To identify published research on the Shock Index (SI) in patients with septic shock or severe sepsis and to describe its main findings and conclusions.
DesignSystematic review of the literature following the recommendations of the PRISMA protocol (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses).
SettingsThe following databases were consulted: Pubmed, Embase, Library Cochrane and Lilacs.
PatientsPatients older than 14 years with septic shock. Pregnant women and population with COVID-19 were excluded.
InterventionsStudies reporting measurement of the shock index or its modified variants.
Main variables of interestAbsolute frequencies and relative frequencies were assessed with measures of central tendency and dispersion. Effect estimators (OR, RR and HR) were extracted according to the context of each study.
ResultsSeventeen articles were included, of which 11 investigated the SI as a predictor of mortality. Seven of them found significant differences in the SI when comparing survivors to non-survivors and observed a relationship between the SI evolution and clinical outcomes. Additional research evidenced a relation between the Modified Shock Index and myocardial depression, as well as mortality. Furthermore, they identified a relationship between the Diastolic Shock Index, the dose of administered dobutamine, and mortality.
ConclusionsThe results suggest that both the SI and its modified versions, particularly in serial assessments, can be considered for evaluating patient prognosis. The SI can also aid in determining fluid management for patients.
Identificar las investigaciones publicadas sobre el Índice de Shock (IS) en pacientes con choque séptico o sepsis severa y describir sus principales resultados y conclusiones.
DiseñoRevisión sistemática de la literatura siguiendo las recomendaciones del protocolo PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses).
ÁmbitoSe consultaron las bases de datos: Pubmed, Embase, Library Cochrane y Lilacs.
PacientesPacientes mayores de 14 años con choque séptico. Se excluyeron mujeres embarazadas y población con COVID-19.
IntervencionesEstudios que reportaran la medición del índice de choque o sus variantes modificadas.
Variables de interés principalesSe evaluaron frecuencias absolutas y frecuencias relativas con medidas de tendencia central y dispersión. Se extrajeron estimadores de efecto (OR, RR y HR) según el contexto de cada estudio.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 17 artículos, de los cuales 11 investigaron el IS como un predictor de mortalidad. 7 encontraron diferencias significativas en el IS al comparar supervivientes de no supervivientes, y observaron una relación entre la evolución del IS y los resultados clínicos. Investigaciones adicionales evidenciaron una relación entre el Índice de Shock Modificado y la depresión miocárdica, así como con la mortalidad. Además, identificaron una relación entre el Índice de Shock Diastólico, la dosis de dobutamina administrada y la mortalidad.
ConclusionesLos resultados sugieren que tanto el IS como sus versiones modificadas, principalmente en evaluaciones seriadas, pueden ser tenidos en cuenta para evaluar el pronóstico del paciente. El IS también puede ser útil en definir el uso de líquidos en los pacientes.
The Shock Index (SI) is defined as the ratio between heart rate (HR) and systolic blood pressure (SBP). This index is a simple and quick measure that is part of the initial evaluation of a patient’s hemodynamic status in emergency settings,1 and is primarily used in patients with hemorrhagic shock, where it has been associated with various clinical outcomes or tissue perfusion parameters.2
Although it has an easily understandable physiological rationale, few studies have explored its measurement in patients diagnosed with sepsis or septic shock.3 A previous systematic review identified only five publications that evaluated SI in patients with septic shock.4 However, in recent years, new studies have been published that continue to highlight the importance of this index in prognosis,3 and recently other forms of evaluating SI have been described, such as the Modified Shock Index (MSI) and the Diastolic Shock Index (DSI), considering the pathophysiological basis of sepsis, with results suggesting a benefit in using it as a prognostic tool and potentially for the management of these patients.5,6
The latest version of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) recommends measuring mean arterial pressure and establishes a therapeutic target for this measure during the initial management of patients with septic shock. Additionally, they suggest measuring blood lactate and capillary refill time as a way to evaluate tissue perfusion status, recommending their normalization when altered. Although other hemodynamic and tissue perfusion variables have been investigated, the SSC does not offer recommendations on evaluating other types of physiological variables.7 SI may be a useful measure to complement patient care, particularly due to its ease of measurement in any medical care setting. The objective of this review is to determine the association of SI and its various derivatives with clinical outcomes and mortality in patients with septic shock.
Patients and methodsWe conducted a systematic literature review, including observational studies (cohorts, case-controls, cross-sectional) and experimental studies in humans, published in any language from 1969 through September 2023, which included adult patients diagnosed with severe sepsis or septic shock (using a standardized definition), and evaluated SI (heart rate/systolic blood pressure) or some modified version including the MSI (HR/MAP) (MAP, mean arterial pressure) and the DSI (HR/DBP) (DBP, diastolic blood pressure). Studies published in abstract format or that could not be obtained in full text, studies in COVID-19 patients, and obstetric populations were excluded. The protocol for this systematic review was registered in PROSPERO with No. CRD42023473588.
Search structureA systematic literature search was conducted across various databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Lilacs. In PubMed, the search structure used was: ((((shock index) OR Modified shock index) OR index shock) OR (Diastolic shock index)) AND (((((((“Sepsis”[Mesh]) OR “Sepsis”) OR septic shock) OR severe sepsis) OR “Shock, Septic”[Mesh]) OR septic) OR sepsis septic) Filters: Humans. In the Lilacs database, the structure used was: ((tw:((tw:(choque septico)) OR (tw:(sepsis)) OR (tw:(septico)) OR (tw:(septicemia)) OR (tw:(sepsis severa)))) AND (tw:((tw:(index shock)) OR (tw:(shock index)))). A manual search of all references of articles that met the inclusion criteria was also conducted, and sources of grey literature including Google Scholar, OpenGrey, and ClinicalTrials.gov were reviewed.
Article selection and data curationInitially, studies were selected based on titles and abstracts. Studies that initially met the eligibility criteria were read in full text to confirm these criteria. This process was carried out independently by JPC, FD, and JT. Disagreements were assessed by a third author (JJDF) when pertinent. Rayyan software (R) was used for the selection process.8
Data curation was performed by 2 authors (JJDF and JPC). Data about the study objective, methods including the statistical analysis plan and sample size, main results related to the shock index, and conclusions of each study were obtained. An Excel format was designed for this process.
Risk of bias assessmentThe risk of bias for each study was determined using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) checklist forms based on each study design. Two authors (JJDF and JPC) applied the tool to the various articles and categorized the overall risk of bias for each study using 3 levels: high, moderate, and low risk. The level of inter-rater agreement was calculated using the Kappa-Cohen test, which was then categorized as null (0.0–0.2), low (0.2–0.4), moderate (0.4–0.6), good (0.6–0.8), and very good agreement (0.8–1.0).9
Effect measuresTo determine the effect of SI as a prognostic factor in different contexts and outcomes, absolute and relative frequencies mentioned in the text were extracted, as well as the respective measures of central tendency and dispersion. When possible, effect estimators including Odds Ratio (OR), Relative Risk (RR), and Hazard Ratio (HR) were extracted according to the context and methodological setting of each study.
Ethical considerationsThe study was approved by the School of Medicine Research and Ethics Committee of the Health Sciences University Foundation, under Act No. 636 (DI-I-0555-21).
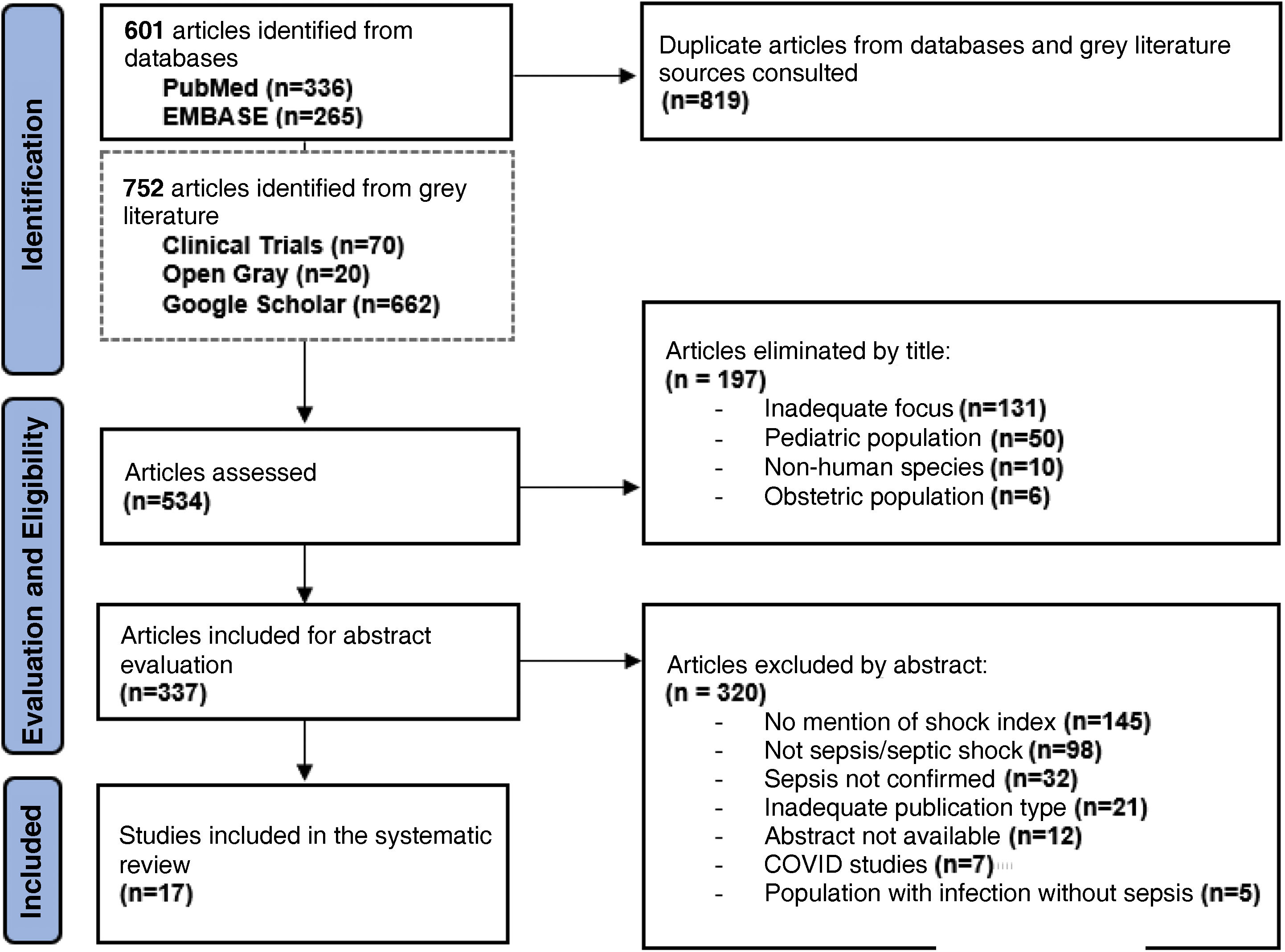
ResultsThe search identified a total of 601 articles, 67 of which were duplicates. Additionally, 752 articles from grey literature sources were identified. After applying the selection criteria, 337 manuscripts were selected for abstract review. Finally, 17 articles were identified for inclusion in the review (Fig. 1).
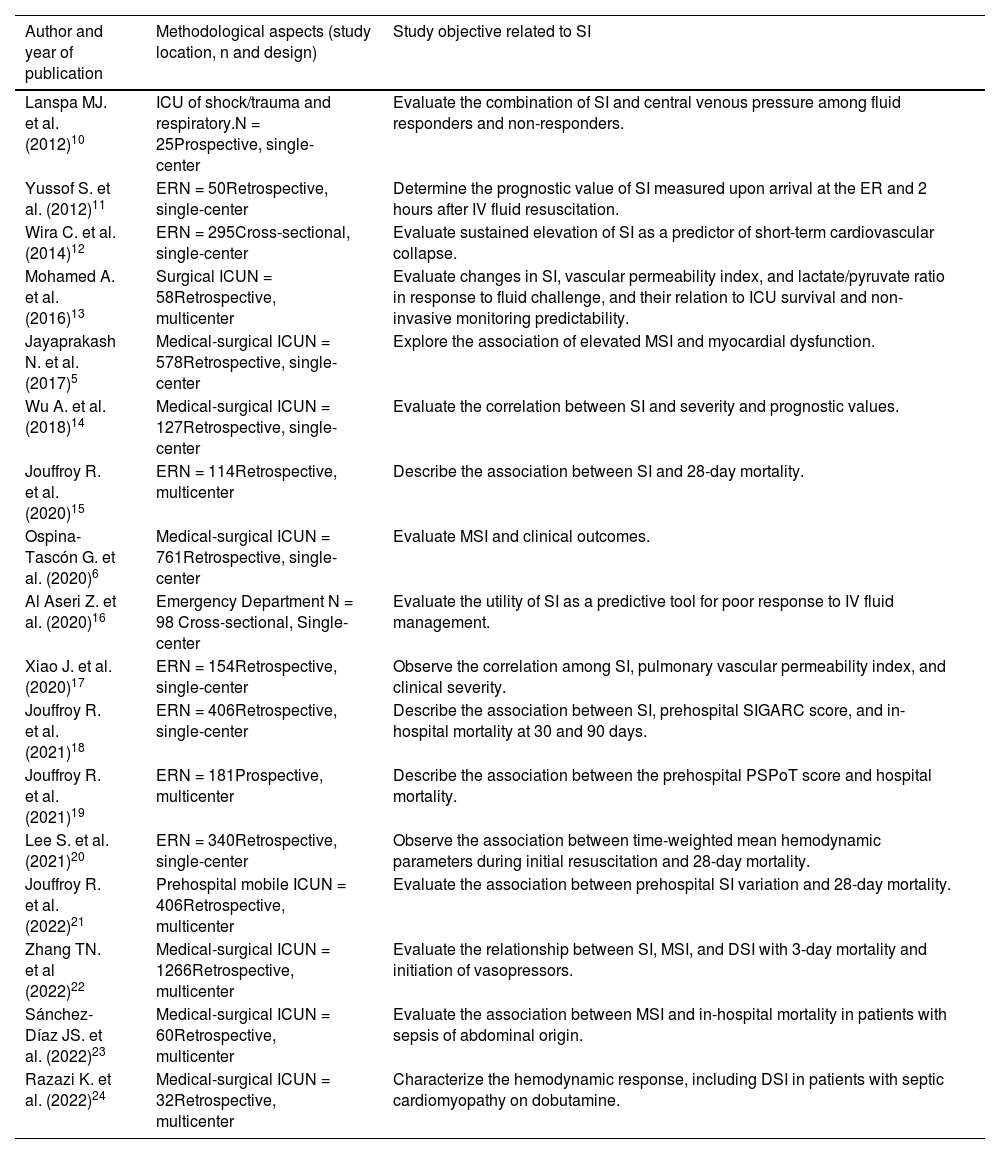
Table 1 shows the characteristics, methodology, and objectives of the included studies.
Descriptive data of included studies.
| Author and year of publication | Methodological aspects (study location, n and design) | Study objective related to SI |
|---|---|---|
| Lanspa MJ. et al. (2012)10 | ICU of shock/trauma and respiratory.N = 25Prospective, single-center | Evaluate the combination of SI and central venous pressure among fluid responders and non-responders. |
| Yussof S. et al. (2012)11 | ERN = 50Retrospective, single-center | Determine the prognostic value of SI measured upon arrival at the ER and 2 hours after IV fluid resuscitation. |
| Wira C. et al. (2014)12 | ERN = 295Cross-sectional, single-center | Evaluate sustained elevation of SI as a predictor of short-term cardiovascular collapse. |
| Mohamed A. et al. (2016)13 | Surgical ICUN = 58Retrospective, multicenter | Evaluate changes in SI, vascular permeability index, and lactate/pyruvate ratio in response to fluid challenge, and their relation to ICU survival and non-invasive monitoring predictability. |
| Jayaprakash N. et al. (2017)5 | Medical-surgical ICUN = 578Retrospective, single-center | Explore the association of elevated MSI and myocardial dysfunction. |
| Wu A. et al. (2018)14 | Medical-surgical ICUN = 127Retrospective, single-center | Evaluate the correlation between SI and severity and prognostic values. |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2020)15 | ERN = 114Retrospective, multicenter | Describe the association between SI and 28-day mortality. |
| Ospina-Tascón G. et al. (2020)6 | Medical-surgical ICUN = 761Retrospective, single-center | Evaluate MSI and clinical outcomes. |
| Al Aseri Z. et al. (2020)16 | Emergency Department N = 98 Cross-sectional, Single-center | Evaluate the utility of SI as a predictive tool for poor response to IV fluid management. |
| Xiao J. et al. (2020)17 | ERN = 154Retrospective, single-center | Observe the correlation among SI, pulmonary vascular permeability index, and clinical severity. |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2021)18 | ERN = 406Retrospective, single-center | Describe the association between SI, prehospital SIGARC score, and in-hospital mortality at 30 and 90 days. |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2021)19 | ERN = 181Prospective, multicenter | Describe the association between the prehospital PSPoT score and hospital mortality. |
| Lee S. et al. (2021)20 | ERN = 340Retrospective, single-center | Observe the association between time-weighted mean hemodynamic parameters during initial resuscitation and 28-day mortality. |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2022)21 | Prehospital mobile ICUN = 406Retrospective, multicenter | Evaluate the association between prehospital SI variation and 28-day mortality. |
| Zhang TN. et al (2022)22 | Medical-surgical ICUN = 1266Retrospective, multicenter | Evaluate the relationship between SI, MSI, and DSI with 3-day mortality and initiation of vasopressors. |
| Sánchez-Díaz JS. et al. (2022)23 | Medical-surgical ICUN = 60Retrospective, multicenter | Evaluate the association between MSI and in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis of abdominal origin. |
| Razazi K. et al. (2022)24 | Medical-surgical ICUN = 32Retrospective, multicenter | Characterize the hemodynamic response, including DSI in patients with septic cardiomyopathy on dobutamine. |
SI: shock index; ICU: intensive care unit; MSI: modified shock index; DSI: diastolic shock index; SIGARC: shock index ≥ 1; Glasgow coma scale < 13; age > 65; respiratory rate > 22; Comorbidity; PSPoT: prehospital shock precautions on triage.
All included studies were observational, with only one being prospective,10 and 8 (47.1%) being conducted in the ER.11,12,15–20 Sample sizes ranged from 25 to 1266 patients. Twelve articles (70.5%) evaluated the SI,10–21 4 evaluated the MSI or DSI,5,6,23,24 and 1 study evaluated the SI, MSI, and DSI.22
Regarding the risk of bias assessment determined using the JBI tool, two reviewers conducted a paired and independent evaluation of the risk of each included study according to the epidemiological design. There was a statistically significant agreement between the reviewers (p < 0.001); however, the level of this agreement was low (0.286). We found that all included articles presented a “low risk” assessment in 60% or more of the content of each. Concerns identified in the included studies according to their design revealed deficiencies in the identification and management of confounding factors in cross-sectional, case-control, and cohort studies. Additionally, in cohort studies, further concerns were identified related to strategies employed to address incomplete follow-up in some cases. The risk of bias assessment for the studies is shown in Fig. 2.
Averaged risk of bias assessment by 2 independent reviewers, according to the Joanna Briggs Institute recommendations9 adjusted to each epidemiological design.
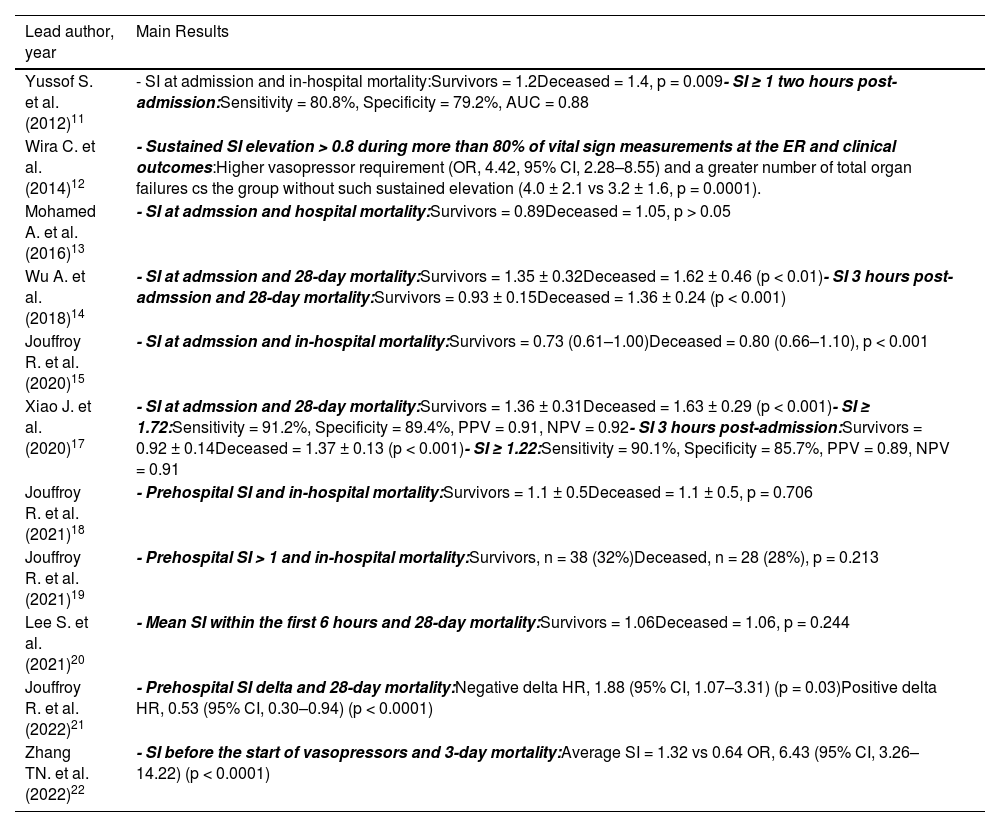
Among the studies that evaluated the prognostic value of SI, 4 showed statistically significant differences between the admission SI value in the survivor vs the non-survivors group,11,14,15,17 and one more in the evaluation of SI before the initiation of vasopressors.22 Two more studies showed favorable results between the average of several SI measures in the emergency department or the variation of prehospital SI and clinical outcomes.12,21 In contrast, in 4 studies, prehospital SI,18,19 admission SI,13 or the average SI within the first 6 hours were not associated with mortality.20 See Table 2.
Prognostic evaluation of SI value in septic shock population.
| Lead author, year | Main Results |
|---|---|
| Yussof S. et al. (2012)11 | - SI at admission and in-hospital mortality:Survivors = 1.2Deceased = 1.4, p = 0.009- SI ≥ 1 two hours post-admission:Sensitivity = 80.8%, Specificity = 79.2%, AUC = 0.88 |
| Wira C. et al. (2014)12 | - Sustained SI elevation > 0.8 during more than 80% of vital sign measurements at the ER and clinical outcomes:Higher vasopressor requirement (OR, 4.42, 95% CI, 2.28–8.55) and a greater number of total organ failures cs the group without such sustained elevation (4.0 ± 2.1 vs 3.2 ± 1.6, p = 0.0001). |
| Mohamed A. et al. (2016)13 | - SI at admssion and hospital mortality:Survivors = 0.89Deceased = 1.05, p > 0.05 |
| Wu A. et al. (2018)14 | - SI at admssion and 28-day mortality:Survivors = 1.35 ± 0.32Deceased = 1.62 ± 0.46 (p < 0.01)- SI 3 hours post-admssion and 28-day mortality:Survivors = 0.93 ± 0.15Deceased = 1.36 ± 0.24 (p < 0.001) |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2020)15 | - SI at admssion and in-hospital mortality:Survivors = 0.73 (0.61–1.00)Deceased = 0.80 (0.66–1.10), p < 0.001 |
| Xiao J. et al. (2020)17 | - SI at admssion and 28-day mortality:Survivors = 1.36 ± 0.31Deceased = 1.63 ± 0.29 (p < 0.001)- SI ≥ 1.72:Sensitivity = 91.2%, Specificity = 89.4%, PPV = 0.91, NPV = 0.92- SI 3 hours post-admission:Survivors = 0.92 ± 0.14Deceased = 1.37 ± 0.13 (p < 0.001)- SI ≥ 1.22:Sensitivity = 90.1%, Specificity = 85.7%, PPV = 0.89, NPV = 0.91 |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2021)18 | - Prehospital SI and in-hospital mortality:Survivors = 1.1 ± 0.5Deceased = 1.1 ± 0.5, p = 0.706 |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2021)19 | - Prehospital SI > 1 and in-hospital mortality:Survivors, n = 38 (32%)Deceased, n = 28 (28%), p = 0.213 |
| Lee S. et al. (2021)20 | - Mean SI within the first 6 hours and 28-day mortality:Survivors = 1.06Deceased = 1.06, p = 0.244 |
| Jouffroy R. et al. (2022)21 | - Prehospital SI delta and 28-day mortality:Negative delta HR, 1.88 (95% CI, 1.07–3.31) (p = 0.03)Positive delta HR, 0.53 (95% CI, 0.30–0.94) (p < 0.0001) |
| Zhang TN. et al. (2022)22 | - SI before the start of vasopressors and 3-day mortality:Average SI = 1.32 vs 0.64 OR, 6.43 (95% CI, 3.26–14.22) (p < 0.0001) |
SI: shock index; AUC: area under the ROC Curve; OR: odds ratio; PPV: positive predictive value; NPV: negative predictive value; HR: hazard ratio.
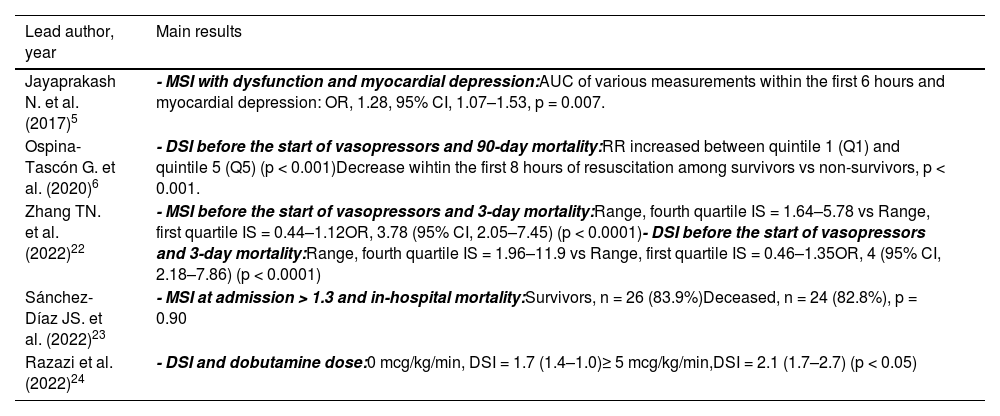
Among the 3 studies that evaluated the MSI, 2 showed a favorable relationship with clinical outcomes such as myocardial depression5 and mortality,22 while 1 was not associated with mortality whatsoever.23 Three other studies that evaluated the DSI showed a relationship with mortality6,22 and the dose of dobutamine received.24 It is important to note that Zhang et al.22 conducted several statistical adjustment models to determine the association between DSI and mortality. Among them, only the model adjusted for age, sex, race, and ICU management was significant. However, when also adjusting for SOFA scale values, it was evident that DSI was not associated with mortality in hospitalized patients. Table 3 summarizes the studies with prognostic evaluation of the MSI and DSI values in the septic shock population.
Prognostic evaluation of MSI and DSI values in septic shock population.
| Lead author, year | Main results |
|---|---|
| Jayaprakash N. et al. (2017)5 | - MSI with dysfunction and myocardial depression:AUC of various measurements within the first 6 hours and myocardial depression: OR, 1.28, 95% CI, 1.07–1.53, p = 0.007. |
| Ospina-Tascón G. et al. (2020)6 | - DSI before the start of vasopressors and 90-day mortality:RR increased between quintile 1 (Q1) and quintile 5 (Q5) (p < 0.001)Decrease wihtin the first 8 hours of resuscitation among survivors vs non-survivors, p < 0.001. |
| Zhang TN. et al. (2022)22 | - MSI before the start of vasopressors and 3-day mortality:Range, fourth quartile IS = 1.64–5.78 vs Range, first quartile IS = 0.44–1.12OR, 3.78 (95% CI, 2.05–7.45) (p < 0.0001)- DSI before the start of vasopressors and 3-day mortality:Range, fourth quartile IS = 1.96–11.9 vs Range, first quartile IS = 0.46–1.35OR, 4 (95% CI, 2.18–7.86) (p < 0.0001) |
| Sánchez-Díaz JS. et al. (2022)23 | - MSI at admission > 1.3 and in-hospital mortality:Survivors, n = 26 (83.9%)Deceased, n = 24 (82.8%), p = 0.90 |
| Razazi et al. (2022)24 | - DSI and dobutamine dose:0 mcg/kg/min, DSI = 1.7 (1.4–1.0)≥ 5 mcg/kg/min,DSI = 2.1 (1.7–2.7) (p < 0.05) |
SI; shock index: MSI; modified shock index: DSI; diastolic shock index: AUC; area under the ROC Curve: OR; odds ratio.
Finally, two studies evaluated the response of SI to certain medical interventions. Lanspa et al.10 demonstrated that a CVP ≥ 8 mmHg had an NPV of 83% for predicting fluid response, while for SI ≤ 1, it was 88%, and for the combination of CVP ≥ 8 + SI ≤ 1, the NPV increased to 93%. Al Aseri et al.16 showed a lower SI in patients who responded to fluid management vs those who did not, with a SI = 1.03 (0.3) beats/min/mmHg vs 1.28 (0.5), respectively, p = 0.007. An SI ≥ 0.875 had a sensitivity of 81% and specificity of 72% to predict poor response to fluids and the need to initiate norepinephrine.
DiscussionThe present systematic review demonstrates that the IS has been studied in recent years in the context of patients with septic shock, showing potential value in prognosis and utility for fluid management. The main feature of this variable is its easy measurement, allowing it to be obtained in any hospital care setting and repeated as often as necessary, which is important for close monitoring and follow-up of patients with this disease.
When analyzing the studies that evaluated the prognostic value of the variable, we observed that the results were inconsistent. Several aspects must be considered in this regard. First, the method of evaluating prognosis varied; in some studies, the IS was assessed as a continuous variable, yielding median and mean differences, while in other cases, it was assessed as a categorical variable, resulting in different outcomes depending on the type of analysis. Second, when analyzed as a categorical variable, choosing the cutoff point is crucial. Studies conducted on IS in patients with other pathologies use different cutoff points, some to define normality and others to establish cutoffs related to prognosis. Values from 0.5 to 1.3 beats/min/mmHg have been used.3,25 This wide range of values was seen in our results. This aspect affects the operational performance of the IS in different evaluations, making it difficult to compare studies. Third, some of the included studies did not show statistically significant differences in their results, possibly due to the small sample size in some or the clinical heterogeneity of the patients given the complexity of each case.11,13,19 Specifically, in the study by Jouffroy et al.,18 an IS > 1 was observed in 57% of non-survivors vs 32% of survivors (p = 0.21). Even though the p-value does not show statistical significance, the percentage difference can be considered important from a clinical perspective. Therefore, “statistical significance” for exclusive reasons of p-values should not preclude the interpretation or clinical importance of a result. Additionally, while clinical relevance is crucial, it is important to recognize that some studies, after applying statistical adjustments for possible confounding variables, indicate a lack of association between various iterations of the IS and in-hospital mortality.22 Consequently, when interpreting the results, it is recommended to exercise special caution and consider both clinical utility and the statistical tools applied.
The temporal progression of physiological variables during the resuscitation of a patient with septic shock is of high importance. The so-called “lactate clearance” is the classic example, in which the percentage reduction of lactate during the first hours of resuscitation is evaluated. This variable has shown an important relationship with the patient's prognosis26,27 and is recommended as a therapeutic goal by the latest Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines.7 In this regard, various studies have shown the importance of the temporal evolution of the IS. Wira et al.12 demonstrated a worse prognosis in patients who maintained a sustained elevation of the IS during resuscitation at the ER. Mohamed et al.13 showed greater importance of the IS measurement two hours after ICU admission vs the admission measurement, similar to Yussof et al.,11 who showed a higher AUC for mortality of the IS measured 2 hours after the ER admission vs the admission IS, while Ospina et al.6 showed that the IS decreased significantly in the survivor vs to non-survivors group, and Xiao et al.17 showed that the mean IS measured 3 hours after resuscitation was higher in non-survivors vs survivors, with a higher AUC for prognosis evaluation. Similarly, Jouffroy et al.21 incorporated the IS delta as an independent variable for predicting the 28-day mortality rate. Interestingly, the authors concluded that a negative IS delta could help physicians identify patients with severe sepsis and septic shock at a higher risk regarding the 28-day mortality rate. This type of analysis suggests that this measure should be used repeatedly during initial resuscitation, paying special attention to patients who do not show a decrease in the variable, indicating the need for closer monitoring and adjustment in management if possible.
Regarding the clinical and hemodynamic response to IV fluid volume, Monnet et al. reported that in a group of 37 patients, a 10% increase in stroke volume or a 15% increase in pulse pressure were highlighted as simple and significant clinical indicators for predicting fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients during passive leg raising.28
The IS was also investigated during fluid administration maneuvers. Mohamed et al.13 provided data showing a decrease in IS measured 15 minutes after fluid administration in both survivors and non-survivors, without observing significant differences between both groups. Lanspa et al.10 conducted an interesting study showing how the combined measurement of CVP with IS identifies those labeled as “non-responders to fluids”, patients who do not increase cardiac output by more than 15% after a fluid challenge in a short time (fluid challenge). This is important, considering that identifying this “response” is seen as fundamental to managing these patients and is part of the recommendations of the current Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines,7 which require the use of special monitoring that is not always available in all patient care units.29,30 Al Aseri et al.16 evaluated the IS to estimate a cutoff point that identifies the patient with hemodynamic collapse who will require vasopressors, with an IS > 0.87 identifying the patient who will not respond to fluids, meaning they will require vasopressors, with greater specificity and sensitivity. Similarly, according to Razazi et al.,24 the IS could function as a clinical marker of response to dobutamine resuscitation in patients with septic cardiomyopathy, regardless of the dose used.
In 3 studies, the DSI was evaluated, an index presented not only as a variable contributing to patient prognosis but also as one with potential utility in patient management as it can identify patients requiring early vasopressor intervention, an important concept today.31,32 The proposal is based on the fact that the loss of arterial elastance is a key element in the pathophysiology of circulatory compromise in septic shock. This condition leads to a decrease in DBP and, therefore, a compromised DSI. Ospina et al. identified that the risk of higher mortality was more clearly identified with DSI rather than IS or DBP, suggesting that this index could be used as a variable to define interventions in the management of these patients. These hypotheses on the potential clinical use of IS and DSI in management algorithms should be evaluated in studies designed for this purpose.
The limitations of IS are notable due to its static nature, which makes it difficult to objectively evaluate the clinical and hemodynamic progression of patients from their admission and during treatment. Additionally, IS is problematic for assessing the effect of volume administration on cardiac output, as other clinical variables can modify blood pressure readings, indirectly affecting the IS value.33–35
Moreover, it is important to note that fluid responsiveness does not guarantee better oxygen consumption. It is estimated that only about half (56%) of patients who respond to fluids experience an increase in their oxygen consumption. Therefore, even if there are increases in blood pressure or even cardiac output, this does not necessarily guarantee an increase in tissue perfusion.36 For this reason, it is suggested that IS should be integrated into fluid resuscitation protocols in septic patients.
IS has been frequently studied in patients with septic shock; few studies have been identified with other versions of IS. The results suggest that both IS and its modified versions in single and serial evaluations can be considered for evaluating patient prognosis.
Our study presents several limitations. First, all studies, except for one, are retrospective, which is associated with certain biases inherent to these designs, mainly confounding bias. Second, there is notable clinical heterogeneity in the presentation and measurement of the variables of interest, including variability in the timing of measurement during the length of stay and the different contexts and places where the variables are determined, such as emergency services, hospitalization wards, and intensive care units. Additionally, there are other potentially confounding factors, such as comorbidities, the patients’ baseline clinical status, and the use of pharmacological therapies. Third, the lack of consistency in study selection criteria limits the generalization of the results to the entire population. Due to the above-mentioned limitations, it is not appropriate to perform a meta-analysis of the results, which prevents providing a weighted effect estimator.
FundingNone declared.
Authors’ contributionsConceptualization: JJDF, JPCG, MASO. Data mining and management: JJDF, JPCG, MASO, JITZ, FEDM. Data analysis: JJDF, JPCG. Project administration: JJDF. Manuscript writing (original draft): JJDF, JPCG. Manuscript review and editing: JJDF, JPCG, MASO, JITZ, FEDM.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.