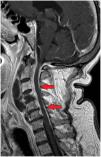
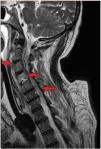
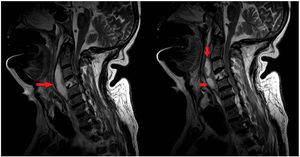
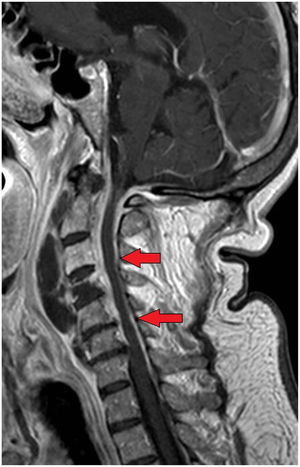
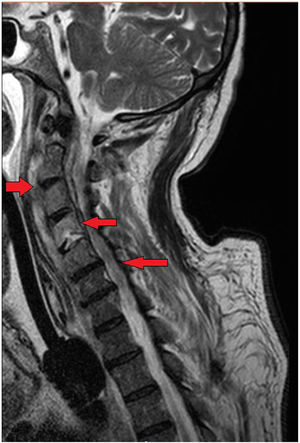
This is the case of a 68-year-old man who works in a pet shop on topical treatment with corticoids and imiquimod. He started having descending palsy and severe respiratory failure. A cervical-dorsal magnetic resonance imaging was performed, and a collection was identified in the C1–C5 paravertebral space that was hyperintense on contrast-enhanced T2-weighted sequence, which was suggestive of an abscessified collection that continues with another C5-D1 collection (Fig. 1). Also, epidural damage on the T1-weighted sequence was found surrounding the medullary cord from C2 to C6 (Fig. 2). The patient underwent emergency surgery and Nocardia abscessus was isolated from the samples obtained. The postoperative magnetic resonance image performed confirmed a reduction of paravertebral collection and the epidural inflammatory component without evidence of collection with persistent hyperintensity on the T2-weighted sequence and damage to the C4 vertebral body (Fig. 3). The patient’s progression was satisfactory with favorable final functional outcome.
Please cite this article as: Martínez de Pinillos Sánchez MV, Amat Serna T, Gordillo Resina MM. Absceso epidural por Nocardia abscessus. Med Intensiva. 2022;46:598–600.