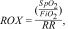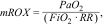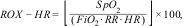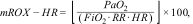To determine whether the ROX index and its variations can predict the risk of intubation in ICU patients receiving NIV ventilation using large public ICU databases.
DesignRetrospective observational cohort study.
SettingPatient data was extracted from both the AmsterdamUMCdb and the MIMIC-IV ICU databases, which contained data related to 20,109 and 50,920 unique patients.
PatientsNon-invasively mechanically ventilated.
InterventionsRetrospective review of variables.
Main variables of interestTo assess the predictive values of models for each index, the ROX and its variations mROX, ROX-HR and mROX-HR were calculated based on mean values of SpO2, respiratory rate, FiO2 and PaO2 from 2-h windows within the first 12 h of NIV.
Results3344 patients were eligible for analysis of which 1344 were intubated, died or returned to NIV within 24 h of ending NIV. NIV failure group had higher SOFA scores and higher CRP levels at admission. There was no difference in duration of NIV therapy or 28-day mortality, but patients who failed NIV had longer length of stay. The best performing index was ROX with an AUROC of 0.626 at 10−12 h. All other indices for all other time windows were less discriminating.
ConclusionsThe performance of ROX index and its variations to predict NIV failure in ICU patients across large public ICU databases was moderate at best and cannot currently be recommended for clinical decision support.
Determinar si el índice ROX y sus variaciones pueden predecir el riesgo de intubación en pacientes de UCI que reciben ventilación VNI, utilizando grandes bases de datos públicas de UCI.
DiseñoEstudio de cohorts observacional retrospectivo.
ÁmbitoLos datos de los pacientes de las bases de datos AmsterdamUMCdb y MIMIC-IV ICU, que contienen datos relacionados con 20.109 y 50.920 pacientes únicos.
PacientesQue recibieron ventilación mecánica no invasiva.
IntervencionesRecogida de variables retrospectiva.
Variables de interés principalesEl cálculo de ROX, mROX, ROX-HR y mROX-HR se basó en valores medios de SpO2, frecuencia respiratoria, FiO2 y PaO2 en periodos de 2 horas durante las primeras 12 horas de VNI. Se utilizó regresión logística para evaluar el valor predictivo de cada modelo.
Resultados3.344 pacientes fueron elegibles para el análisis, de los cuales 1.344 fueron intubados, murieron o regresaron a VNI dentro de las 24 horas posteriores a suspender la VNI. El grupo con fracaso de VNI tenía valores SOFA y niveles de PCR más altos al ingreso. No hubo diferencia en la duración de la terapia de VNI ni en la mortalidad a los 28 días, pero los pacientes que fracasaron en la VNI tuvieron una estancia hospitalaria más prolongada. La mejor actuación la tuvo el índice ROX con un AUROC de 0.626 a las 10−12 horas. Todos los demás índices en todos los demás períodos de tiempo fueron menos discriminatorios.
ConclusiónEl rendimiento del índice ROX y sus variaciones para predecir el fracaso de la VNI en pacientes de UCI a través de grandes bases de datos públicas de UCI fue, en el mejor de los casos, moderado y actualmente no puede recomendarse para el apoyo en decisiones clínicas.
Acute respiratory failure (ARF) is a critical condition marked by the inability of the respiratory system to meet oxygenation or ventilation requirements. Approximately 60% of ARF patients require invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), with a mortality rate of 30% and a leading cause of death in intensive care units (ICUs).1
Non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIV) and high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) are may be used to improve ARF and prevent endotracheal intubation (EI) and invasive mechanical ventilation.2 NIV provides support for ventilation and oxygenation most commonly through a face mask while HFNC mainly supports oxygenation by delivering up to 60 L/min of up to 100% humidified oxygen via the nasal route, may improve dead space CO2 washout and provide a low level of PEEP.3 Both modalities have become prevalent in ICUs.4 Recent guidelines indicate no significant difference in efficacy between HFNC and NIV for ARF treatment, although NIV is preferred in acute pulmonary edema and COPD.5–7 Both NIV and HFNC failure and subsequent delayed intubation can increase the mortality rate by up to 27–56%.8,9
The respiratory rate-oxygenation (ROX) index, defined as the ratio of oxygen saturation (SpO2) to the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) divided by the respiratory rate (RR), can be easily and repetitively calculated from routinely collected data and was shown to have strong predictive performance for HFNC outcomes, and particularly for the need for intubation.10,11 Modified versions, such as the mROX (incorporating PaO2) and ROX-HR (normalization for heart rate), have also demonstrated good predictive performance in this setting.12,13 However, these indices have not been validated for predicting failure of NIV therapy.
This study aims to determine if the ROX index and its variations can predict the risk NIV therapy failure ICU patients using large public ICU databases containing highly granular routinely collected real world data.14
MethodsThis report adheres to the STROBE reporting guidelines.15 Patient data was extracted exclusively from the publicly available AmsterdamUMCdb and MIMIC-IV databases and further ethics review was therefore not required.
Data preprocessingThe European AmsterdamUMCdbn is an ICU database that contains data from a 32-bed mixed surgical-medical academic ICU and a 12-bed high-dependency unit with 1 billion clinical data points related to 23,106 admissions of 20,109 unique patients between 2003 and 2016.16 The Northern American MIMIC-IV is an ICU database with data related to 50,920 unique patients covering 73,181 admissions between 2008 and 2019.16,17 From these databases we selected patients that underwent NIV in PS/CPAP mode. We excluded patients that received NIV after an episode of invasive mechanical ventilation. Only first episode of NIV ventilation for each patient was included.
Patients’ demographic data (age group, height group and gender) was extracted, and SOFA score at admission calculated. For this study we approximated patients’ weight from categorical data using arithmetic mean normalized for body height. Blood oxygen saturation was extracted from blood samples as a priority source, if blood samples were not available, value from pulse oximetry was used. Simultaneous FiO2 values and PaO2 values were extracted in such way that nearest FiO2 from the ventilator or estimated FiO2 based on applied oxygen device was used relative to PaO2 from blood samples. Allowed time difference between those two measurements was 1 h. Respiratory values were taken from ventilator data as a priority source, if not available patient monitor data were used. Outliers were removed upon each variable extraction, and mean values were then taken for each 2-h window for blood oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, heart rate, fraction of inspired oxygen and PaO2 for the time patients were NIV ventilated, and aggregate measures used to calculate respiratory indices.
Indices calculationsThe ROX (I), mROX (II) and two newly emerged variations that add heart rate into calculations, ROX-HR (III) and mROX-HR (IV) were calculated as follows:
where SpO2 is mean blood oxygen saturation from 2-h windows, FiO2 is mean oxygen flow in a 2-h window, PaO2 is the mean arterial oxygen partial pressure in a 2-h window, RR mean respiratory rate for the 2-h window, and HR is the mean heart rate frequency for the specified 2-h window.OutcomesIndices were compared in terms of their distribution and predictive power between two independent groups designated as “NIV success” – patients who were not intubated within 24 h of NIV PS/CPAP episode end, were not returned to NIV within 24 h after NIV episode end, and did not die during NIV ventilation or within 24 h after an end of NIV ventilation episode, and “NIV failure” – patients intubated within 24 h of NIV PS/CPAP episode end, patients returned to NIV within 24 h after NIV episode end, and died during NIV ventilation or within 24 h after an end of NIV ventilation episode.
Statistical analysisNormality of distribution of variables was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The differences between quantitative variables were analyzed using t-test for normally distributed variables and nonparametric tests were applied to variables that were not normally distributed. Continuous variables are shown as mean ± standard deviation, or median (Q1, Q3), as appropriate. The differences between qualitative variables were compared using χ2 test or Fishers exact test (for frequencies less than 5), where necessary. Values are presented as number and corresponding percentage, unless specified otherwise. Logistic regression was performed to assess the predictive value of models, and results graphically presented as ROC-AUROC curves and, to account for potentially unbalanced dataset, precision-recall curves. All statistical analyses were two-tailed, and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. For statistical analysis, Python’s SciPy v.1.9.1 was used, and graphical representations were made using Python’s Matplotlib v.3.2.2.18
Data availabilityData used for this study is available to intensivists and data scientists upon completion of CITI Data or Specimens Only Research training and a referral from an intensivist. The complete code review used for this study is available upon reasonable request to authors.
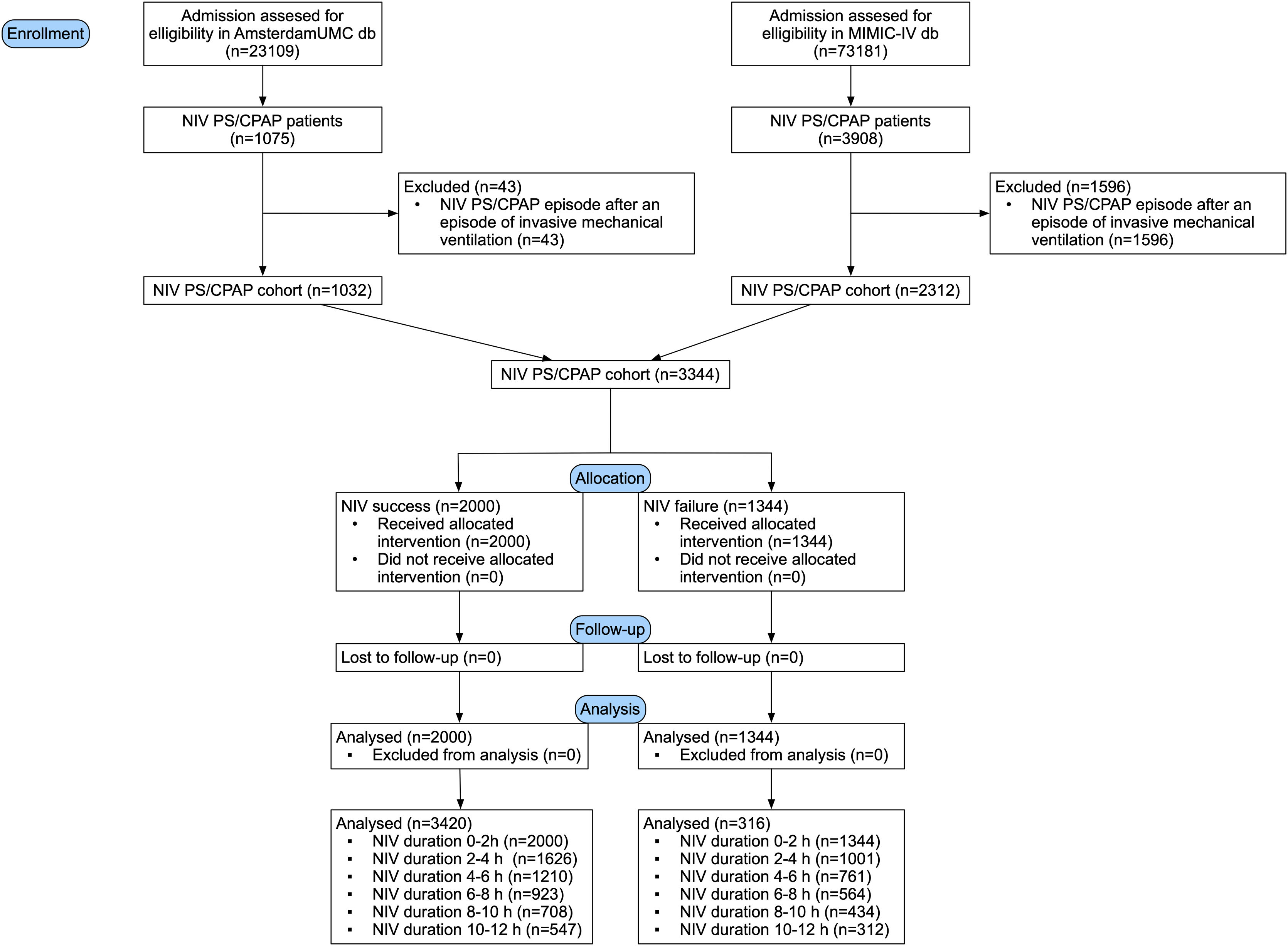
ResultsThe AmsterdamUMCdb database contained 1075 patients who underwent episodes of NIV and we identified 3908 potential patients in MIMIC-IV database. After application of exclusion criteria, a total of 3344 patients were eligible for analysis, with 1344 (40.2%) patients designated as NIV failure within 24 h after an end of a NIV episode. The patient selection process is shown in Fig. 1.
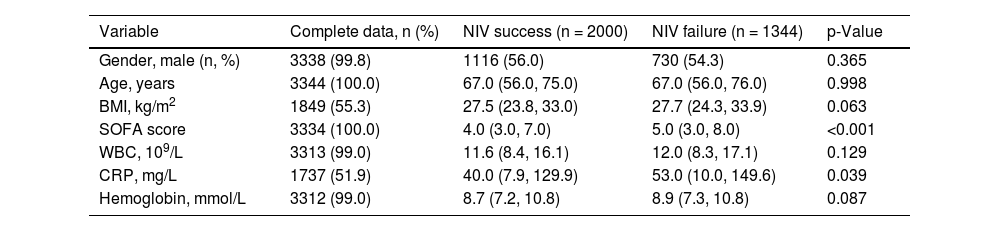
Patients baseline characteristics are presented in Table 1 and are stratified by source database in Appendix A Table 1. NIV failure patients had higher admission SOFA scores and higher CRP values. Patients were ventilated for relatively short periods of time, median 5.5 h (3.0, 11.0) for NIV success group and 5.0 h (2.9, 10.3) for NIV failure group, but without statistically significant difference between the groups.
Patient characteristics at admission.
| Variable | Complete data, n (%) | NIV success (n = 2000) | NIV failure (n = 1344) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, male (n, %) | 3338 (99.8) | 1116 (56.0) | 730 (54.3) | 0.365 |
| Age, years | 3344 (100.0) | 67.0 (56.0, 75.0) | 67.0 (56.0, 76.0) | 0.998 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 1849 (55.3) | 27.5 (23.8, 33.0) | 27.7 (24.3, 33.9) | 0.063 |
| SOFA score | 3334 (100.0) | 4.0 (3.0, 7.0) | 5.0 (3.0, 8.0) | <0.001 |
| WBC, 109/L | 3313 (99.0) | 11.6 (8.4, 16.1) | 12.0 (8.3, 17.1) | 0.129 |
| CRP, mg/L | 1737 (51.9) | 40.0 (7.9, 129.9) | 53.0 (10.0, 149.6) | 0.039 |
| Hemoglobin, mmol/L | 3312 (99.0) | 8.7 (7.2, 10.8) | 8.9 (7.3, 10.8) | 0.087 |
Values are median (Q1, Q3) or n (%). BMI — body mass index, WBC — white blood cell count, CRP — C-reactive protein.
Data completeness for calculating dynamic indices varied across time points and between databases. In the Amsterdam UMC ICU database, the highest availability was observed for the ROX index during the first 2 h of NIV (88.2%), while the mROX-HR index had the lowest availability at 10−12 h (16.5%). In the MIMIC-IV database, availability was generally lower, ranging from 26.6% for the ROX index at 0−2 h to 3.5% for the mROX-HR index at 10−12 h. In contrast, static demographic and baseline clinical data, such as age and gender, were nearly complete across both databases, reflecting the ease of capturing these infrequent, high-granularity variables compared to the time-sensitive, high-frequency ventilatory and hemodynamic data. Full details are provided in Appendix A.
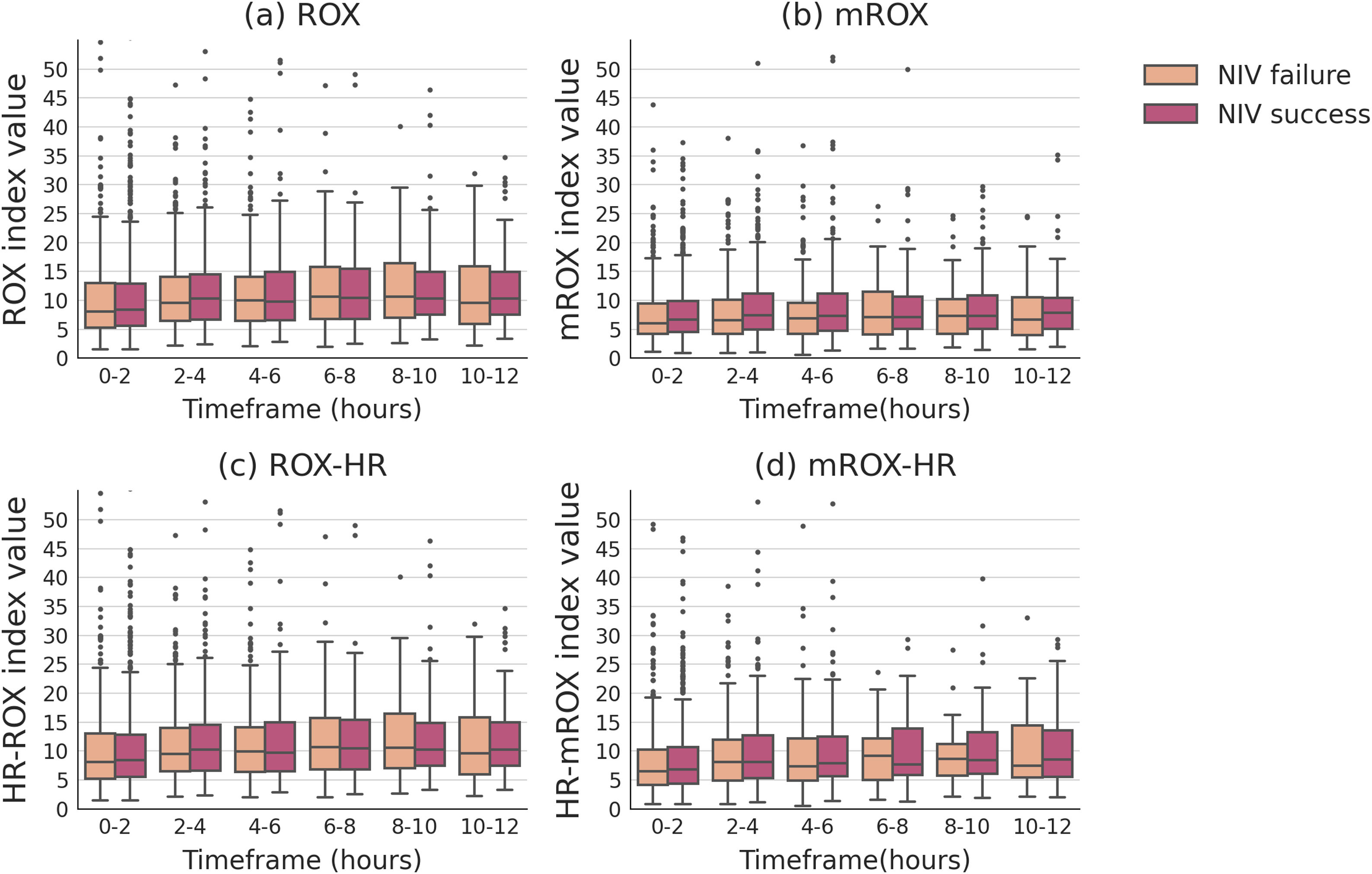
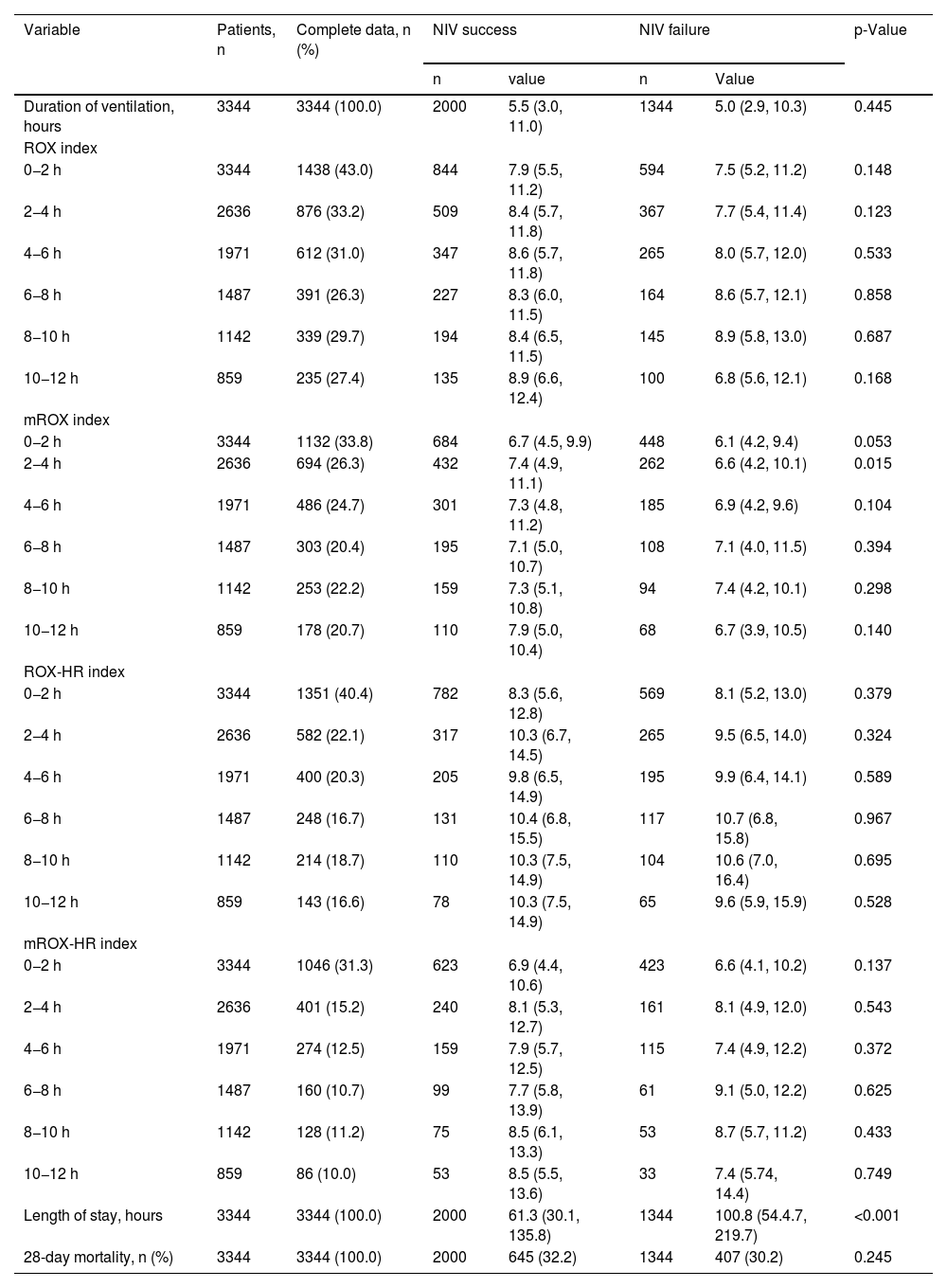
The ROX index did not show statistically significant differences between the NIV success and failure groups across any of the time windows assessed. Similarly, the mROX index showed no significant differences in most time intervals, with the exception of a significant difference observed at the 2−4 h window (p = 0.015). After this period, the differences between the two groups for the mROX index were not statistically significant in the later time points. For the ROX-HR and mROX-HR indices, no statistically significant differences were found between the success and failure groups at any time window. Across all time intervals, both indices demonstrated comparable values between the groups. Additionally, patients in the NIV failure group had a significantly longer median length of hospital stay (100.8 h [54.4, 219.7]) compared to the success group (61.3 h [30.1, 135.8]) (p < 0.001). However, no significant difference in 28-day mortality was observed between the success group (32.2%) and the failure group (30.2%) (p = 0.245). The detailed results are presented in Table 2 and Fig. 2, with complete data available in Appendix A.
Data availability and differences in computed indices and outcomes between NIV success and NIV failure groups.
| Variable | Patients, n | Complete data, n (%) | NIV success | NIV failure | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | value | n | Value | ||||
| Duration of ventilation, hours | 3344 | 3344 (100.0) | 2000 | 5.5 (3.0, 11.0) | 1344 | 5.0 (2.9, 10.3) | 0.445 |
| ROX index | |||||||
| 0−2 h | 3344 | 1438 (43.0) | 844 | 7.9 (5.5, 11.2) | 594 | 7.5 (5.2, 11.2) | 0.148 |
| 2−4 h | 2636 | 876 (33.2) | 509 | 8.4 (5.7, 11.8) | 367 | 7.7 (5.4, 11.4) | 0.123 |
| 4−6 h | 1971 | 612 (31.0) | 347 | 8.6 (5.7, 11.8) | 265 | 8.0 (5.7, 12.0) | 0.533 |
| 6−8 h | 1487 | 391 (26.3) | 227 | 8.3 (6.0, 11.5) | 164 | 8.6 (5.7, 12.1) | 0.858 |
| 8−10 h | 1142 | 339 (29.7) | 194 | 8.4 (6.5, 11.5) | 145 | 8.9 (5.8, 13.0) | 0.687 |
| 10−12 h | 859 | 235 (27.4) | 135 | 8.9 (6.6, 12.4) | 100 | 6.8 (5.6, 12.1) | 0.168 |
| mROX index | |||||||
| 0−2 h | 3344 | 1132 (33.8) | 684 | 6.7 (4.5, 9.9) | 448 | 6.1 (4.2, 9.4) | 0.053 |
| 2−4 h | 2636 | 694 (26.3) | 432 | 7.4 (4.9, 11.1) | 262 | 6.6 (4.2, 10.1) | 0.015 |
| 4−6 h | 1971 | 486 (24.7) | 301 | 7.3 (4.8, 11.2) | 185 | 6.9 (4.2, 9.6) | 0.104 |
| 6−8 h | 1487 | 303 (20.4) | 195 | 7.1 (5.0, 10.7) | 108 | 7.1 (4.0, 11.5) | 0.394 |
| 8−10 h | 1142 | 253 (22.2) | 159 | 7.3 (5.1, 10.8) | 94 | 7.4 (4.2, 10.1) | 0.298 |
| 10−12 h | 859 | 178 (20.7) | 110 | 7.9 (5.0, 10.4) | 68 | 6.7 (3.9, 10.5) | 0.140 |
| ROX-HR index | |||||||
| 0−2 h | 3344 | 1351 (40.4) | 782 | 8.3 (5.6, 12.8) | 569 | 8.1 (5.2, 13.0) | 0.379 |
| 2−4 h | 2636 | 582 (22.1) | 317 | 10.3 (6.7, 14.5) | 265 | 9.5 (6.5, 14.0) | 0.324 |
| 4−6 h | 1971 | 400 (20.3) | 205 | 9.8 (6.5, 14.9) | 195 | 9.9 (6.4, 14.1) | 0.589 |
| 6−8 h | 1487 | 248 (16.7) | 131 | 10.4 (6.8, 15.5) | 117 | 10.7 (6.8, 15.8) | 0.967 |
| 8−10 h | 1142 | 214 (18.7) | 110 | 10.3 (7.5, 14.9) | 104 | 10.6 (7.0, 16.4) | 0.695 |
| 10−12 h | 859 | 143 (16.6) | 78 | 10.3 (7.5, 14.9) | 65 | 9.6 (5.9, 15.9) | 0.528 |
| mROX-HR index | |||||||
| 0−2 h | 3344 | 1046 (31.3) | 623 | 6.9 (4.4, 10.6) | 423 | 6.6 (4.1, 10.2) | 0.137 |
| 2−4 h | 2636 | 401 (15.2) | 240 | 8.1 (5.3, 12.7) | 161 | 8.1 (4.9, 12.0) | 0.543 |
| 4−6 h | 1971 | 274 (12.5) | 159 | 7.9 (5.7, 12.5) | 115 | 7.4 (4.9, 12.2) | 0.372 |
| 6−8 h | 1487 | 160 (10.7) | 99 | 7.7 (5.8, 13.9) | 61 | 9.1 (5.0, 12.2) | 0.625 |
| 8−10 h | 1142 | 128 (11.2) | 75 | 8.5 (6.1, 13.3) | 53 | 8.7 (5.7, 11.2) | 0.433 |
| 10−12 h | 859 | 86 (10.0) | 53 | 8.5 (5.5, 13.6) | 33 | 7.4 (5.74, 14.4) | 0.749 |
| Length of stay, hours | 3344 | 3344 (100.0) | 2000 | 61.3 (30.1, 135.8) | 1344 | 100.8 (54.4.7, 219.7) | <0.001 |
| 28-day mortality, n (%) | 3344 | 3344 (100.0) | 2000 | 645 (32.2) | 1344 | 407 (30.2) | 0.245 |
Values are median (Q1, Q3) or n (%).
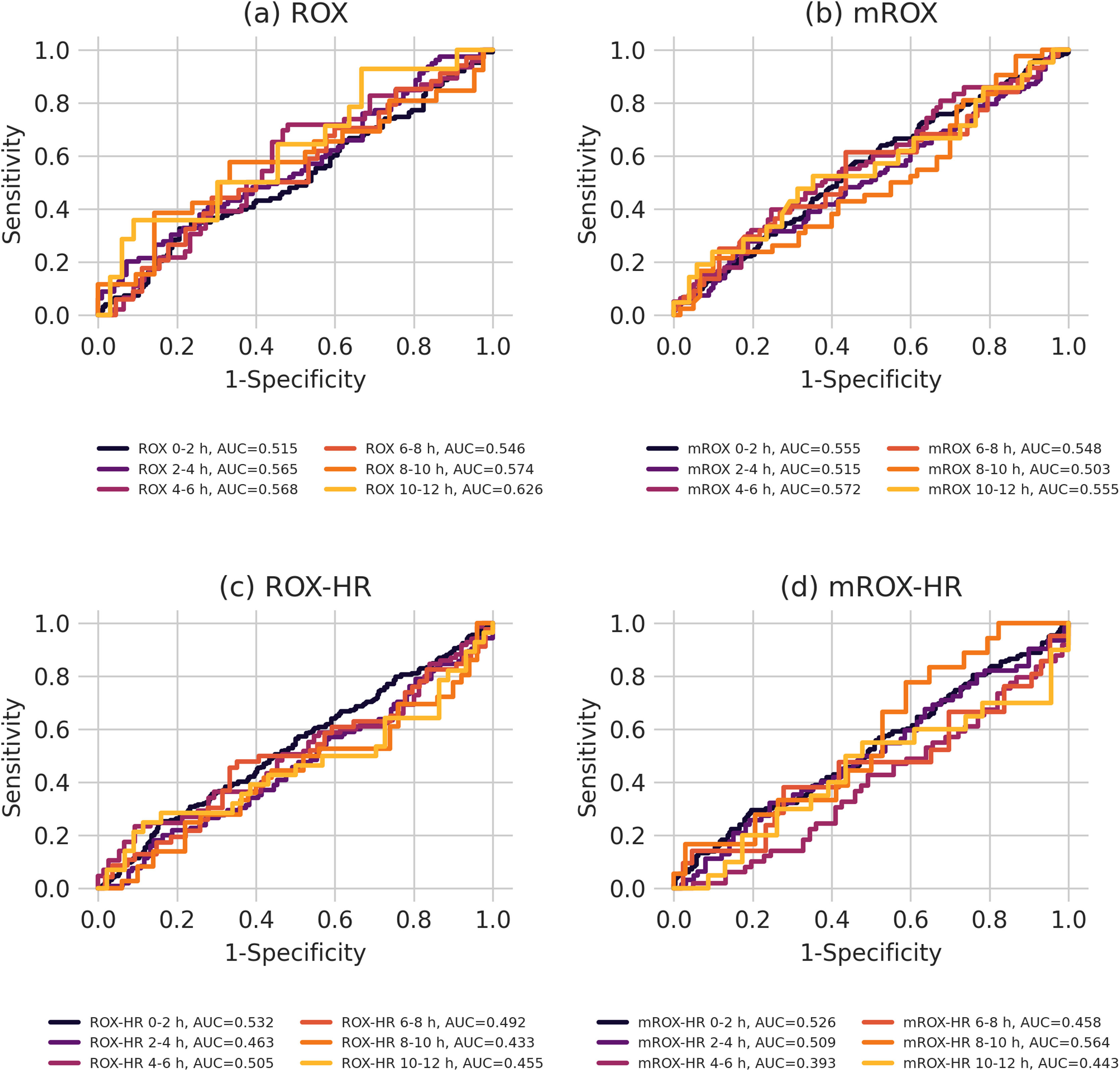
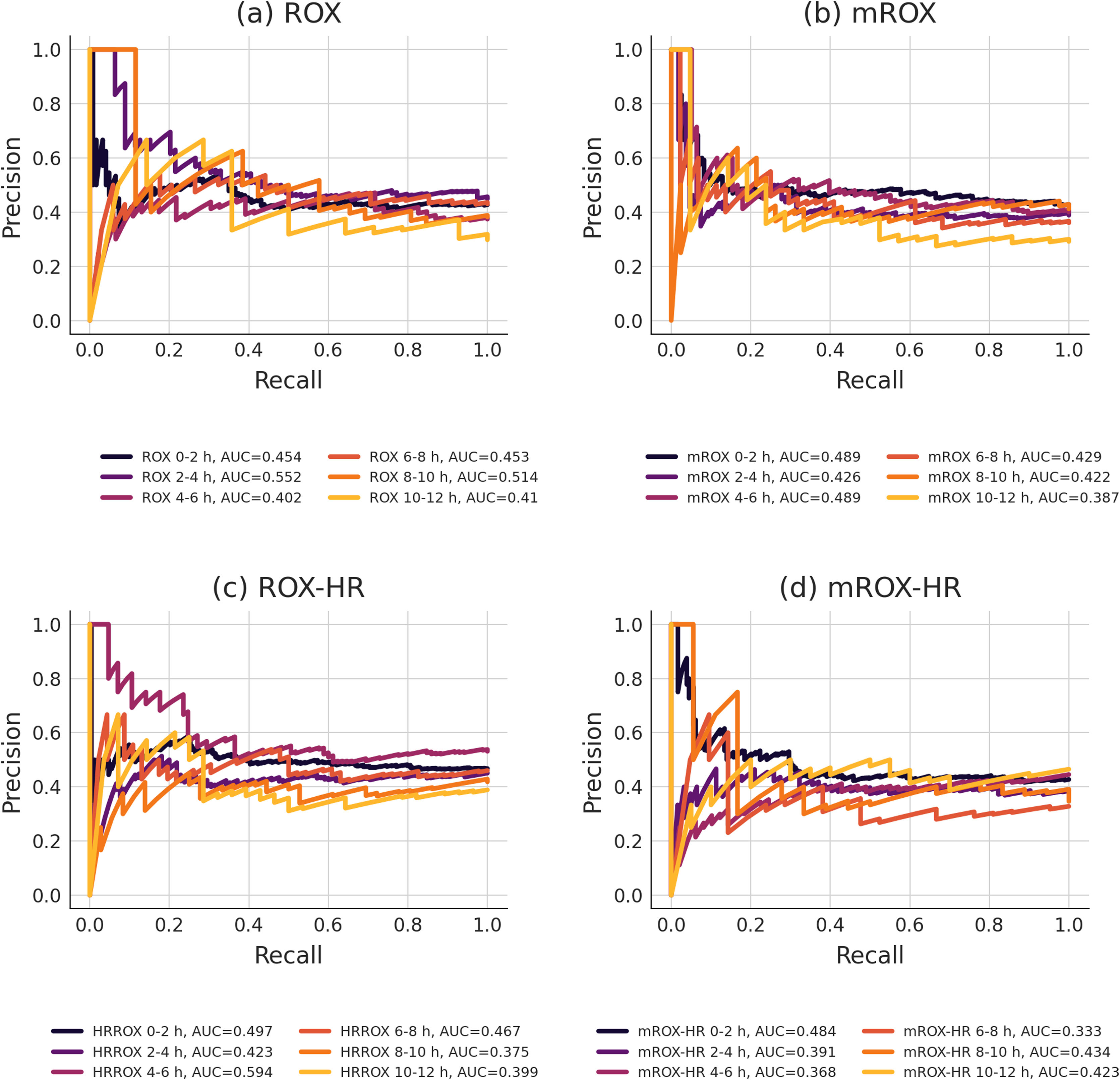
The AUROC and precision-recall (PR) curve analyses for the ROX, mROX, ROX-HR, and mROX-HR indices showed consistently low to moderate predictive accuracy across different time windows. For the ROX index, the AUROC scores remained relatively low overall. The AUROC ranged from 0.515 at 0−2 h to 0.626 at 10−12 h. Precision-recall analysis showed somewhat consistent results, with the PR curve at 2−4 h showing the highest performance with a value of 0.552. The PR curve was lowest at 10−12 h with a value of 0.410. The mROX index demonstrated more stable AUROC values, peaking at 0.572 during the 4–6-h window. However, the precision-recall analysis indicated lower overall performance, with the PR curve ranging from 0.489 at 4−6 h to 0.387 at 10−12 h. Both the AUROC and PR curves displayed consistent performance across most time periods. For the ROX-HR index, the highest AUROC value was observed at 0−2 h (0.532), while the lowest was at 10−12 h (0.455). Precision-recall analysis revealed a higher PR curve value during the 4–6-h window (0.594), while lower values were observed at other time points, such as 0.375 at 8−10 h. Finally, the mROX-HR index had the lowest overall performance in both AUROC and PR curve analyses. The AUROC values remained below 0.526 throughout, with the highest observed for 0−2 h. Precision-recall analysis mirrored these results, with the highest PR curve value reaching 0.484 for 0−2 h and dropping as low as 0.333 at 6−8 h. Results are summarized in Figs. 3 and 4.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the performance of the ROX index and its variations to predict the risk of NIV therapy failure in ICU patients using real world data from two large publicly available ICU databases. We found that ROX index and its variations mROX, ROX-HR, and mROX-HR do not differentiate between NIV therapy success or failure, but their predictive performance must be considered moderate at best with only ROX at 10−12 h after start of NIV ventilation reaching a clinically acceptable value (AUROC = 0.626).
The original ROX index has previously been shown to have good predictive performance for intubation within 24 h for patients on HFNC due to community-acquired pneumonia or SARS-CoV-2 ARF.19,20 Similarly, a recent study has demonstrated the ROX index as a good predictor for invasive IMV in patients receiving HFNC due to pneumonia, with an area under the curve of receiver operating characteristics (AUROC) of 0.77 after 24 h.21
Data on the performance of the original ROX index to predict NIV failure is limited. For patients with de novo acute respiratory failure, the ROX index was used to predict NIV failure at 12 h of ventilation yielding an AUROC of 0.74, comparable to our findings and also moderately discriminating at best.22 Similar to our study, patients with NIV failure had higher SOFA scores (median 4.0 vs. 5.0, p < 0.001) compared to those with NIV success. Our study included a larger sample size (3344 vs. 1286 patients) and had a lower percentage of NIV failure (59.8% vs. 40.1%). A recent retrospective study on the ROX index's predictive value for NIV failure within 48 h after initiation in COVID-19 patients showed an AUROC of 0.86, indicating good predictive performance.23 However, this study involved only 72 patients, with 50 requiring mechanical ventilation and NIV failure of only 26%, with calculated ROX index values while patients were breathing room air before starting ventilatory support.
Variations of the original ROX index include dividing ROX by heart rate to yield the ROX-HR index and substituting SpO2 with PaO2 to yield the mROX and mROX-HR indices. It has been found that the mROX index has AUROC values over 0.8 for predicting HFNC failure two hours after initiation with similar predictive performance reported for ROX-HR and mROX-HR.24 For COVID-19 patients, the mROX had an AUROC of 0.956 after two hours, compared to 0.894 for the ROX index.25 To our knowledge, none of these modified versions of the ROX index have previously been studied as potential tools for predicting the failure of NIV/CPAP ventilation. In our study, the highest AUROC values were 0.626 for ROX at 10−12 h after NIV initiation, with none of the other indices in any of the timepoints reaching at least moderate predicting value.
Reasons for worse performance of ROX index and derivatives for NIV failure compared to HFNC may be versatile. HFNC is easier to tolerate, may be chosen for less severe patients and might deliver lower but more constant flows. ICU ventilators are deigned to compensate for high flows and system leaks for up to 120 L/min but demands in respiratory distress syndrome can go up to 200 L/min of peak inspiratory flow rate if the leak in the circuit is present, affecting the final FiO2 delivered.26,27 Findings based on research on models and ideally breathing subjects suggest that increasing leaks lead to more frequent auto-triggering and miss-triggering, causing constant tidal volume delivery problems.28 Integrating flow considerations into the formula could provide a more accurate assessment of patient status in scenarios with variable leak and flow conditions.
This study comes with limitations. These include lack of data completeness, especially for longer durations of NIV as well as a surprisingly low number of patients who had complete data for NIV ventilation for 10 h or more. Data from Amsterdam UMC has good density of granular data for this type of research, but MIMIC-IV, as suggested by previous research, suffered from lack of granularity.29 Another limitation may be that, due to relatively rare data on PaO2 compared to FiO2, oxygen saturation and respiratory rate available in the database, values had to be extracted in such way that the nearest FiO2 from the ventilator or estimated FiO2, not more than 1 h apart, had to be used, a design that would certainly be improved if the study was prospective. Additionally, in some cases databases designate modes of respiratory support under a combined CPAP/NIV label, making it impossible to assess whether the effect of the indices differs between CPAP and NIV specifically.
In conclusion, neither ROX index nor any of the modified indices demonstrated sufficient predictive value to be useful tools for predicting NIV failure and cannot currently be recommend for clinical use. Predictive power should be tested in addition to other tools used for respiratory monitoring.
CRediT authorship contribution statementLL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Data curation, Writing, Visualization, Formal Analysis. PE: Supervision, Writing – Rewriting & Editing, Methodology, Resources. TR, NK, MV: Writing – Rewriting & Editing.
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing processNo generative AI system has been used in the writing or editing of this manuscript.
FinancingNone.