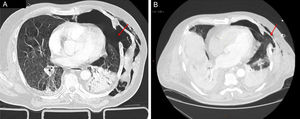
Varón de 73 años con traumatismo torácico cerrado. Se realizó TAC de tórax con hallazgo de fracturas costales bilaterales, contusión pulmonar, neumotórax izquierdo y defecto de continuidad en la pared torácica asociada a rotura de musculatura intercostal (fig. 1A). La colocación de drenaje torácico y el inicio de ventilación mecánica con reexpansión pulmonar puso de manifiesto, a las 72 h, la herniación de un segmento de la língula (fig. 1B). Se realizó reparación quirúrgica el noveno día de ingreso con resultado favorable. La hernia pulmonar traumática es una entidad poco frecuente. La TAC de tórax es el estudio radiológico de elección que permite confirmar la lesión, y ofrece información sobre el saco herniario, la amplitud del defecto de la pared, así como el compromiso originado sobre el tejido pulmonar.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025