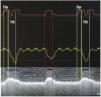
Ultrasonography of the diaphragm is increasingly used in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and constitutes an innovating tool for the detection of asynchrony. We present an image showing the perfect correlation between esophageal pressure and diaphragmatic displacement, with the possibility of establishing a precise diagnosis of reverse trigger (RT). The upper part of the image shows the curves corresponding to airway pressure, esophageal pressure and diaphragmatic excursion through ultrasonography. In the first respiratory cycle, initial elevation of the diaphragm corresponds to passive motion due to lung insufflation, followed by a further elevation corresponding to an involuntary contraction (RT). The combination of respiratory curve monitoring with ultrasonography of the diaphragm allows us to detect asynchronies without the need for an esophageal balloon figura 1.
Conflicts of interestNone.
Financial supportNone.