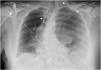
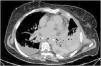
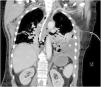
This is the case of a 67-year-old woman admitted to the ICU with refractory distributive shock. The thoracic x-ray (Fig. 1) revealed the presence of a left-sided hydropneumothorax, with a 5 cm apical pleural leave separation and contralateral mediastinal shift (⋆). The CAT scan performed (Fig. 2) revealed the presence of a hydropneumothorax and pleural empyema and periesophageal pneumomediastinum in the lower third of the esophagus (⋆). Thoracic drainage is performed, with the release of air and foul-smelling cloudy fluid containing "abundant bacteria, fat droplets, and fibers suggestive of food remnants." Upon suspicion of esophageal perforation, the new CAT scan performed with the administration of oral contrast (Fig. 3) reveals the presence of contrast extravasation at left lateral margin level of the lower esophagus, consistent with perforation, and contrast passage into the left pleural cavity (⋆). Emergency surgery is eventually performed.
Authors’ contributionsAll the authors have jointly and equally reviewed, selected, and drafted the article.