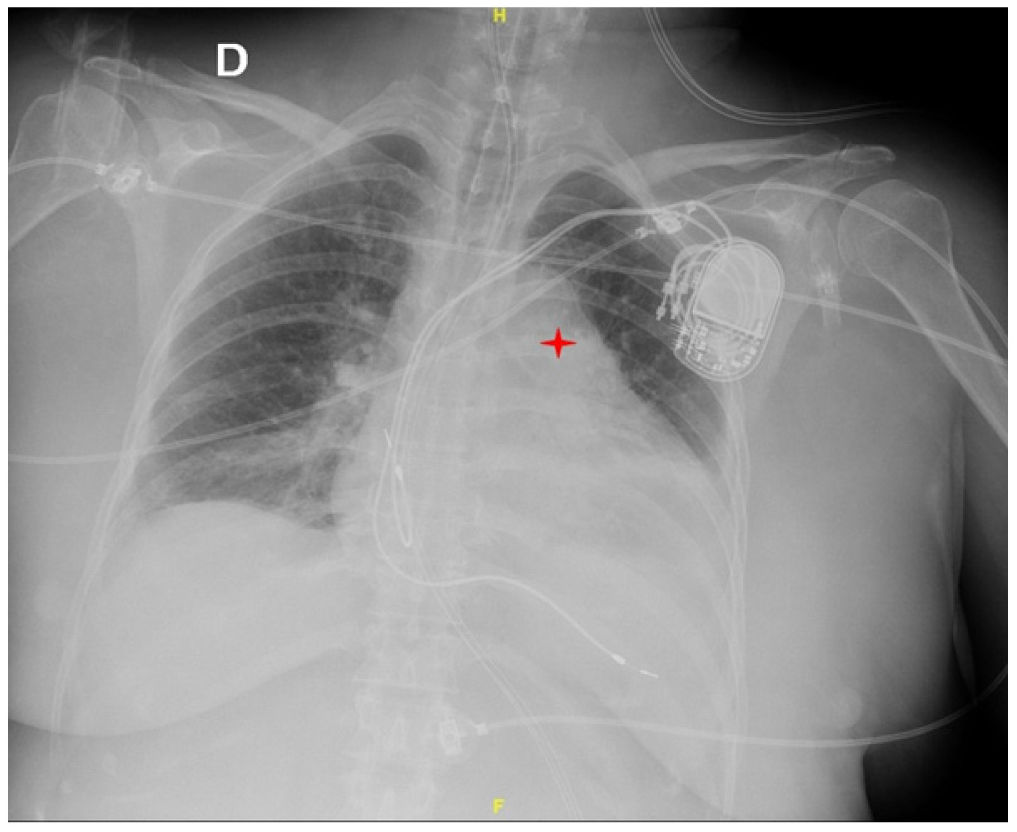
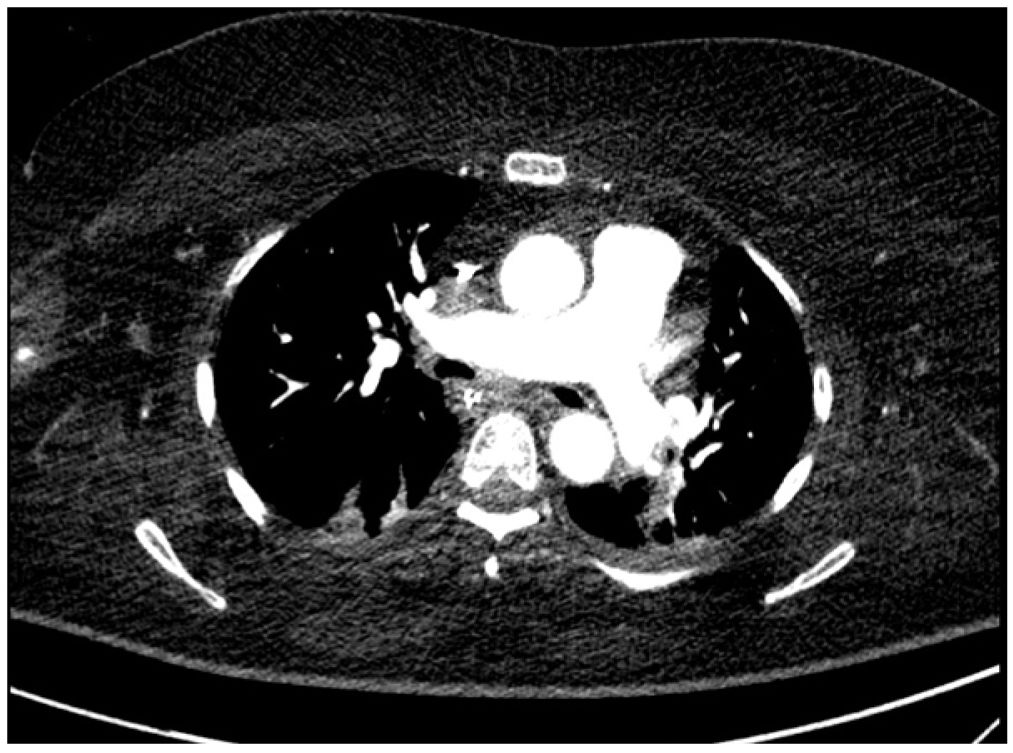
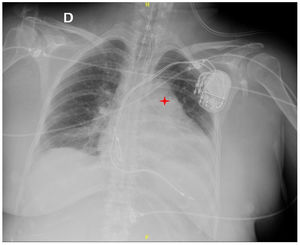
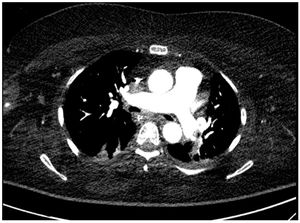
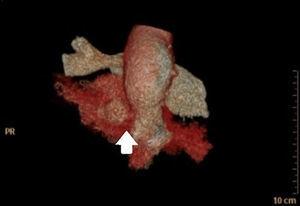
This is the case of a 68-year-old woman with a past medical history of Kearns-Sayre syndrome (mitochondrial myopathy) admitted to the intensive care unit with cardiac arrest. During the ICU stay she suffered several episodes of acute respiratory failure initially due to bronchospasm. A fiber bronchoscopy was performed (Appendix B; video1) that revealed the presence of main bronchi collapse. The thoracic X-ray confirmed the presence of pulmonary artery dilatation (Fig. 1). Transthoracic echocardiography revealed the presence of severe pulmonary trunk and right pulmonary artery dilatation (Appendix B; video 2). Thoracic computed axial tomography confirmed the pulmonary trunk and right pulmonary artery dilatation with main bronchi compression (Fig. 2). Transesophageal echocardiography ruled out the presence of right ventricular cavity dilatation (Appendix B; video 3). A Swan-Ganz catheter was implanted that ruled out the presence of pulmonary hypertension. This is a case of pulmonary artery dilatation without pulmonary hypertension and with bronchial compression that has not been widely reported in the medical literature.
Conflicts of interestNone whatsoever.