To analyze the effectiveness of a teaching-learning methodology for teletraining in basic life support (BLS) based on communication through smart glasses.
DesignPilot quasi-experimental non-inferiority study.
ParticipantsSixty college students.
InterventionsRandomization of the participants in: tele-training through smart glasses (SG) and traditional training (C) groups. Both training sessions were very brief (less than 8 min) and included the same BLS content. In SG, the instructor trained through a video call with smart glasses.
Main variables of interestThe BLS protocol, the use of AED, the quality of resuscitation and the response times were evaluated.
ResultsIn most of the BLS protocol variables, the resuscitation quality and performance times, there were no statistically significant differences between groups. There were significant differences (in favor of the SG) in the assessment of breathing (SG: 100%, C: 81%; p = 0.013), the not-to-touch warning before applying the shock (SG: 79%, C: 52%; p = 0.025) and compressions with correct recoil (SG: 85%, C: 32%; p = 0.008).
ConclusionsLaypeople BLS-AED brief tele-training through smart glasses could potentially be, at least, as effective as traditional training methods. In addition, smart glasses could be more advantageous than traditional teaching for certain points of the BLS protocol and chest compressions quality, probably due to the capability of real-time visualization of images which supports the BLS sequence. Augmented reality supported teaching should be considered for BLS training, although caution is required in extrapolating findings, and further in-depth studies are needed to confirm its potential role depending on concrete target populations and environments.
Analizar la efectividad de una metodología de enseñanza-aprendizaje de teleformación en soporte vital básico (SVB) basada en la comunicación a través de smart glasses.
DiseñoEstudio piloto cuasi experimental de no inferioridad.
ParticipantesSesenta estudiantes universitarios.
IntervencionesAleatorización de los participantes en: grupo de teleformación a través de smart glasses (SG) y formación tradicional (C). Ambas sesiones de entrenamiento fueron muy breves (<8 minutos) e incluyeron el mismo contenido en de SVB. En SG, el entrenamiento fue comunicándose a través de una videollamada con smart glasses.
Variables de interés principalesSe evaluó el protocolo del SVB, el uso de DEA, la calidad de la reanimación y los tiempos de actuación.
ResultadosEn la mayoría de las variables del protocolo del SVB, la calidad de la reanimación y los tiempos de ejecución, no hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre grupos. Hubo mejor actuación de SG al valorar la respiración (SG: 100%, C: 81%; p = 0,013), el avisar antes de la descarga del DEA (SG: 79%, C: 52%; p = 0,025) y las compresiones con buena reexpansión (SG: 85%, C: 32%; p = 0,008).
ConclusionesEl tele-entrenamiento en SVB-DEA para legos con smart glasses podría llegar a ser, al menos, tan efectivo como un método tradicional de enseñanza. Además, las smart glasses podrían ser más ventajosas para ciertos aspectos del protocolo del SVB y la calidad de las compresiones, probablemente debido a la capacidad de visualización de imágenes en tiempo real. La enseñanza basada en la realidad aumentada debe considerarse para la capacitación en SVB, aunque se requiere tanto cautela en la extrapolación de hallazgos como estudios futuros con mayor profundidad.
The European Resuscitation Council (ERC) recommends the teaching of basic life support (BLS) so that any person may act correctly when witnessing out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA).1 The protocol includes knowing how to recognize OHCA, how to use an automated external defibrillator (AED), and how to perform high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).2 Given the relationship between the quality of CPR and recovery from OHCA,3 several BLS educational programs for laypeople have been proposed – all with different characteristics in terms of duration, frequency, contextualization and the use of communication technologies. The traditional BLS education protocols are face-to-face programs with a long duration and are spaced over time, though they have evolved towards more brief and continuous protocols of demonstrated efficacy.4–6 There are even very short programs lasting under 10 min, that have been shown to be useful.7
Developments in communication technology have also made it possible to teach BLS on a remote basis. Telematic training programs through smartphones could afford results comparable to those obtained with face-to-face protocols, with the added advantage of having better material and human resources, and of being accessible to almost anyone.8 In relation to communication technologies, smart glasses have been proposed as a new teletraining tool.9–13 A recent pilot study involving this communication technology found teleassistance with augmented reality based on the use of smart glasses to be useful in teaching BLS and the use of an AED.13 However, optimum results in terms of resuscitation quality were not obtained, possibly due to the short training time involved. The authors underscored the potential of this wearable, and considered that further studies are needed to compare its efficacy against more traditional training programs.13
Accordingly, the present study was carried out to analyze the effectiveness of a teaching-learning methodology for teletraining in BLS involving communication through smart glasses, and to compare it with a traditional face-to-face training program.
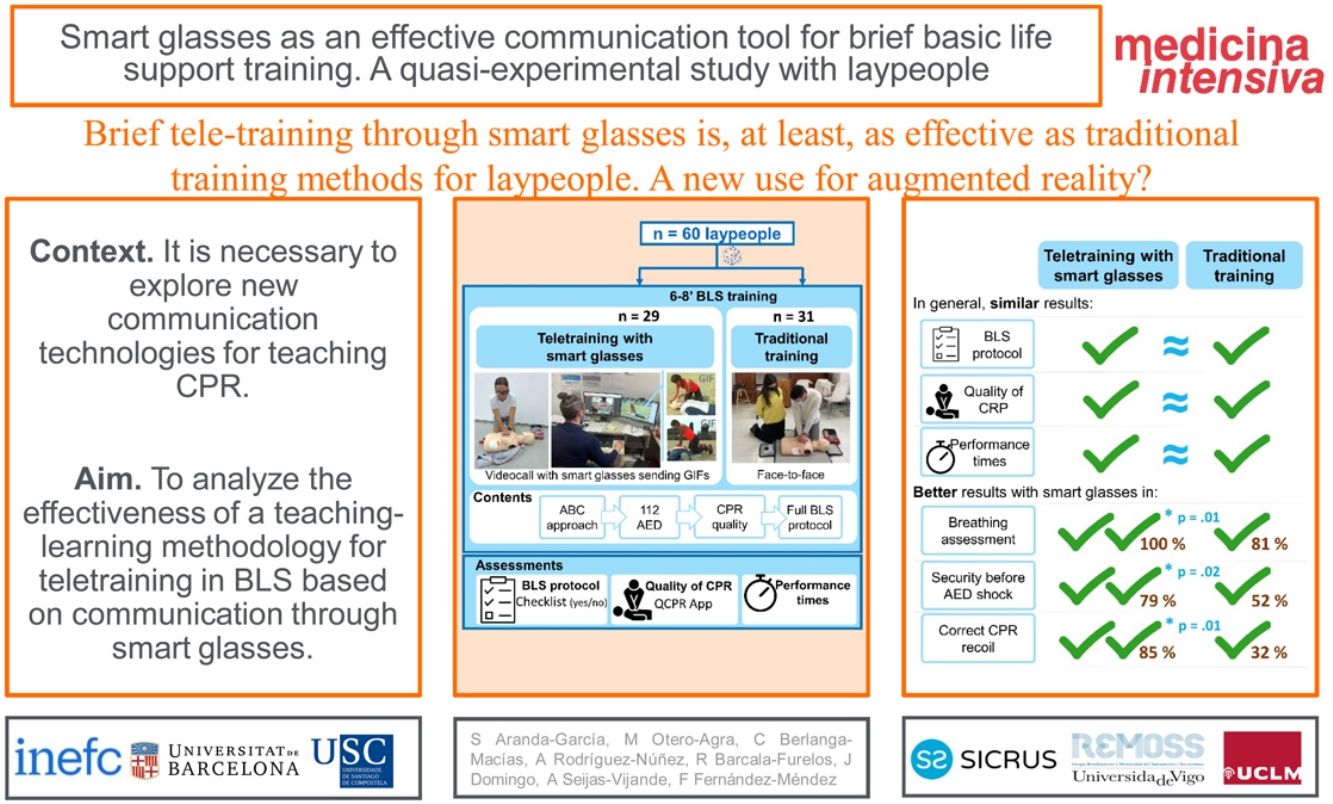
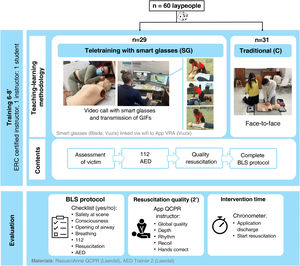
Patients and methodsA quasi-experimental non-inferiority pilot study was carried out, involving a total of 60 health sciences and nursing university students of the University of Vigo (Pontevedra, Spain). The participants were required to have had no training in BLS during the previous two years, and no physical problems preventing them from performing chest compressions (CC). The convenience sample was randomized to a teletraining intervention group with smart glasses (SG) and a traditional face-to-face training control group (C) (Fig. 1). The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee for Clinical Research of the Catalan Sports Council (reference number 026/CEICGC/2022), and all the participants signed the corresponding informed consent before randomization.
The participants underwent a brief 6−8 min individual training session imparted by an ERC-certified instructor. Use was made of a Resusci Anne QCPR simulator (Laerdal, Norway) and a training AED (AED Trainer 2, Laerdal, Norway). The training of both groups followed the same sequence, distributed into four blocks: (i) ABC assessment: safety at the scene, check of consciousness, opening of the airway and check of breathing; (ii) alert the emergency medical services (dial 112), set up the AED and follow instructions for use; (iii) perform continuous quality CC: adequate compression point, rhythm with metronome, depth and compression-decompression ratio; and (iv) complete intervention protocol. In the first three blocks, the instructor provided an explanation/demonstration of each of the techniques, and the student then reproduced them with the necessary corrections from the instructor. In the fourth block, the student carried out the complete intervention protocol as learned, with corrections from the instructor as needed.
With regard to the teaching methodology, each group was instructed differently. The teletraining intervention group received a brief training session through the smart glasses (Vuzix Blade AR, Vuzix, USA) linked to the instructor via wifi 4 G with the App Vuzix Remote Assist (Vuzix, USA),11–13 located at a control post some distance from the training/evaluation area. The SG instructor explained the techniques verbally, sending supporting animated images that the participant could see with the smart glasses11: opening of the airway, evaluation of breathing, compression point and position for performing CC (in frontal and lateral view). The corrections were made from the control post based on what the instructor was hearing and seeing through the smart glasses in the subjective viewing of the participant.
On the other hand, the C underwent a brief traditional face-to-face training session with the instructor in the same physical space as the participant, explaining and showing the techniques, and correcting the student as needed.
Immediately after the training session, the performance of each individual participant in response to a simulated cardiac arrest was evaluated. Placing the situation in context, the participants were instructed to imagine a person fainting in their presence, and to respond as if the situation were real, using what they had just learned (see supplementary video).
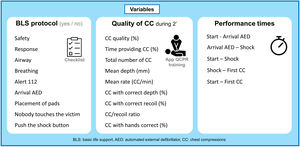
The study variables were evaluated in three main blocks: (a) application of the BLS protocol and use of the AED, assessed with a dichotomic checklist (Yes = correctly performed, and No = not performed or incorrectly performed); (b) quality of CC assessed after discharge of the AED and during two consecutive minutes with the simulator connected to the App QCPR training (Laerdal, Norway); and (c) response times (Fig. 2).
The data were reported as measures of central tendency (median [Me]) and dispersion (interquartile range [IQR]) in the case of continuous variables, and as absolute and relative frequencies in the case of categorical variables. Data homogeneity was assessed with plot techniques and the Shapiro–Wilk test. The comparison of means of variables exhibiting a normal distribution was carried out using the Student t-test, while the Mann–Whitney U-test was used in the absence of normal data distribution. In those comparisons showing statistically significant differences, the effect size (ES) was calculated with the Rosenthal test, classified as follows: insignificant (<0.2), small (0.2−0.5), moderate (0.5−0.8), important (0.8–1.3) and very important (>1.3). Categorical variables in turn were compared with the chi-square test, calculating the ES with Cramer’s V-test, and classified as follows: insignificant (<0.1), small (0.1−0.3), medium (0.3−0.5) and large (>0.5). Statistical significance was considered for p < 0.05. The SPSS version 20.0 statistical package (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used throughout.
ResultsThe study included 60 participants (75% women: 86% women in SG and 65% in C; p = 0.053), with a median age of 20 years (range 18–22), a height of 1.65 m (range 1.6–1.7), and a weight of 63 kg (range 56–69) kg.
Following training, most of the participants in both groups correctly performed the different steps of the BLS protocol as established by the recommendations of the ERC (Table 1).2 No significant differences were observed between SG and C in relation to the different variables, with the exception of the assessment of breathing (SG: 100%, C: 81%; p = 0.013) and the warning not to touch the victim before AED discharge (SG: 79%, C: 52%; p = 0.025).
Basic life support sequence by groups.
| Smart glasses (N = 29) | Control (N = 31) | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | (%) | N | (%) | ||
| Safety | 13 | (45 %) | 20 | (65 %) | p = 0.13a |
| Level of consciousness | 24 | (83 %) | 20 | (65 %) | p = 0.11 a |
| Airway | 29 | (100 %) | 30 | (97 %) | p = 0.33 a |
| Breathing | 29 | (100 %) | 25 | (81 %) | p = 0.013a (ES = 0.32) |
| Alert emergency medical service | 28 | (97 %) | 29 | (94 %) | p = 0.59a |
| About AED | 29 | (100 %) | 31 | (100 %) | – |
| Placing of electrodes | 25 | (86 %) | 26 | (84 %) | p = 0.80a |
| Check nobody touches the victim | 23 | (79 %) | 16 | (52 %) | p = 0.025a (ES = 0.29) |
| Apply discharge | 29 | (100 %) | 31 | (100 %) | – |
AED, Automated external defibrillator; N, Absolute frequency; ES, effect size. (%), Relative frequency.
aChi-square test (p = 0.05).
With regard to the quality of CC, there were no statistically significant differences between the groups, with the exception of the percentage of compressions with correct recoil (SG: 85%, C: 32%; p = 0.008) (Table 2). In both groups the quality of CC did not reach 70%, the mean depth was slightly under 50 mm, and the rhythm was equal to or slightly above 120 compressions/minute, with no significant differences between the groups (Table 2).
Quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) by groups.
| Smart glasses (N = 29) | Control (N = 31) | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Me | IQR | Me | IQR | ||
| Quality of CC (%) | 49 | (11–76) | 66 | (34–84) | p = 0.10a |
| Time performing CC (%) | 100 | (100−100) | 100 | (100−100) | p = 0.18a |
| Total number of CC | 249 | (223–263) | 237 | (219–250) | p = 0.25b |
| Mean depth (mm) | 43 | (34–54) | 48 | (39–58) | p = 0.06b |
| Mean rhythm (CC/min) | 126 | (112–132) | 120 | (110–128) | p = 0.32b |
| CC with adequate depth (%) | 16 | (0–61) | 30 | (1–53) | p = 0.44a |
| CC with adequate recoil (%) | 85 | (37–100) | 32 | (6–85) | p = 0.008a (ES = 0.34) |
| CC/decompression ratio | 1.00 | (0.77–1.18) | 0.92 | (0.79–1.04) | p = 0.29a |
| CC with correct position of hands (%) | 100 | (100−100) | 100 | (100−100) | p = 0.07a |
CC: Chest compressions. Me: Median. IQR: Interquartile range (Q1 - Q3). ES: Effect size.
aMann–Whitney U-test (p = 0.05).
bStudent t-test for independent samples (p = 0.05).
The time from the start of the intervention to the arrival of the AED was short and significantly longer (8 s more) in SG than in C (SG: 38 s, C: 30 s; p = 0.041). However, there were no statistically significant differences between the groups in terms of the time to application of the discharge or the start of CC (Table 3).
Response times by groups.
| Smart glasses (N = 29) | Control (N = 31) | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Me | IR | Me | IR | ||
| From start to setup of AED (s) | 38 | (30–47) | 30 | (21–46) | p = 0.041a (ES = 0.26) |
| From setup of AED to discharge (s) | 65 | (56–71) | 67 | (58–75) | p = 0.36a |
| From start to discharge (s) | 102 | (86–119) | 96 | (80–116) | p = 0.38a |
| From discharge to start of CC (s) | 10 | (8–13) | 10 | (8–11) | p = 0.69b |
| From start to first CC (s) | 116 | (99–127) | 102 | (88–125) | p = 0.29a |
AED, Automated external defibrillator; CC, chest compressions; Me, Median; IQR, Interquartile range. (Q1–Q3). S = Seconds. ES: Effect size.
aMann–Whitney U-test (p = 0.05).
bStudent t-test for independent samples (p = 0.05).
To our knowledge, this is the first quasi-experimental study on the efficacy of a BLS-AED teletraining protocol with smart glasses targeted to first-aid laypeople. The results obtained indicate that this kind of training is as effective as traditional face-to-face training in terms of most of the variables related to the BLS protocol, the quality of CC, and the response times. Furthermore, training with smart glasses is comparatively superior in some aspects related to the quality of the intervention, particularly the ABC assessment approach (evaluation of breathing), use of the AED (warning not to touch the victim) and the quality of CC (recoil).
Regarding the specific results of the BLS sequence and quality of CC, the two groups showed strong compliance with the recommendations of the ERC.2 Both short training methods were useful in teaching the BLS protocol to laypeople. All of the participants showed very good performance in certain parameters related to the quality of resuscitation (e.g., correct placement of the hands during CC, avoiding interruptions, and with good CC rhythm). However, in our study, the quality of CT was sub-optimal, mainly because CC was too superficial (between 40 and 50 mm instead of the desired 50−60 mm).2 As in previous studies,8,14,15 this caused the global quality of resuscitation (chest compressions) to be acceptable, but below the established arbitrary minimum criterion.16 Thus, while both methods were useful for learning the BLS protocol, they were not optimum in securing high-quality CC. Nevertheless, it was not our intention to achieve maximum resuscitation quality but rather to compare two teaching methods involving the same dedication time, and we chose this particular format because there are numerous examples of brief training protocols.17 Brief training strategies have advantages and disadvantages that fall beyond the scope of this study. In very short protocols of this kind, where the students have very little time to train, it is common to not always reach optimum resuscitation quality.7 In this regard, the ERC recommends frequent repetitive trainings, spaced and divided into short cycles, in order to maintain competence in resuscitation.1,6
Recently, new technological tools such as virtual or augmented reality have been proposed for the training of laypeople.1 In this regard, augmented reality training with smart glasses could prove adequate for “very brief” teletraining protocols, because the results obtained are similar to those of face-to-face training strategies.
To date, no experimental or quasi-experimental studies have analyzed the efficacy of smart glasses in laypeople versus face-to-face training; nevertheless, some studies have demonstrated their applicability in the training of healthcare professionals in clinical contexts18 or in laypeople, but with the lack of a control group.13 In healthcare professionals, the applicability of smart glasses in simulated neonatal resuscitation training,19 and resuscitation quality in in-hospital pediatric cardiac arrest, have been studied.20 In laypeople, Aranda-García et al., following training based on the experience of cardiac arrest video-assisted with smart glasses (the same communication system as that used in our study), reported that the participants were able to perform a good BLS protocol, with good handling of the AED.13
In the present study, the participants in SG performed significantly better than those in C in three aspects: evaluation of breathing, making sure nobody touches the victim at discharge, and CC recoil. The evaluation of breathing is crucial for determining whether the victim is under cardiac arrest and requires CC and AED.2 Ensuring safety at the scene before discharge is important for the rescuer and for the efficacy of discharge.21,22 In turn, the improved CC recoil recorded in SG (53% more CC with good recoil than in C) is decisive at the clinical level, since it reflects the CC in which full chest recoil occurs, and thus adequate cardiac output is maintained. In this respect, the fact that the participants in C were significantly taller could have influenced the poorer results in terms of recoil.23
Intervention in the case of OHCA must be made as quickly as possible, since survival and morbidity in this type of emergency are time-dependent.24 In this regard, augmented reality could be considered useful given the quickness of resuscitation, since the time to AED discharge and the start of CC was less than two minutes from the start of the scene (in both groups).24 The controls (C) were 8 s faster in terms of arrival of the AED, though this difference was considered to be clinically negligible, since it did not influence the time to discharge.
As both interventions were similar regarding training time, content and the individualization of corrections (proportion 1 instructor: 1 student), the possible reasons for the differences in favor of SG are not fully clear. However, the explanation could be related to the real-time visioning of animated images in SG. Although the purpose of transmitting these images to the smart glasses was to show the participant the BLS skills (e.g., the opening of the airway, evaluation of breathing), it may have caused the student to pay special attention to these techniques and therefore to make a greater effort to perform them very well. In any case, it is considered to be very positive that remote training guided by smart glasses yields results that are not inferior to and may even be better than those obtained with the gold standard (individualized face-to-face training).
In coincidence with our findings, other studies have also evaluated the impact upon resuscitation quality of other learning methods based on new technologies, such as virtual reality and augmented reality. In the same way, as with smart glasses, these alternatives compared with the traditional protocols offer the opportunity of a new effective and very realistic method – though further studies are needed to be able to establish solid recommendations.25–27 In any case, given its broad applicability and the lesser need to mobilize human and material resources, interventions based on smart glasses could become a protocolized very brief BLS training tool. In terms of practical applicability, this type of training could be particularly interesting in remote or rural settings with good internet connectivity but with limited access to resuscitation training due to instructor travel costs or the site where teaching is to take place.28 However, securing all the contemplated resources might not be feasible in certain scenarios; further studies in this line therefore could afford data on which to base future political and sociosanitary interventions in this field. As an example, approximately 18% of the Scottish population and 16% of the Spanish population live in remote or rural areas29,30 where emergency services take longer in arriving on site, and where a greater proportion of trained bystanders could improve the survival rates.8 This type of training involving the use of smart glasses as a remote method outside the classroom could allow individualized training adapted to the needs of each student, in line with the proposal of the ERC.3 Likewise, this study could constitute a starting point for the long-term development of educational programs with repeated and periodic updates. In this sense, it would be advisable for future studies to address the retaining of knowledge and skills over the middle and long term (3, 6 and more months), in order to assess consolidation of the learning gained with this type of training.
The present study has limitations that make it necessary to interpret the findings with caution: (i) the sample size and target population involved could limit the extrapolation of the results to the general population and the identification of differences between groups. Although the participants in our study were laypeople in terms of knowledge and skills in BLS-AED, their previous knowledge in truncal disciplines such as anatomy and/or pathophysiology could bias the results obtained; (ii) although wifi allowed the study to be carried out under optimum conditions, real-life circumstances could pose limitations in the application of this technology due to online connectivity issues; (iii) the autonomy of smart glasses is limited, though continuous advances in research evidencing the benefits of these devices may favor their development and compensate this limitation; (iv) although the global quality of resuscitation in SG was not inferior to that observed in C, based on training with previously validated methodologies, the quality of the chest compressions in both groups fell short of the current recommendations. Nevertheless, the observed non-inferiority of SG allows us to view video communication with smart glasses as a potentially useful tool for training in BLS-AED, and could open future lines of research in this field – including analyses of the barriers preventing the recommended quality levels from being met. Thus, further studies on communication with smart glasses are needed, involving population samples from different contexts, with middle and long-term evaluation of the retaining of learning. Likewise, assessment is required of the efficacy of individualized training sessions that might not be so short but which are imparted periodically in the context of the “brief rolling refresher” concept31,32 involving augmented reality settings.
In conclusion, brief BLS-AED teletraining with smart glasses for laypeople could become at least as effective as the traditional training methods. Furthermore, smart glasses could be more advantageous than traditional training in relation to certain aspects of the BLS protocol and the quality of chest compressions, probably due to the capacity for real-time visualization of images supporting the BLS sequence. Teaching based on augmented reality should be considered for training in BLS, though caution is required in extrapolating the findings, and future studies are needed to evaluate new theoretical and practical teaching methods allowing laypeople or healthcare professionals to acquire and retain adequate quality in performing chest compressions. Hence, with due caution, the potential of such technology should be explored in different settings and target populations, with methodological differences in terms of the established training and refresher or retraining times.
Authors' contributionSAG and RBF designed the study. SAG and RBF were the principal investigators. ARN and FFM established the methodology. SAG, RBF, and ARN coordinated the study. SAG, CBM, RBF, MOA, JD, ASV, and FFM conducted the data collection for the study. MOA and JD performed the data information dump and statistical analysis. SAG wrote the manuscript with the support of CBM and ARN. Finally, all authors read, revised, and approved the manuscript.
Conflict of interestNo conflict of interest to declare.
Funding
No financing to declare.