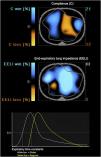
A 61-year-old patient with a history of COPD was in the postoperative phase of a right single lung transplant, requiring a high-flow oxygen cannula due to acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. An electrical impedance tomography (Pulmovista V500 - Dräger, Germany) was used to assess regional changes in tidal ventilation and end-expiratory lung volume (EELV). An inspiratory flow rate of 60L/min and an inspired oxygen fraction of 0.4 were employed. Fig. 1 shows the changes in VT before and after the use of HFNC. In the non-transplanted lung, an increase in aeration is observed due to regional elevation of EELV (blue area) caused by increased expiratory resistance, leading to air trapping and alveolar overdistension (orange area). Consequently, expiratory time constants were prolonged (Fig. 2).
Financial supportThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of interestNone.