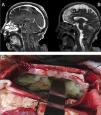
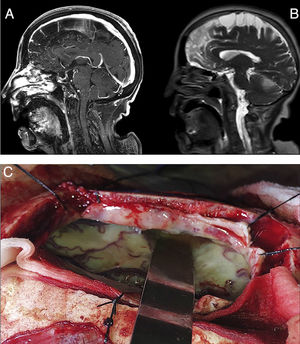
A 72-year-old female patient with history of high blood pressure presented to the emergency with right hemiparesis, aphasia and seizures. Brain computed tomography did not find hemorrhagic lesions and brain magnetic resonance imaging showed no vascular lesions but revealed laminar subdural collection in the right parietal convexity with restriction on the diffusion sequence together with multiple areas of restriction in the subarachnoid space on the bihemispheric convexity (Fig. 1, Panel A and B). It evolved with Glasgow coma scale 8/15, fever and saturation 87% due to aspiration, proceeding to endotracheal intubation. Blood cultures and lumbar puncture were performed. It showed glucose 49mg/dl (serum glucose 484mg/dl), protein level of 946g/dl, leukocytes 3744/mm3 (95% neutrophils), 1.000erythrocytes/mm3. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid cultures revealed the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Neurosurgical intervention was decided with craniectomy and drainage of meningeal empyema (Panel C). The patient completed 8 weeks of ceftriaxone with good clinical outcome.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more