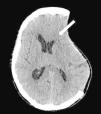
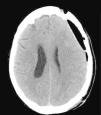
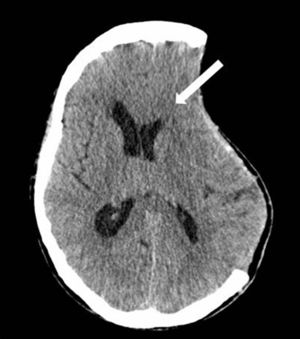
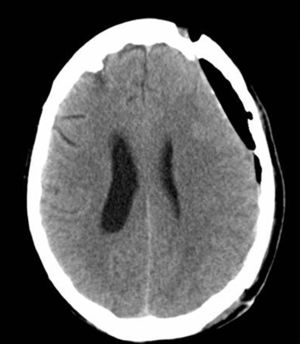
Sixty-seven-year-old female admitted to the ICU due to severe traumatic brain injury with left-sided frontoparietal subdural hematoma. Drainage and decompressive craniectomy were conducted with favorable progression of the patient. On day+25 she showed a decreased level of consciousness that became worse with sedation and was accompanied by paresis in her right upper limb. The cranial CT scan performed (Fig. 1) confirmed the collapse of the left lateral ventricle and subfalcine herniation (arrow). One cranioplasty was performed. The cranial CT scan performed (day+30) (Fig. 2) showed pneumocephalus and correction of the subfalcine herniation. The progression of the patient was favorable, she recovered her level of consciousness without neurological deficits, and she was transferred to her hospital room on day+35. The “syndrome of the trephined” is a late complication of decompressive craniectomy. As in the case presented above, it is characterized by new neurological deficits that resolve after the cranioplasty. When it occurs four (4) weeks after surgery is considered an unusual complication.
Please cite this article as: Balandin Moreno B, Lipperheide Valhonrat I, Fernández Simón I. Complicación tras craniectomía descompresiva: el «síndrome del paciente trepanado» de aparición precoz. Med Intensiva. 2018;42:e16.