Non-cryptogenic organising pneumonia (OP) secondary to a Pneumocystis jirovecii infection is a rare condition described in HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection, lung and liver transplantation; in this brief report we discuss the first clinical case in a patient not severely immunocompromised.
He was a 63 year-old man who consulted our centre's Emergency Department referring a 2 month long history of progressive dyspnoea and purulent sputum, oriented by general practitioner as an acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and treated with bronchodilators and amoxicillin-clavulanate. Two weeks before consulting dyspnoea became severe. Twenty-four hours before admission he referred fever (38°C) and left pleural chest pain.
He was an active smoker (45 packs/year), ex-alcoholic, suffered from epilepsy well controlled with valproic acid for the last 2 years, hemochromatosis without organic impairment, an arytenoid carcinoma removed in 2009 endoscopically without relapse and a seronegative arthritis treated with methotrexate since 2009 with irregular medication intake (white blood cell count two months before admission was 10,200 leucocytes, 8520 neutrophils, 1560 lymphocytes).
He had worked as a subway driver, did not travel, and neither had pets.
Initial tests performed in the Emergency Department were: chest X-ray showing cardiomegaly; blood testing showing 9400 leukocytes, 8836 neutrophils, 654 lymphocytes; haemostasis, renal and hepatic functions were under normal parameters.
A lower respiratory tract infection was diagnosed and treated empirically with 40mg/day corticosteroids, azytromicin, ceftriaxone and cotrimoxazole. Blood and sputum cultures, typical and atypical pneumonia antigenurias (urinary pneumococcal antigen detection) and serologies were negative as well as HIV. Antinuclear and antinuclear extractable auto-antibodies resulted negative.
He developed a progressive severe respiratory insufficiency with increasing interstitial opacities in chest X-ray, and the 7th day after admission he required intubation, mechanical ventilation with an oxygen injection fraction of 1, being transferred to the Intensive Care Unit. Trans-thoracic echocardiography ruled out valvular alterations or decreased ventricular ejection fraction.
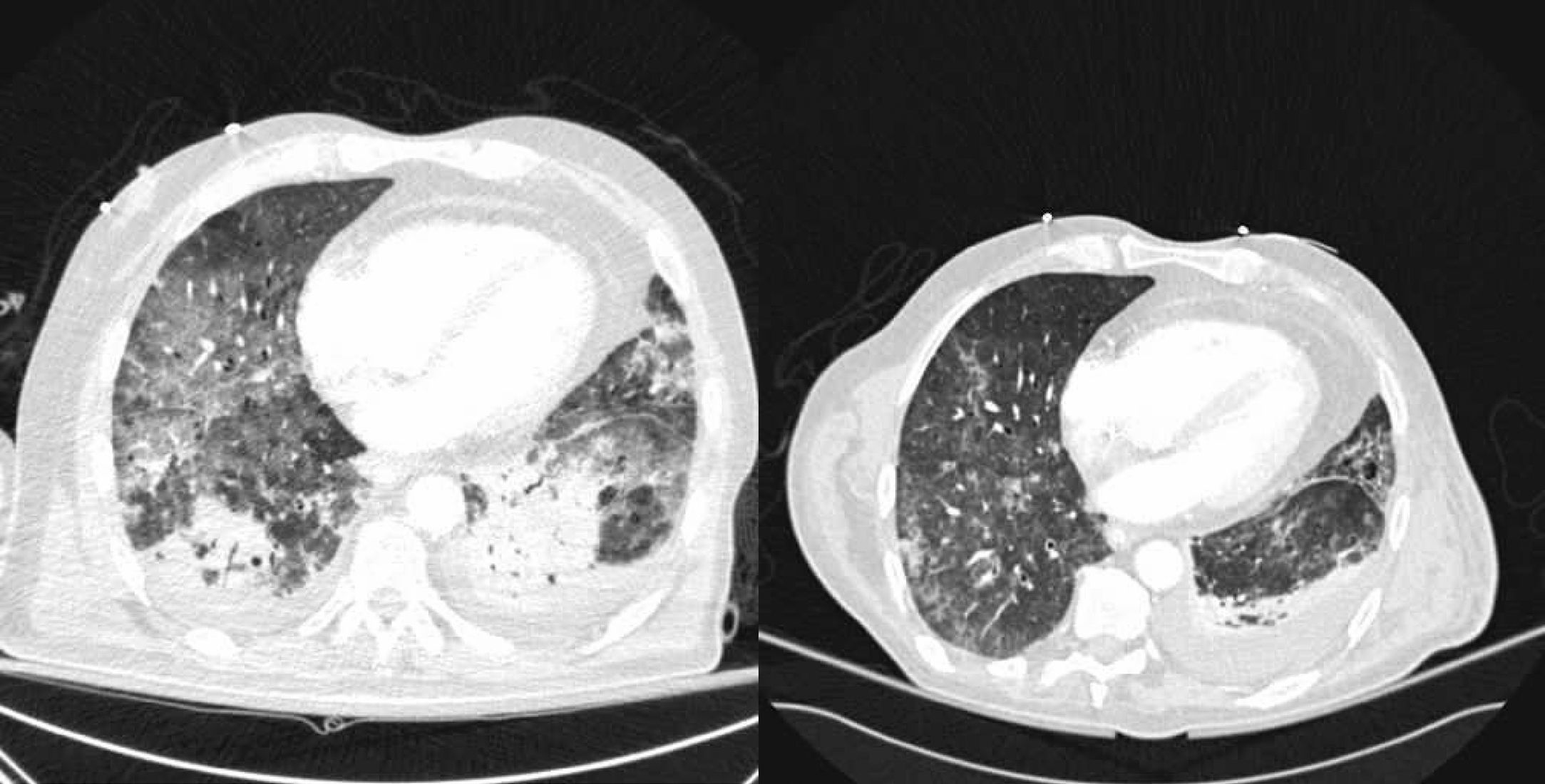
Suspecting lung interstitial pathology a biopsy by fibrobronchoscopy was performed and three metilprednisolone 1g boluses were administered empirically. The patient improved after 2 days and computerised tomography scanning (CT scanning) was performed (Fig. 1), showing diffuse acute pulmonary damage, composed of ground glass areas associated to consolidation zones in inferior lobes, mild pleural effusion and cystic images suggestive of emphysema.
Initial results from transbronchial biopsy showed absence of malignancy, presence of widened septums due to fibrosis, mild inflammatory component with a lymphocytic predominance, and fribrin depots in the alveoli, all being diagnostic of an acute organising pneumonia.
The patient kept diminishing oxygen demands and the 11th day after admission the final biopsy result showed presence of P. jirovecii, in spite of being treated with cotrimoxazole 800mg/day.
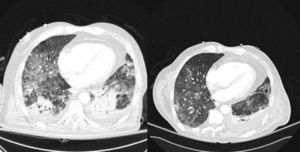
Control thoracic CT scanning was performed the 16th day since admission, showing residual ground glass areas and a mild left pleural effusion. The patient was extubated the 18th day after admission.
The patient was oriented as a non-cryptogenic organising pneumonia, secondary to a P. jirovecii infection. He kept receiving 60mg/day of metilprednisolone for a month and later was tapered down gradually. He also completed 3 weeks of treatment against the infection, replacing cotrimoxazole for inhaled pentamidine due to hyperkalemia. He completed a 6 month follow up, with radiologic resolution of the infiltrates, mild ventilatory obstruction and remaining clinically asymptomatic without treatment.
In 1990, Liote et al.1 described for the first time HIV patients suffering from P. jirovecii infection who developed synchronically bronchiolitis obliterans, nowadays known as OP, that was thought to appear in context of a great inflammatory reaction induced by the infection. Afterwards other authors described the same process in lung and liver transplanted subjects.2–4 The underlying pathogenic mechanism is still unknown but reports of P. jirovecii-related type 1 pneumocytes related damage or proteolysis,5,6 as well as documentation of acute alveolar damage7 in HIV patients, may show an important inflammatory background that could lead to the formation of the interstitial pneumonia architecture.
OP is an exclusion diagnosis8 and obtaining a biopsy specimen is mandatory. This case report, after ruling out HIV, bacterial or viral agents different from P. jirovecii; collagen diseases or other interstitial entities, could represent the first non-cryptogenic OP associated to P. jirovecii pneumonia reported in a patient who does not meet the conditions described before in literature. He had no lymphopenia, and neither neutropenia in previous tests, which are the best markers for immunosuppression due to methotrexate; although immunosuppressor intake and the subject's previous medical history may raise reasonable doubts about a completely intact immune system function. Drug induced pulmonary damage was not considered responsible because it had been introduced 2 years before at low doses and biopsy did not match with toxicity. The fact that the patient responded well and fast to high corticosteroid doses, instead to cotrimoxazole and medium corticosteroid doses, suggests that acute OP was the main responsible of the clinic. Acute onset OP has been associated to a poor prognosis9 and high dose corticosteroids are the main treatment.
Diagnosis of OP includes systematic ruling out of other aetiologies and a corresponding biopsy. Non-cryptogenic OP associated to P. jirovecii infection has been described in some severely immunosuppressed patients. In this report we describe the first case in a patient that does not meet those medical conditions. High dose corticosteroids and specific antibiotics have shown to be a successful treatment for this patient.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
We would like to acknowledge Prof. Ferran Morell for his support.